LTE终端能力等级 Category
UE category是手机通信能力最重要的指标,没有之一。为什么?是因为这个是标识手机最高通信能力指示。也是芯片公司产品设计、开发能力的标志。为什么说高通的芯片牛,主要是Q的顶级芯片能力比别的公司芯片能力至少高一代,甚至两代。例如海思16年10月发布的麒麟960峰值速率是下行600Mbps,而高通16年2月发布的X16峰值速率是1gbps,Intel的modem至今还是450Mbps的峰值速率。再举个大家都熟悉的例子,Intel给Iphone7提供的芯片是下行峰值450Mbps的能力,而高通给iphone7提供的芯片是下行峰值600Mbps能力。这就是为什么高通芯片在实际网络中速率更高的原因。UE CAT简单的类比就是CPU的主频,能力直接的体现是峰值速率,但是不是峰值速率越高能力越强?对,但不全是。就像Intel的CPU有i3、i5、i7三个系列,每个系列都在演进,UE Cat也在演进,而且有几个路径(类似于i3、i5、i7系列)。从技术上解释一下,为什么会有那么多UE Cat.。主要是因为两个原因:1. 3GPP不同的版本。以LTE为例,第一个版本是rel-8,目前是rel-14即将完成。每个版本都会根据新的feature定义新的UE Cat.。例如在rel-12结束后,针对256QAM调制定义了新的UE Cat(DL CAT-11、DL CAT-12等)。2. 同一个版本内,同时支持高、中、低端手机。例如在rel-10定义了四种下行Cat(CAT-6、7、8、9),其中Cat-8就是高端手机,cat-6、9支持的速率较低。影响UE CAT的主要因素:MIMO天线数、载波聚合数、调制阶数。同一个UE CAT的速率有几种实现方式,例如8天线MIMO+双载波 = 4天线MIMO + 四载波。具体实现方式是芯片厂家的实现选择,例如华为喜欢MIMO,不喜欢CA(这两年有所变化,麒麟960也支持4cc了)。

UE Category
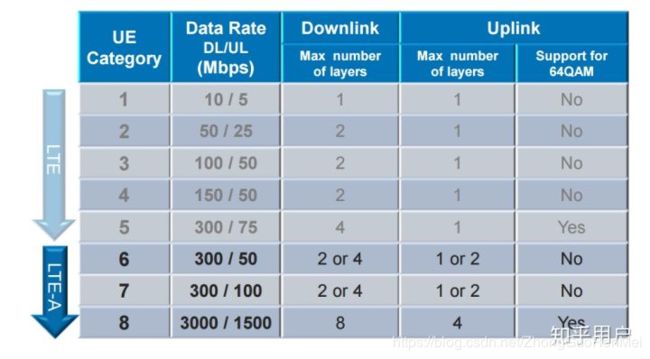
下行峰值速率(Mbps) 下行天线构成 上行峰值速率(Mbps) 上行链路的64QAM
其中蓝字部分为Release8中规定的内容,绿字部分为Release10规定的内容。UE Category 有时也被称作 UE Class。eNodeB和UE之间需用通过UE Category来确定UE的传输能力。eNodeB根据UE Category来调整自己的参数设定,合理地与UE进行通信(不可以超过UE的能力)。
Category终端能力等级,表明了终端所支持的数据处理能力(下载、上传速率)、最大的空分复用、调制编码能力等。
详细可参考 3GPP36.306。在R8版本中定义了5类终端,在R10中定义了8类终端....随着版本演进,不断有新的终端被定义!
| R8 |
R9 |
R10 |
R11 |
R12 |
| Category 1 |
Category 1 |
Category 1 |
Category 1 |
Category 1 |
| Category 2 |
Category 2 |
Category 2 |
Category 2 |
Category 2 |
| Category 3 |
Category 3 |
Category 3 |
Category 3 |
Category 3 |
| Category 4 |
Category 4 |
Category 4 |
Category 4 |
Category 4 |
| Category 5 |
Category 5 |
Category 5 |
Category 5 |
Category 5 |
| - |
- |
Category 6 |
Category 6 |
Category 6 |
| - |
- |
Category 7 |
Category 7 |
Category 7 |
| - |
- |
Category 8 |
Category 8 |
Category 8 |
| - |
- |
- |
Category 9 |
Category 9 |
| - |
- |
- |
Category 10 |
Category 10 |
| - |
- |
- |
Category 11 |
Category 11 |
| - |
- |
- |
Category 12 |
Category 12 |
| - |
- |
- |
- |
Category 13 |
| - |
- |
- |
- |
Category 14 |
| - |
- |
- |
- |
Category 15 |
目前3GPP更新到了R12,15类终端,但还有很多信息没有说清楚!以RC40版本来说,信息如下!
下行物理信道参数设置
| UE 类别 |
Maximum number of DL-SCH transport block bitsreceived within a TTI |
Maximum number of bits of a DL-SCH transport blockreceived within a TTI |
软信道比特总数 |
支持下行空分复用的最大层数 |
| Category1 |
10296 |
10296 |
250368 |
1 |
| Category2 |
51024 |
51024 |
1237248 |
2 |
| Category3 |
102048 |
75376 |
1237248 |
2 |
| Category4 |
150752 |
75376 |
1827072 |
2 |
| Category5 |
299552 |
149776 |
3667200 |
4 |
| Category6 |
301504 |
149776 (4layers) |
3654144 |
2 or4 |
| 75376 (2layers) |
||||
| Category7 |
301504 |
149776 (4layers) |
3654144 |
2 or4 |
| 75376 (2layers) |
||||
| Category8 |
2998560 |
299856 |
35982720 |
8 |
| Category9 |
452256 |
149776 (4layers) |
5481216 |
2 or4 |
| 75376 (2layers) |
||||
| Category10 |
452256 |
149776 (4layers) |
5481216 |
2 or4 |
| 75376 (2layers) |
||||
| Category11 |
603008 |
149776 (4layers, 64QAM) |
7308288 |
2 or4 |
| 195816 (4layers, 256QAM) |
||||
| 75376 (2layers, 64QAM) |
||||
| 97896 (2layers, 256QAM) |
||||
| Category12 |
603008 |
149776 (4layers, 64QAM) |
7308288 |
2 or4 |
| 195816 (4layers, 256QAM) |
||||
| 75376 (2layers, 64QAM) |
||||
| 97896 (2layers, 256QAM) |
上行物理信道参数配置
| UECategory |
Maximum number of UL-SCH transport block bits transmittedwithin a TTI |
Maximum number of bits of an UL-SCH transport blocktransmitted within a TTI |
| Category1 |
5160 |
5160 |
| Category2 |
25456 |
25456 |
| Category3 |
51024 |
51024 |
| Category4 |
51024 |
51024 |
| Category5 |
75376 |
75376 |
| Category6 |
51024 |
51024 |
| Category7 |
102048 |
51024 |
| Category8 |
1497760 |
149776 |
| Category9 |
51024 |
51024 |
| Category10 |
102048 |
51024 |
| Category11 |
51024 |
51024 |
| Category12 |
102048 |
51024 |
这里需要说明终端的最大下行速率和最大上行速率
以下行举例来说,有2个参数:
Maximum number of DL-SCH transport block bitsreceived within a TTI
//在一个TTI内可接收的最大DL-SCH传输块bit数
Maximum number of bits of a DL-SCH transport blockreceived within a TT
//在一个TTI内可接收一个传输块的DS-SCH传输块最大bit数
一个TTI就是1ms
举例来说:Category3
Maximum number of DL-SCH transport block bitsreceived within a TTI =102048
那么下行速率可达100Mbps
Maximum number of bits of a DL-SCH transport blockreceived within a TTI =75376
一个传输块的下行速率可达75Mbps
Category3最大可支持2层传输,2个传输块的最大传输速率可达=75376*2=150Mbps
但Maximum number of DL-SCH transport block bitsreceived within a TTI最大速率只有100Mbps,所以Category3最大速率=MIN(Maximum number of DL-SCH transport block bits receivedwithin a TTI, Maximum number of bits of a DL-SCH transport blockreceived within a TTI*层数)=100Mbps
上行所支持的最大速率同样类似
| Category |
支持的最大层数 |
最大速率 |
||
| 下行 |
上行 |
下行 |
上行 |
|
| Category 1 |
1 |
1 |
10 |
5 |
| Category 2 |
2 |
1 |
50 |
25 |
| Category 3 |
2 |
1 |
100 |
50 |
| Category 4 |
2 |
1 |
150 |
50 |
| Category 5 |
4 |
1 |
300 |
75 |
| Category 6 |
2 |
1 |
150 |
50 |
| 4 |
1 |
300 |
||
| Category 7 |
2 |
? |
150 |
? |
| 4 |
300 |
|||
| Category 8 |
8 |
1 |
300 |
150 |
| Category 9 |
2 |
1 |
150 |
50 |
| 4 |
450 |
|||
| Category 10 |
2 |
? |
190 |
? |
| 4 |
600 |
|||
| Category 11 |
2 |
1 |
190 |
50 |
| 4 |
600 |
|||
| Category 12 |
2 |
? |
190 |
? |
| 4 |
600 |
|||
在调制方式方面,下行方向从CAT11开始支持256QAM调制方式,上行方向部分终端已开始支持64QAM了
| Category |
数据信道支持的调制方式 |
|
| 下行 |
上行 |
|
| Category 1 |
QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM |
QPSK, 16QAM |
| Category 2 |
QPSK, 16QAM |
|
| Category 3 |
QPSK, 16QAM |
|
| Category 4 |
QPSK, 16QAM |
|
| Category 5 |
QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM |
|
| Category 6 |
QPSK, 16QAM |
|
| Category 7 |
QPSK, 16QAM |
|
| Category 8 |
QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM |
|
| Category 9 |
QPSK, 16QAM |
|
| Category 10 |
QPSK, 16QAM |
|
| Category 11 |
QPSK, 16QAM |
QPSK, 16QAM |
| Category 12 |
QPSK, 16QAM |
|
| Category 13 |
QPSK, 16QAM |
|
| Category 14 |
QPSK, 16QAM |
|
| Category 15 |
QPSK, 16QAM, 64QAM |
|
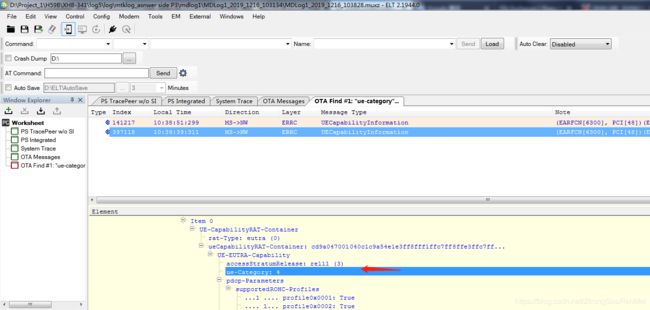
如何查看终端的category呢?可以通过信令来确认,在信令UECapabilityInformation的UE-EUTRA-Capability中有ue-Category的信息。
– UE-EUTRA-Capability
The IEUE-EUTRA-Capability is used to convey the E-UTRA UE Radio AccessCapability Parameters [5] to the network.
UE-EUTRA-Capability information element
-- ASN1START
UE-EUTRA-Capability::= SEQUENCE {
accessStratumRelease AccessStratumRelease,
ue-Category INTEGER(1..16), -- value range FFS
pdcp-Parameters PDCP-Parameters,
phyLayerParameters PhyLayerParameters,
rf-Parameters RF-Parameters,
measurementParameters MeasurementParameters,
interRAT-Parameters SEQUENCE {
utraFDD IRAT-UTRA-FDD-Parameters OPTIONAL,
utraTDD128 IRAT-UTRA-TDD128-Parameters OPTIONAL,
……
– UECapabilityInformation
TheUECapabilityInformation message is used to transfer of UEradio access capabilities requested by the E‑UTRAN.
Signalling radio bearer:SRB1
RLC-SAP: AM
Logical channel:DCCH
Direction: UE toE‑UTRAN
UECapabilityInformation message
-- ASN1START
UECapabilityInformation::= SEQUENCE {
rrc-TransactionIdentifier RRC-TransactionIdentifier,
criticalExtensions CHOICE {
c1 CHOICE{
ueCapabilityInformation-r8 UECapabilityInformation-r8-IEs,
spare7 NULL,
spare6 NULL, spare5 NULL, spare4 NULL,
spare3 NULL, spare2 NULL, spare1 NULL
},
criticalExtensionsFuture SEQUENCE {}
}
}
UECapabilityInformation-r8-IEs::= SEQUENCE (SIZE(1..maxRAT-Capabilities)) OF SEQUENCE {
rat-Type RAT-Type,
ueCapabilitiesRAT-Container OCTET STRING,
nonCriticalExtension SEQUENCE{} OPTIONAL
}
-- ASN1STOP
| UECapabilityInformation field descriptions |
| ueCapabilitesRAT-Container Container forthe UE capabilities of the indicated RAT. The encoding is definedin the specification of each RAT: For E‑UTRA: the encoding of UE capabilities is defined inIE UE-EUTRA-Capability. For UTRA: theencoding of UE capabilities is defined in IE [FFS] TS 25.331[19]. For GERAN: theencoding of UE capabilities is defined in IE [FFS] [24.008 and/ or44.018; FFS]. ForCDMA2000-1xRTT Bandclass: the encoding of UE capabilities isdefined in IE [A.S.0008; FFS] |
