【Spring Data Access】JdbcTemplate 批量插入
JdbcTemplate批量插入
JdbcTemplate支持批量命令的操作,我们先简单了解一下JdbcTemplate的API接口支持情况:
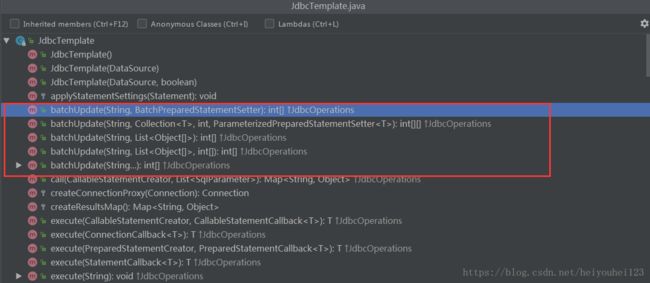
从上面的截图中我们可以了解当前有5个方法,注意这些方法都是JdbcTemplate实现JdbcOperations接口而来的方法
int[] batchUpdate(String sql, final BatchPreparedStatementSetter pss) throws DataAccessException;
int[] batchUpdate(String sql, List<Object[]> batchArgs) throws DataAccessException;
int[] batchUpdate(String sql, List<Object[]> batchArgs, int[] argTypes) throws DataAccessException;
<T> int[][] batchUpdate(String sql, Collection<T> batchArgs, int batchSize,
ParameterizedPreparedStatementSetter<T> pss) throws DataAccessException;
int[] batchUpdate(String... sql) throws DataAccessException;
下面对其中的方法进行简单的解释:
1. int[] batchUpdate(String sql, final BatchPreparedStatementSetter pss) throws DataAccessException
使用这个方法的时候需要我们去提供BatchPreparedStatementSetter接口的实现,下面是这个接口的定义:
public interface BatchPreparedStatementSetter {
/**
* Set parameter values on the given PreparedStatement.
* @param ps the PreparedStatement to invoke setter methods on
* @param i index of the statement we're issuing in the batch, starting from 0
* @throws SQLException if a SQLException is encountered
* (i.e. there is no need to catch SQLException)
*/
void setValues(PreparedStatement ps, int i) throws SQLException;
/**
* Return the size of the batch.
* @return the number of statements in the batch
*/
int getBatchSize();
}
因此实现这个方法的时候,我们得明确的提供批操作中的语句数量,通过getBatchSize方法给出,另外我们要给出批操作中每个独立语句的内容,这种情况下我们需要实现的就是setValues这个方法。
示例:
- Config.java文件
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
/**
* @author jiangjian
*/
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
@PropertySource("classpath:jdbc.properties")
public class Config {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource dataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.driver-class-name"));
dataSource.setUrl(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.url"));
dataSource.setUsername(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.username"));
dataSource.setPassword(env.getProperty("spring.datasource.password"));
return dataSource;
}
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate() {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource());
}
}
- jdbc.prperites文件
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&allowMultiQueries=true&autoReconnect=true&failOverReadOnly=false&autoReconnectForPools=true&serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
- 测试主类 JdbcTemplateBatchOperationSample.java
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BatchPreparedStatementSetter;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author jiangjian
*/
public class JdbcTemplateBatchOperationSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = ac.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class);
//准备环境
jdbcTemplate.execute("drop table if exists user ");
jdbcTemplate.execute("create table user(id int auto_increment primary key, name varchar(40))");
//这里面我们需要批量插入多个用户,所以我们这里先定义了待插入用户的列表,
// 这个列表可以方便实现BatchPreparedStatementSetter接口,比如:获取
// 批操作的大小 <==> uses.size()即可
List<String> users = Arrays.asList("Alice", "Bob");
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate("insert into user(name) values(?)", new BatchPreparedStatementSetter() {
@Override
public void setValues(PreparedStatement ps, int i) throws SQLException {
ps.setString(1, users.get(i));
}
@Override
public int getBatchSize() {
return users.size();
}
});
Long count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(*) from user", Long.class);
System.out.println("count is :" + count);
//清空环境
jdbcTemplate.execute("drop table user");
}
}
2. int[] batchUpdate(String sql, List batchArgs) throws DataAccessException;
这个方法操作同上面介绍的区别在于它是直接通过传入操作自身来判断上述对应的batchSize, 而每个独立语句的参数则是通过内部的Object[]提供,下面写出如果使用当前方法的写法(其他部分代码都类似):
//另外一种方式去批量插入
List<Object[]> users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add(new Object[]{"Jim"});
users.add(new Object[]{"Tom"});
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate("insert into user(name) value(?)", users);
Long count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject("select count(*) from user", Long.class);
System.out.println("count is :" + count);
preparedStatement的参数是通过List中的Object[]给出,底层根据Object[]中元素对应的java 类型,来调用合适的preparedStatement.setXXX方法,但是这样操作可能会存在问题,比如如果给出的值是null这时候会导致问题的方式,Spring默认会通过调用ParameterMetaData.getParameterType方法来获取对应placeholder的类型,这种操作对于某些jdbc driver或者数据库产品(比如: n Oracle 12c (SPR-16139))会造成很大的性能开销,如果出现这种情况,可以尝试使用int[] batchUpdate(String sql, List方法,来显示指定具体的place holder的类型, 另外可以通过配置spring.jdbc.getParameterType.ignore为true来禁用上面的ParameterMetaData.getParameterType的操作。
3. int[][] batchUpdate(String sql, Collection batchArgs, int batchSize,
ParameterizedPreparedStatementSetter pss) throws DataAccessException;
这个方法看起来好可怕,这么多参数,这个方法主要的用途是将一个batch操作分为多个子batch操作,主要的应用场景就是大数据量的批操作,比如我们有2w个用户用插入,用一个batch提交会造成很大的性能瓶颈,此时我们可以试着每100个用户作为一个batch提交。
上面的方法各个参数也很容易理解:
sql: 待执行的sql语句;
batchArgs: 这里面就是待处理的数据集,比如:2w个用户;
batchSize:用来指定batch的总共大小,它会根据batchArgs的大小来计算每个batch应该处理的数据集(比如: batchArgs / batchSize);
pss: 这个接口主要用来提供构造ParameterStatement的实现;
下面通过一个例子来感受一下:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author jiangjian
*/
public class BatchOperationWithMultiBatchesSample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(Config.class);
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = ac.getBean(JdbcTemplate.class);
jdbcTemplate.execute("drop table if exists user ");
jdbcTemplate.execute("create table user(id int auto_increment primary key, name varchar(40))");
List<User> users = Arrays.asList(new User("alice"),
new User("bob"),
new User("cindy"),
new User("dave"));
int[][] batchResult = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate("insert into user(name) values(?)", users, 2, (ps, argument) -> {
ps.setString(1, argument.getName());
});
//batchResult这个数组的最上层的长度表示batch的数量,而第二级的数组长度表示每次batch包含的update语句数量,
// 而每个具体数组的值包含着当前update语句修改记录的数量(由jdbc driver提供)
//上面的例子中,users分两个批次,每个批次应该为2, 而且每个批次里面的statement数量为2,具体每个statement的
//update 数量为1(因为当前是insert语句),所以batchResult应该是int[2][2]维度的数组,而且值都为1,
System.out.println("第一维度长度为:" + batchResult.length);
System.out.println("第二维度长度为:" + batchResult[0].length);
//下面是输出所有的值
for(int i = 0; i < batchResult.length; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < batchResult[0].length; j++) {
System.out.println(batchResult[i][j]);
}
}
List<User> findUsers = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from user",
(rs, rowNum) -> new User(rs.getLong(1), rs.getString(2)));
findUsers.forEach(System.out::println);
jdbcTemplate.execute("drop table user");
}
}
User类定义如下:
package com.together.learning.spring.dataaccess.jdbc.step7_batch_operation_with_multi_batches;
public class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
public User() {
}
public User(Long id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
其他的Config.java和jdbc.properties同上面的示例;
4. int[] batchUpdate(String… sql) throws DataAccessException;
这个方法比较简单,将提供的sql列表作为一个batch进行执行,每个sql的update count可以通过返回int[]进行了解。