学习Linux-4.12内核网路协议栈(3.2)——网路层的发包处理
上篇文章介绍了接口层将IP包传给网络层以后的处理过程,主要是包括传给上层,转发和丢包处理。这篇文章将介绍传输层怎么将包传递给网络层,以及传给网络层以后的处理过程。这里主要分两部分:TCP包的发送和UDP包的发送。
在TCP中,将TCP段打包成IP数据报的方法根据TCP段类型的不同而有多种接口,最常用的就是ip_queue_xmit,而ip_build_and_send_pkt和ip_send_unicast_reply只有在发送特定段时才会调用。
在UDP中使用的输出接口有ip_append_data, ip_ufo_append_data和ip_push_pending_frames
最后在IP层实现对GSO的支持,这个部分我们有机会专门找个主题进行分析,现在暂时不进行了解。
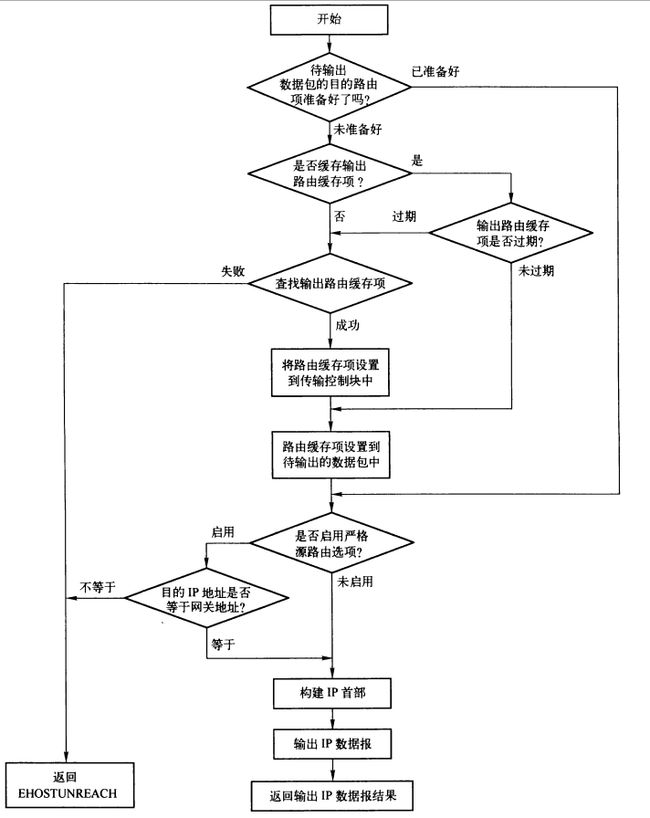
1. ip_queue_xmit
该函数是TCP传输中被调用得最多的函数,普通数据输出都是由它进行打包处理:
424 /* Note: skb->sk can be different from sk, in case of tunnels */
425 int ip_queue_xmit(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb, struct flowi *fl)
426 {
427 struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
428 struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
429 struct ip_options_rcu *inet_opt;
430 struct flowi4 *fl4;
431 struct rtable *rt;
432 struct iphdr *iph;
433 int res;
434
435 /* Skip all of this if the packet is already routed,
436 * f.e. by something like SCTP.
437 */
438 rcu_read_lock();
439 inet_opt = rcu_dereference(inet->inet_opt);
440 fl4 = &fl->u.ip4;
441 rt = skb_rtable(skb);
442 if (rt) //如果输出的数据报已经准好路由缓存,则无需再查找路由,直接跳转到pccket_routed处理部分
443 goto packet_routed;
444
445 /* Make sure we can route this packet. */
446 rt = (struct rtable *)__sk_dst_check(sk, 0); //如果输出该数据的传输数据块中缓存了输出路由缓存项,则需要检测该路由缓存项是否过期
447 if (!rt) { //如果路由缓存项过期,则重新通过输出网络设备dev,目的地址,源地址等信息查找输出路由缓存项。如果查找到对应的路由缓存项,则将其缓存到输出
//控制块中,否则丢弃该数据包
448 __be32 daddr;
449
450 /* Use correct destination address if we have options. */
451 daddr = inet->inet_daddr;
452 if (inet_opt && inet_opt->opt.srr) //如果有option则获取正确的目的IP地址
453 daddr = inet_opt->opt.faddr;
454
455 /* If this fails, retransmit mechanism of transport layer will
456 * keep trying until route appears or the connection times
457 * itself out.
458 */
459 rt = ip_route_output_ports(net, fl4, sk, //根据这些参数查找路由
460 daddr, inet->inet_saddr,
461 inet->inet_dport,
462 inet->inet_sport,
463 sk->sk_protocol,
464 RT_CONN_FLAGS(sk),
465 sk->sk_bound_dev_if);
466 if (IS_ERR(rt))
467 goto no_route;
468 sk_setup_caps(sk, &rt->dst);
469 }
470 skb_dst_set_noref(skb, &rt->dst); //如果没有过期则使用缓存再传输控制块中的路由缓存项
471
472 packet_routed:
473 if (inet_opt && inet_opt->opt.is_strictroute && rt->rt_uses_gateway) //查找到输出路由以后,先进行严格源路由选项的处理,如果存在严格源路由选项,
//并且路由使用网关地址,则丢弃
474 goto no_route;
475
476 /* OK, we know where to send it, allocate and build IP header. */
477 skb_push(skb, sizeof(struct iphdr) + (inet_opt ? inet_opt->opt.optlen : 0)); //现在只要要往哪里发送了,申请并创建IP头部
478 skb_reset_network_header(skb); //重新设置网络层头部指针skb->network_header
479 iph = ip_hdr(skb);
480 *((__be16 *)iph) = htons((4 << 12) | (5 << 8) | (inet->tos & 0xff));
481 if (ip_dont_fragment(sk, &rt->dst) && !skb->ignore_df) //如果有设置不需要分片,则设置相应位
482 iph->frag_off = htons(IP_DF);
483 else
484 iph->frag_off = 0;
485 iph->ttl = ip_select_ttl(inet, &rt->dst); //设置IP头部的TTL
486 iph->protocol = sk->sk_protocol; //设置IP头部的协议
487 ip_copy_addrs(iph, fl4); //地址赋值
488
489 /* Transport layer set skb->h.foo itself. */
490
491 if (inet_opt && inet_opt->opt.optlen) { //如果有option,则需要给IP头部添加option域
492 iph->ihl += inet_opt->opt.optlen >> 2;
493 ip_options_build(skb, &inet_opt->opt, inet->inet_daddr, rt, 0);
494 }
495
496 ip_select_ident_segs(net, skb, sk,
497 skb_shinfo(skb)->gso_segs ?: 1);
498
499 /* TODO : should we use skb->sk here instead of sk ? */
500 skb->priority = sk->sk_priority;
501 skb->mark = sk->sk_mark;
502
503 res = ip_local_out(net, sk, skb); //它最终通过netfilter调用dst_output函数,我们前面知道,对于单播包使用的是ip_output,多播使用的是ip_mc_output
504 rcu_read_unlock();
505 return res;
506
507 no_route:
508 rcu_read_unlock();
509 IP_INC_STATS(net, IPSTATS_MIB_OUTNOROUTES);
510 kfree_skb(skb);
511 return -EHOSTUNREACH;
512 }
513 EXPORT_SYMBOL(ip_queue_xmit);
2. ip_build_and_send_pkt
此函数用于TCP建立过程中,打包输出SYN+ACK类型的TCP段:
139 /*
140 * Add an ip header to a skbuff and send it out. //这个函数和ip_queue_xmit函数很像,只是省略了对路由的查找
141 *
142 */
143 int ip_build_and_send_pkt(struct sk_buff *skb, const struct sock *sk, //skb是待封装成IP报文的TCP段; sk是传输该tcp段的传输控制块
144 __be32 saddr, __be32 daddr, struct ip_options_rcu *opt) //源IP,目的IP, IP选项信息
145 {
146 struct inet_sock *inet = inet_sk(sk);
147 struct rtable *rt = skb_rtable(skb);
148 struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
149 struct iphdr *iph;
150
151 /* Build the IP header. */
152 skb_push(skb, sizeof(struct iphdr) + (opt ? opt->opt.optlen : 0));
153 skb_reset_network_header(skb);
154 iph = ip_hdr(skb);
155 iph->version = 4;
156 iph->ihl = 5;
157 iph->tos = inet->tos;
158 iph->ttl = ip_select_ttl(inet, &rt->dst);
159 iph->daddr = (opt && opt->opt.srr ? opt->opt.faddr : daddr);
160 iph->saddr = saddr;
161 iph->protocol = sk->sk_protocol;
162 if (ip_dont_fragment(sk, &rt->dst)) {
163 iph->frag_off = htons(IP_DF);
164 iph->id = 0;
165 } else {
166 iph->frag_off = 0;
167 __ip_select_ident(net, iph, 1);
168 }
169
170 if (opt && opt->opt.optlen) {
171 iph->ihl += opt->opt.optlen>>2; //建立IP的optin,如果有option,则头部大小要适当加长
172 ip_options_build(skb, &opt->opt, daddr, rt, 0);
173 }
174
175 skb->priority = sk->sk_priority;
176 skb->mark = sk->sk_mark;
177
178 /* Send it out. */
179 return ip_local_out(net, skb->sk, skb);
180 }
3. ip_send_unicast_reply
主要用于构成并输出RST和ACK段,在tcp_v4_send_reset()和tcp_v4_send_ack中被调用:
1584 /*
1585 * Generic function to send a packet as reply to another packet.
1586 * Used to send some TCP resets/acks so far.
1587 */
1588 void ip_send_unicast_reply(struct sock *sk, struct sk_buff *skb,
1589 const struct ip_options *sopt,
1590 __be32 daddr, __be32 saddr,
1591 const struct ip_reply_arg *arg, //一些参数集合,包括待输出的数据、tcp伪首部校验和以及tcp首部中
//检验和字段在首部中的偏移
1592 unsigned int len)
1593 {
1594 struct ip_options_data replyopts;
1595 struct ipcm_cookie ipc;
1596 struct flowi4 fl4;
1597 struct rtable *rt = skb_rtable(skb);
1598 struct net *net = sock_net(sk);
1599 struct sk_buff *nskb;
1600 int err;
1601 int oif;
1602
1603 if (__ip_options_echo(&replyopts.opt.opt, skb, sopt))
1604 return;
1605
1606 ipc.addr = daddr;
1607 ipc.opt = NULL;
1608 ipc.tx_flags = 0;
1609 ipc.ttl = 0;
1610 ipc.tos = -1;
1611
1612 if (replyopts.opt.opt.optlen) {
1613 ipc.opt = &replyopts.opt;
1614
1615 if (replyopts.opt.opt.srr)
1616 daddr = replyopts.opt.opt.faddr;
1617 }
1618
1619 oif = arg->bound_dev_if;
1620 if (!oif && netif_index_is_l3_master(net, skb->skb_iif))
1621 oif = skb->skb_iif;
1622
1623 flowi4_init_output(&fl4, oif,
1624 IP4_REPLY_MARK(net, skb->mark),
1625 RT_TOS(arg->tos),
1626 RT_SCOPE_UNIVERSE, ip_hdr(skb)->protocol,
1627 ip_reply_arg_flowi_flags(arg),
1628 daddr, saddr,
1629 tcp_hdr(skb)->source, tcp_hdr(skb)->dest,
1630 arg->uid);
1631 security_skb_classify_flow(skb, flowi4_to_flowi(&fl4));
1632 rt = ip_route_output_key(net, &fl4);
1633 if (IS_ERR(rt))
1634 return;
1635
1636 inet_sk(sk)->tos = arg->tos;
1637
1638 sk->sk_priority = skb->priority;
1639 sk->sk_protocol = ip_hdr(skb)->protocol;
1640 sk->sk_bound_dev_if = arg->bound_dev_if;
1641 sk->sk_sndbuf = sysctl_wmem_default;
1642 sk->sk_mark = fl4.flowi4_mark;
1643 err = ip_append_data(sk, &fl4, ip_reply_glue_bits, arg->iov->iov_base,
1644 len, 0, &ipc, &rt, MSG_DONTWAIT);
1645 if (unlikely(err)) {
1646 ip_flush_pending_frames(sk);
1647 goto out;
1648 }
1649
1650 nskb = skb_peek(&sk->sk_write_queue);
1651 if (nskb) {
1652 if (arg->csumoffset >= 0)
1653 *((__sum16 *)skb_transport_header(nskb) +
1654 arg->csumoffset) = csum_fold(csum_add(nskb->csum,
1655 arg->csum));
1656 nskb->ip_summed = CHECKSUM_NONE;
1657 ip_push_pending_frames(sk, &fl4);
1658 }
1659 out:
1660 ip_rt_put(rt);
1661 }
4. ip_append_data
LINUX网络协议栈--UDP
Linux网络协议栈--ip_append_data函数分析
到这里基本上将接口层,网络层的内容有个大概的了解了,我暂时没有打算去写传输层相关的东西,原因有两个:
1. 自身工作的原因,我们的设备没有工作在传输层,它只涉及到驱动,接口层和网络层,至于什么设备大家应该也能猜个一二;而且传输层的性能主要表现在服务器方面。
2. 传输层的内容太广,主要集中在TCP上面,机制太多,算法太多,它是TCP/IP的核心,但是暂时没那么多时间关注这一块
所以传输层这一块会先放放。后面的文章将会对套接层进行一个介绍,因为有了它,我们对内核网络的了解才能够通透,才能够说清楚协议栈和应用层的关系。