概念 binary search tree 二叉搜索树的性质: 设 x 是 binary search tree中的一个节点。 如果y是x左子树中的一个节点, 那么y.key<=x.key 如果y是x右子树中的一个节点, 那么y.key>=x.key
BST 数据结构参考: https://www.cnblogs.com/zzyzz/p/13000550.html
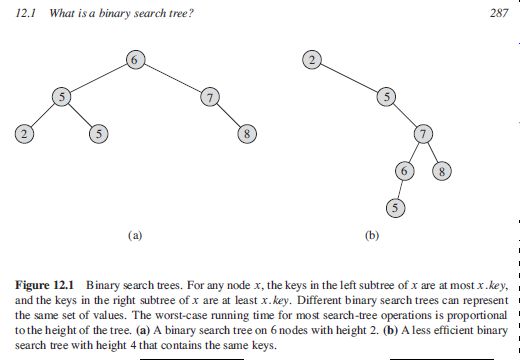
Python Programming BST 支持 search, minimum, maximum, successor, predecessor 相关查询操作. Search 查询: 1. Search 查询的递归版本
2. Search 查询的 while 循环版本
# 递归版本
def tree_search(k, x, T): # x : sub-tree , k : the target key. keys = [2,4,5,6,7,8] if k not in keys: return 'NIL' ind = keys.index(x.root) obj = T[ind] if obj.key == k: return obj else: if k < obj.key: return tree_search(k, obj.left,T) else: return tree_search(k, obj.right,T)
# while 版本
def iterative_tree_search( k, x, T): # x : sub-tree , k : the target key. keys = [2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8] if k not in keys: return 'NIL' ind = keys.index(x.root) obj = T[ind] while k != obj.key: if k < obj.key: obj = obj.left else: obj = obj.right return obj if __name__ == '__main__': keys = [2,4,5,6,7,8] parent = [4,6,4,'NIL',6,7] left = ['NIL',2,'NIL',4,'NIL', 'NIL'] right = ['NIL',5,'NIL',7,8,'NIL'] root = 6 #BST 数据结构: https://www.cnblogs.com/zzyzz/p/13000550.html T = binary_search_tree(keys,parent,left,right,root) for j in [2,4,5,6,7,8,10]: x = tree_search(j,T,T) if isinstance(x, tree_element): print('recursive search : ',x.key, x) else: print('recursive search : ', x, 'Not Found: ' + str(j)) for k in [2, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 10]: y = iterative_tree_search(k,T,T) if isinstance(y, tree_element): print('While search : ', y.key, y) else: print('While search : ', y, 'Not Found: ' + str(k)) 结果打印: recursive search : 2 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029DDCC0> recursive search : 4 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029DDDD8> recursive search : 5 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029DDCF8> recursive search : 6 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029DDFD0> recursive search : 7 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029DDD68> recursive search : 8 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029DDE10> recursive search : NIL Not Found: 10 While search : 2 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029DDE48> While search : 4 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029DDE80> While search : 5 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029DDEB8> While search : 6 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029DDFD0> While search : 7 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029DDF98> While search : 8 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029DDF60> While search : NIL Not Found: 10
Minimum / Maximum:
def tree_minimum(x, T): x = T[T.keys.index(x.root)] while x.left != 'NIL': x = x.left return x def tree_maximum(x, T): x = T[T.keys.index(x.root)] while x.right != 'NIL': x = x.right return x if __name__ == '__main__': keys = [2,4,5,6,7,8] parent = [4,6,4,'NIL',6,7] left = ['NIL',2,'NIL',4,'NIL', 'NIL'] right = ['NIL',5,'NIL',7,8,'NIL'] root = 6 T = binary_search_tree(keys,parent,left,right,root)
for i in T.keys:
print('The sub-tree with a root of : ', i)
inorder_tree_walk(T, i, 'N')
print('=' * 33)
for obj in T: print('The sub-tree with a root of : ', obj.root) print('min', tree_minimum(obj,T).key, tree_minimum(obj,T)) print('max', tree_maximum(obj,T).key, tree_minimum(obj,T)) print('=' * 33) 结果打印: #子 BST 的结构 The sub-tree with a root of : 2 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 4 Left Child : 2 Right Child : 5 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 5 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 6 Left Child : 2 Left Child : 4 Right Child : 5 Right Child : 7 Right Child : 8 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 7 Right Child : 8 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 8 ================================= # minimum / maximum The sub-tree with a root of : 2 min 2 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029B1CC0> max 2 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029B1CC0> ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 4 min 2 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029B1C88> max 5 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029B1C88> ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 5 min 5 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029B1CF8> max 5 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029B1CF8> ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 6 min 2 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029B1E48> max 8 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029B1E48> ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 7 min 7 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029B1D68> max 8 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029B1D68> ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 8 min 8 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029B1E10> max 8 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029B1E10> =================================
Successor / predecessor:
概念; 给定一个 BST 中的一个结点 x,
则结点 x 的 successor 是 大于 x.key 的结点中 key 属性值最小的结点, 如果 x 是该 BST 中最大的结点则返回 NIL;
结点 x 的 predecessor 是 小于 x.key 的结点中 key 属性值最大的结点, 如果 x 是该 BST 中最小的结点则返回 NIL.
def tree_successor(x,T): if x.right != 'NIL': return tree_minimum(x.right,T) y = T[T.keys.index(x.p)] if y.right == 'NIL': return y while y != 'NIL' and x.key == y.right.key: x = y if y.p == 'NIL': return y.p y = T[T.keys.index(y.p)] return y if __name__ == '__main__': keys = [2,4,5,6,7,8] parent = [4,6,4,'NIL',6,7] left = ['NIL',2,'NIL',4,'NIL', 'NIL'] right = ['NIL',5,'NIL',7,8,'NIL'] root = 6 T = binary_search_tree(keys,parent,left,right,root) # 子 BST for i in T.keys: print('The sub-tree with a root of : ', i) inorder_tree_walk(T, i, 'N') print('=' * 33) for obj4 in T: print('The sub-tree with a root of : ', obj4.root) s = tree_successor(obj4, T) if isinstance(s, str): print('successor ->' + str(obj4.key), s) else: print('successor ->' + str(obj4.key), s.key, s, obj4.p) print('=' * 33) 结果打印 # 子 BST The sub-tree with a root of : 2 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 4 Left Child : 2 Right Child : 5 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 5 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 6 Left Child : 2 Left Child : 4 Right Child : 5 Right Child : 7 Right Child : 8 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 7 Right Child : 8 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 8 ================================= # 每一个子 BST 的 successor ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 2 successor ->2 4 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029C7DD8> 4 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 4 successor ->4 5 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029C7CF8> 6 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 5 successor ->5 6 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029C7FD0> 4 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 6 successor ->6 7 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029C7D68> NIL ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 7 successor ->7 8 <__main__.tree_element object at 0x00000000029C7E10> 6 ================================= The sub-tree with a root of : 8 successor ->8 NIL =================================
Reference,
1. Introduction to Algorithms