ReentrantReadWriteLock使用
ReentrantReadWriteLock下图来源《Java并发编程的艺术》一书
锁在同一时刻只允许一个线程进行访问,而读写锁在同一时刻可以允许多个读线程访问,但是在写线程访问时,所有的读
线程和其他写线程均被阻塞。读写锁维护了一对锁,一个读锁和一个写锁,通过分离读锁和写锁,使得并发性相比一般的排他锁有了很大提升。一般情况下,读写锁的性能都会比排它锁好,因为大多数场景读是多于写的。在读多于写
的情况下,读写锁能够提供比排它锁更好的并发性和吞吐量。Java并发包提供读写锁的实现是
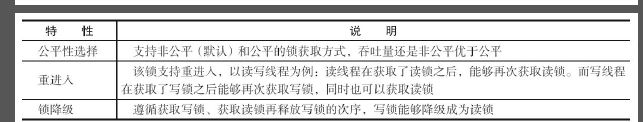
ReentrantReadWriteLock,它提供的特性如表5-8所示。
简单的示例代码
package reentrant;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
/**
* @author sun
* @date 2019/8/20
*/
public class ReentrantReadWriteLockDemo {
static Map datas = new HashMap();
static ReentrantReadWriteLock lock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
static Lock r = lock.readLock();
static Lock w = lock.writeLock();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0;i<10000;i++)
setData(i+"",i+"");
}
}.start();
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i=0;i<10000;i++)
getData(i+"");
}
}.start();
}
public static void setData(String name ,String value){
try{
w.lock();
datas.put(name,value);
System.out.println("写入的值是:"+value);
}finally {
w.unlock();
}
}
public static void getData(String name){
try{
r.lock();
System.out.println("读取的值是:"+ datas.get(name));
}finally {
r.unlock();
}
}
}
ReentrantReadWriteLock的实现主要包括:读写状态的设计、写锁的获取与释放、读锁的获取与释放以及锁降,ReentrantReadWriteLock与其他锁不同他包含两个锁,一个读锁一个写锁通过一个整型变量来维护,高16位表示读锁,低16位表示写锁
我们自先来看写锁源码
write.lock()
调用
和reentrantlock类似最后调用的是静态内部类Sync的tryAcquire方法
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If read count nonzero or write count nonzero
* and owner is a different thread, fail.
* 2. If count would saturate, fail. (This can only
* happen if count is already nonzero.)
* 3. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for lock if
* it is either a reentrant acquire or
* queue policy allows it. If so, update state
* and set owner.
*/
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
int w = exclusiveCount(c);//判断是否为写锁,写锁为独占锁,这里清掉高16位的值,如果w=0表示被读锁占有
if (c != 0) {//c不为0表明被读锁占有
// (Note: if c != 0 and w == 0 then shared count != 0)
if (w == 0 || current != getExclusiveOwnerThread())//如果写锁状态为0或者不是当前线程占有写锁,则返回失败
return false;
if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT) //MAX_COUNT该值为65535 大于这个值表示写锁已经超过最大获取次数
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
// Reentrant acquire
setState(c + acquires);//更新AQS中state状态
return true;
}
if (writerShouldBlock() ||
!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires))
return false;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
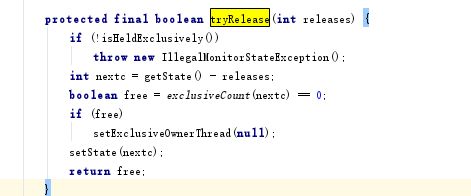
}写锁的释放
最终调用AQS中的
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}再调用Sync中的
读锁的获取
调用Sync内部类中的
再调用AQS中的
调用Sync中的
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
/*
* Walkthrough:
* 1. If write lock held by another thread, fail.
* 2. Otherwise, this thread is eligible for
* lock wrt state, so ask if it should block
* because of queue policy. If not, try
* to grant by CASing state and updating count.
* Note that step does not check for reentrant
* acquires, which is postponed to full version
* to avoid having to check hold count in
* the more typical non-reentrant case.
* 3. If step 2 fails either because thread
* apparently not eligible or CAS fails or count
* saturated, chain to version with full retry loop.
*/
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)//是写锁或者当前线程不是获得锁的线程
return -1;
int r = sharedCount(c);//将低16位清0,剩下的就是高16位
if (!readerShouldBlock() &&//读线程是否应该被阻塞、并且小于最大值、并且比较设置成功
r < MAX_COUNT &&
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
if (r == 0) {
firstReader = current;//设置第一个读线程
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {//第一个读线程重入
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {// 读锁数量不为0并且不为当前线程
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;//获取本地计数器
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))// 计数器为空或者计数器的tid不为当前正在运行的线程的tid
cachedHoldCounter = rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
}
return 1;
}
return fullTryAcquireShared(current);
}final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) {//该方法与tryAcquireShared类似
/*
* This code is in part redundant with that in
* tryAcquireShared but is simpler overall by not
* complicating tryAcquireShared with interactions between
* retries and lazily reading hold counts.
*/
HoldCounter rh = null;
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) {
if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
// else we hold the exclusive lock; blocking here
// would cause deadlock.
} else if (readerShouldBlock()) {
// Make sure we're not acquiring read lock reentrantly
if (firstReader == current) {
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
} else {
if (rh == null) {
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current)) {
rh = readHolds.get();
if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.remove();
}
}
if (rh.count == 0)
return -1;
}
}
if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
if (sharedCount(c) == 0) {
firstReader = current;
firstReaderHoldCount = 1;
} else if (firstReader == current) {
firstReaderHoldCount++;
} else {
if (rh == null)
rh = cachedHoldCounter;
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
else if (rh.count == 0)
readHolds.set(rh);
rh.count++;
cachedHoldCounter = rh; // cache for release
}
return 1;
}
}
}
读锁的释放
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
if (firstReader == current) {//是否为第一个获得读锁的线程
// assert firstReaderHoldCount > 0;
if (firstReaderHoldCount == 1)
firstReader = null;//只有一次直接清空
else
firstReaderHoldCount--;//减少重入次数
} else {
HoldCounter rh = cachedHoldCounter;//获取本地计数器
if (rh == null || rh.tid != getThreadId(current))
rh = readHolds.get();
int count = rh.count;
if (count <= 1) {
readHolds.remove();
if (count <= 0)
throw unmatchedUnlockException();
}
--rh.count;
}
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc))
// Releasing the read lock has no effect on readers,
// but it may allow waiting writers to proceed if
// both read and write locks are now free.
return nextc == 0;
}
}
锁降级
有写得更好的https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxi/p/9140541.html