HashSet与HashMap源码解析
HashSet作为一个散列集,包含了散列集的特点。
散列集:
链表和数组可以按照人们的医院排列顺序,,但是如果人们想要查看某个指定元素,但却又忘记了他的位置,就需要遍历所有元素,直到找到为止,如果集合包含了很多元素,比那里整个集合需要耗费很长的时间。,如果我们不需要在于元素的顺序,可以通过散列码的方法按照其有利于操作目的的原则组织数据。
Set是没有重复元素的集合,将散列码与Set集结合构成HashSet类,用来快速地查看是否某个元素以及出现在集合中,他只在某个桶中查找元素,而不必查看集合中的所有元素。
HashSet实现如下(构造方法,add方法以及contain):
private transient HashMap map;
// Dummy value to associate with an Object in the backing Map
private static final Object PRESENT = new Object();
/**
* Constructs a new, empty set; the backing HashMap instance has
* default initial capacity (16) and load factor (0.75).
*/
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap<>();
}
/**
* 默认的无参构造器,构造一个空的HashSet。
*
* 实际底层会初始化一个空的HashMap,并使用默认初始容量为16和加载因子0.75。
*/
public HashSet() {
map = new HashMap();
}
/**
* 构造一个包含指定collection中的元素的新set。
*
* 实际底层使用默认的加载因子0.75和足以包含指定collection中所有元素的初始容量来创建一个HashMap。
* @param c 其中的元素将存放在此set中的collection。
*/
public HashSet(Collection c) {
map = new HashMap(Math.max((int) (c.size()/.75f) + 1, 16));
addAll(c);
}
/**
* 以指定的initialCapacity和loadFactor构造一个空的HashSet。
*
* 实际底层以相应的参数构造一个空的HashMap。
* @param initialCapacity 初始容量。
* @param loadFactor 加载因子。
*/
public HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
map = new HashMap(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
/**
* 以指定的initialCapacity构造一个空的HashSet。
*
* 实际底层以相应的参数及加载因子loadFactor为0.75构造一个空的HashMap。
* @param initialCapacity 初始容量。
*/
public HashSet(int initialCapacity) {
map = new HashMap(initialCapacity);
}
/**
* 以指定的initialCapacity和loadFactor构造一个新的空链接哈希集合。此构造函数为包访问权限,不对外公开,
* 实际只是是对LinkedHashSet的支持。
*
* 实际底层会以指定的参数构造一个空LinkedHashMap实例来实现。
* @param initialCapacity 初始容量。
* @param loadFactor 加载因子。
* @param dummy 标记。
*/
HashSet(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor, boolean dummy) {
map = new LinkedHashMap(initialCapacity, loadFactor);
}
/**
* @param e 将添加到此set中的元素。
* @return 如果此set尚未包含指定元素,则返回true。
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
return map.put(e, PRESENT)==null;
}
/**
* 如果此set包含指定元素,则返回true。
* 更确切地讲,当且仅当此set包含一个满足(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))的e元素时,返回true。
*
* 底层实际调用HashMap的containsKey判断是否包含指定key。
* @param o 在此set中的存在已得到测试的元素。
* @return 如果此set包含指定元素,则返回true。
*/
public boolean contains(Object o) {
return map.containsKey(o);
}
/**
* 如果指定元素存在于此set中,则将其移除。更确切地讲,如果此set包含一个满足(o==null ? e==null : o.equals(e))的元素e,
* 则将其移除。如果此set已包含该元素,则返回true
*
* 底层实际调用HashMap的remove方法删除指定Entry。
* @param o 如果存在于此set中则需要将其移除的对象。
* @return 如果set包含指定元素,则返回true。
*/
public boolean remove(Object o) {
return map.remove(o)==PRESENT;
}
/**
* 返回此HashSet实例的浅表副本:并没有复制这些元素本身。
*
* 底层实际调用HashMap的clone()方法,获取HashMap的浅表副本,并设置到HashSet中。
*/
public Object clone() {
try {
HashSet newSet = (HashSet) super.clone();
newSet.map = (HashMap) map.clone();
return newSet;
} catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) {
throw new InternalError();
}
}
}
对于 HashSet 中保存的对象,请注意正确重写其 equals 和 hashCode 方法,以保证放入的对象的唯一性。这两个方法是比较重要的,希望大家在以后的开发过程中需要注意一下。
HashMap的数据结构:
HashMap实际上是一个“链表散列”的数据结构,即数组和链表的结合体
HashMap的源码构建如下:
public HashMap(int initialCapacity, float loadFactor) {
if (initialCapacity < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal initial capacity: " +
initialCapacity);
if (initialCapacity > MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
initialCapacity = MAXIMUM_CAPACITY;
if (loadFactor <= 0 || Float.isNaN(loadFactor))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal load factor: " +
loadFactor);
// Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1;
this.loadFactor = loadFactor;
threshold = (int)Math.min(capacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1);
table = new Entry[capacity]; ***************重点***************
useAltHashing = sun.misc.VM.isBooted() &&
(capacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD);
init();
}
我们能够发现在狗仔HashMap时代码创建了一个数组。而数组类型如下:
static class Entry implements Map.Entry {
final K key;
V value;
Entry next;
final int hash;
……
}
可知每个数组中都是以key-value键值对组成的链表。
HashMap核心方法解读如下:
/**
* Associates the specified value with the specified key in this map.
* If the map previously contained a mapping for the key, the old
* value is replaced.
*
* @param key key with which the specified value is to be associated
* @param value value to be associated with the specified key
* @return the previous value associated with key, or
* null if there was no mapping for key.
* (A null return can also indicate that the map
* previously associated null with key.)
*/
public V put(K key, V value) {
//其允许存放null的key和null的value,当其key为null时,调用putForNullKey方法,放入到table[0]的这个位置
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
//通过调用hash方法对key进行哈希,得到哈希之后的数值。该方法实现可以通过看源码,其目的是为了尽可能的让键值对可以分不到不同的桶中
int hash = hash(key);
//根据上一步骤中求出的hash得到在数组中是索引i
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
//如果i处的Entry不为null,则通过其next指针不断遍历e元素的下一个元素。
for (Entry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
}
当我们 put 的时候,如果 key 存在了,那么新的 value 会代替旧的 value,并且如果 key 存在的情况下,该方法返回的是旧的 value,如果 key 不存在,那么返回 null。当我们往 HashMap 中 put 元素的时候,先根据 key 的 hashCode 重新计算 hash 值,根据 hash 值得到这个元素在数组中的位置(即下标),如果数组该位置上已经存放有其他元素了,那么在这个位置上的元素将以链表的形式存放,新加入的放在链头,最先加入的放在链尾。如果数组该位置上没有元素,就直接将该元素放到此数组中的该位置上。
/**
* Adds a new entry with the specified key, value and hash code to
* the specified bucket. It is the responsibility of this
* method to resize the table if appropriate.
*
* Subclass overrides this to alter the behavior of put method.
*/
void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) {
resize(2 * table.length);
hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0;
bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length);
}
createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex);
}
void createEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) {
// 获取指定 bucketIndex 索引处的 Entry
Entry e = table[bucketIndex];
// 将新创建的 Entry 放入 bucketIndex 索引处,并让新的 Entry 指向原来的 Entr
table[bucketIndex] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
size++;
}
当系统决定存储 HashMap 中的 key-value 对时,完全没有考虑 Entry 中的 value,仅仅只是根据 key 来计算并决定每个 Entry 的存储位置。我们完全可以把 Map 集合中的 value 当成 key 的附属,当系统决定了 key 的存储位置之后,value 随之保存在那里即可。
hash值的计算如下:
final int hash(Object k) {
int h = 0;
if (useAltHashing) {
if (k instanceof String) {
return sun.misc.Hashing.stringHash32((String) k);
}
h = hashSeed;
}
//得到k的hashcode值
h ^= k.hashCode();
//进行计算
h ^= (h >>> 20) ^ (h >>> 12);
return h ^ (h >>> 7) ^ (h >>> 4);
}
为了使hash值计算后分布均匀,优化查询速度。
我们首先想到的就是把 hash 值对数组长度取模运算,这样一来,元素的分布相对来说是比较均匀的
在 HashMap 中是这样做的:调用 indexFor(int h, int length) 方法来计算该对象应该保存在 table 数组的哪个索引处。indexFor(int h, int length) 方法的代码如下
这个方法非常巧妙,它通过 h & (table.length -1) 来得到该对象的保存位,而 HashMap 底层数组的长度总是 2 的 n 次方,这是 HashMap 在速度上的优化。在 HashMap 构造器中有如下代码
/**
* Returns index for hash code h.
*/
static int indexFor(int h, int length) {
return h & (length-1);
}
// Find a power of 2 >= initialCapacity
int capacity = 1;
while (capacity < initialCapacity)
capacity <<= 1;
这段代码保证底层数组的长度总是2的N次方。如下举个例子为什么我们需要将底层数组的长度设置为2的n次方。
假设数组长度分别为15和16,根据上述代码可以计算出将数据存储在数组的第几位。
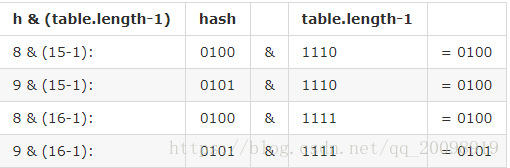
如上图,若是数组长度为15时,根据代码实现,计算出的index始终为0100,数字8和9都需要存储在这个位置,即通过链表形式存储,我们在HashMap中查找的时候便需要遍历链表结构,大大增加了查询的速度。
同时可以发现,‘与’对象的最后一位为0,则 0001,0011,0101,1001,1011,0111,1101 这几个位置永远都不能存放元素了,空间浪费相当大,更糟的是这种情况中,数组可以使用的位置比数组长度小了很多,这意味着进一步增加了碰撞的几率,减慢了查询的效率。
引用极客学院李大辉的一句对HashMap的总结来说:
当程序试图将一个key-value对放入HashMap中时,程序首先根据该 key 的 hashCode() 返回值决定该 Entry 的存储位置:如果两个 Entry 的 key 的 hashCode() 返回值相同,那它们的存储位置相同。如果这两个 Entry 的 key 通过 equals 比较返回 true,新添加 Entry 的 value 将覆盖集合中原有 Entry 的 value,但key不会覆盖。如果这两个 Entry 的 key 通过 equals 比较返回 false,新添加的 Entry 将与集合中原有 Entry 形成 Entry 链,而且新添加的 Entry 位于 Entry 链的头部——具体说明继续看 addEntry() 方法的说明。
简单地说,HashMap 在底层将 key-value 当成一个整体进行处理,这个整体就是一个 Entry 对象。HashMap 底层采用一个 Entry[] 数组来保存所有的 key-value 对,当需要存储一个 Entry 对象时,会根据 hash 算法来决定其在数组中的存储位置,在根据 equals 方法决定其在该数组位置上的链表中的存储位置;当需要取出一个Entry 时,也会根据 hash 算法找到其在数组中的存储位置,再根据 equals 方法从该位置上的链表中取出该Entry。
使用HashMap的几个注意点:
在HashMap中的数据越来越多后,在数组中的碰撞几率会越来越大,若对这种情况置之不理则会导致HashMap的性能大大降低。在HashMap构造中,为了提高HashMap的查询效率。为了扩容HashMap,性能消耗点便出现了:原数组中的数据必须重新计算其在新数组中的位置,并放进去,这就是 resize。
当HashMap中的数据数量超过了*loadFactor时,便会进行数组扩容。
HashMap 包含如下几个构造器:
HashMap():构建一个初始容量为 16,负载因子为 0.75 的 HashMap。
HashMap(int initialCapacity):构建一个初始容量为 initialCapacity,负载因子为 0.75 的
HashMap。 HashMap(int initialCapacity, floatloadFactor):以指定初始容量、指定的负载因子创建一个 HashMap。
负载因子 loadFactor 衡量的是一个散列表的空间的使用程度,负载因子越大表示散列表的装填程度越高,反之愈小。对于使用链表法的散列表来说,查找一个元素的平均时间是 O(1+a),因此如果负载因子越大,对空间的利用更充分,然而后果是查找效率的降低;如果负载因子太小,那么散列表的数据将过于稀疏,对空间造成严重浪费。
HashMap的遍历方式
HashMap 的两种遍历方式
第一种
Map map = new HashMap();
Iterator iter = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Map.Entry entry = (Map.Entry) iter.next();
Object key = entry.getKey();
Object val = entry.getValue();
}
效率高,以后一定要使用此种方式!
第二种
Map map = new HashMap();
Iterator iter = map.keySet().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
Object key = iter.next();
Object val = map.get(key);
}
效率低(?为什么??)
引文:
http://wiki.jikexueyuan.com/project/java-collection/hashmap.html