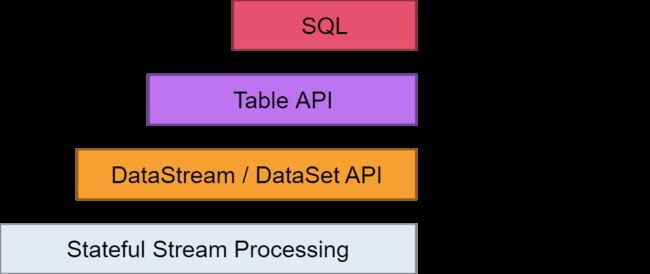
从flink的官方文档,我们知道flink的编程模型分为四层,sql层是最高层的api,Table api是中间层,DataStream/DataSet Api 是核心,stateful Streaming process层是底层实现。
其中,
flink dataset api使用及原理 介绍了DataSet Api
flink DataStream API使用及原理介绍了DataStream Api
flink中的时间戳如何使用?---Watermark使用及原理 介绍了底层实现的基础Watermark
flink window实例分析 介绍了window的概念及使用原理
Flink中的状态与容错 介绍了State的概念及checkpoint,savepoint的容错机制
上上篇<使用flink Table &Sql api来构建批量和流式应用(1)Table的基本概念>介绍了Table的基本概念及使用方法
上篇<使用flink Table &Sql api来构建批量和流式应用(2)Table API概述>
本篇主要看看Flink Sql 有哪些功能及背后的原理
1. sql功能
体现在org.apache.flink.table.api.TableEnvironment,目前flink仅支持select和insert操作
(1) select
/** * Evaluates a SQL query on registered tables and retrieves the result as a {@link Table}. * ** * @param query The SQL query to evaluate. * @return The result of the query as Table */ Table sqlQuery(String query);All tables referenced by the query must be registered in the TableEnvironment. * A {
@link Table} is automatically registered when its {@link Table#toString()} method is * called, for example when it is embedded into a String. * Hence, SQL queries can directly reference a {@link Table} as follows: * ** {@code * Table table = ...; * String tableName = table.toString(); * // the table is not registered to the table environment * tEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT * FROM tableName"); * } *
(2) update(当前仅支持insert)
/** * Evaluates a SQL statement such as INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE; or a DDL statement; * NOTE: Currently only SQL INSERT statements are supported. * ** * @param stmt The SQL statement to evaluate. */ void sqlUpdate(String stmt); /** * Evaluates a SQL statement such as INSERT, UPDATE or DELETE; or a DDL statement; * NOTE: Currently only SQL INSERT statements are supported. * *All tables referenced by the query must be registered in the TableEnvironment. * A {
@link Table} is automatically registered when its {@link Table#toString()} method is * called, for example when it is embedded into a String. * Hence, SQL queries can directly reference a {@link Table} as follows: * ** {@code * // register the configured table sink into which the result is inserted. * tEnv.registerTableSink("sinkTable", configuredSink); * Table sourceTable = ... * String tableName = sourceTable.toString(); * // sourceTable is not registered to the table environment * tEnv.sqlUpdate(s"INSERT INTO sinkTable SELECT * FROM tableName"); * } *
All tables referenced by the query must be registered in the TableEnvironment. * A {
@link Table} is automatically registered when its {@link Table#toString()} method is * called, for example when it is embedded into a String. * Hence, SQL queries can directly reference a {@link Table} as follows: * *
* {@code
* // register the configured table sink into which the result is inserted.
* tEnv.registerTableSink("sinkTable", configuredSink);
* Table sourceTable = ...
* String tableName = sourceTable.toString();
* // sourceTable is not registered to the table environment
* tEnv.sqlUpdate(s"INSERT INTO sinkTable SELECT * FROM tableName", config);
* }
*
*
* @param stmt The SQL statement to evaluate.
* @param config The {@link QueryConfig} to use.
*/
void sqlUpdate(String stmt, QueryConfig config);
2. sql解析原理
Apache Calcite面向Hadoop新的sql引擎,它提供了标准的SQL语言、多种查询优化和连接各种数据源的能力。除此之外,Calcite还提供了OLAP和流处理的查询引擎。它2013年成为了Apache孵化项目以来,在Hadoop中越来越引人注目,并被众多项目集成。比如Flink/Storm/Drill/Phoenix都依赖它做sql解析和优化。
先从demo跑起来,看看sql 解析都经历了什么工程?
(1) select
package org.apache.flink.table.examples.java; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.datastream.DataStream; import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.environment.StreamExecutionEnvironment; import org.apache.flink.table.api.Table; import org.apache.flink.table.api.java.StreamTableEnvironment; import java.util.Arrays; /** * Simple example for demonstrating the use of SQL on a Stream Table in Java. * *This example shows how to: * - Convert DataStreams to Tables * - Register a Table under a name * - Run a StreamSQL query on the registered Table *
*/ public class StreamSQLExample { // ************************************************************************* // PROGRAM // ************************************************************************* public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // set up execution environment StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); StreamTableEnvironment tEnv = StreamTableEnvironment.create(env); DataStreamorderA = env.fromCollection(Arrays.asList( new Order(1L, "beer", 3), new Order(1L, "diaper", 4), new Order(3L, "rubber", 2))); DataStream orderB = env.fromCollection(Arrays.asList( new Order(2L, "pen", 3), new Order(2L, "rubber", 3), new Order(4L, "beer", 1))); // convert DataStream to Table Table tableA = tEnv.fromDataStream(orderA, "user, product, amount"); // register DataStream as Table tEnv.registerDataStream("OrderB", orderB, "user, product, amount"); // union the two tables Table result = tEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT * FROM " + tableA + " WHERE amount > 2 UNION ALL " + "SELECT * FROM OrderB WHERE amount < 2"); tEnv.toAppendStream(result, Order.class).print(); env.execute(); } // ************************************************************************* // USER DATA TYPES // ************************************************************************* /** * Simple POJO. */ public static class Order { public Long user; public String product; public int amount; public Order() { } public Order(Long user, String product, int amount) { this.user = user; this.product = product; this.amount = amount; } @Override public String toString() { return "Order{" + "user=" + user + ", product='" + product + '\'' + ", amount=" + amount + '}'; } } }
实现代码如下
override def sqlQuery(query: String): Table = { val planner = getFlinkPlanner // parse the sql query val parsed = planner.parse(query) if (null != parsed && parsed.getKind.belongsTo(SqlKind.QUERY)) { // validate the sql query val validated = planner.validate(parsed) // transform to a relational tree val relational = planner.rel(validated) new TableImpl(this, new PlannerQueryOperation(relational.rel)) } else { throw new TableException( "Unsupported SQL query! sqlQuery() only accepts SQL queries of type " + "SELECT, UNION, INTERSECT, EXCEPT, VALUES, and ORDER_BY.") } }
>>parse the sql query
在calcite中用SqlNode表示
public SqlSelect(SqlParserPos pos, SqlNodeList keywordList, SqlNodeList selectList, SqlNode from, SqlNode where, SqlNodeList groupBy, SqlNode having, SqlNodeList windowDecls, SqlNodeList orderBy, SqlNode offset, SqlNode fetch) { super(pos); this.keywordList = Objects.requireNonNull(keywordList != null ? keywordList : new SqlNodeList(pos)); this.selectList = selectList; this.from = from; this.where = where; this.groupBy = groupBy; this.having = having; this.windowDecls = Objects.requireNonNull(windowDecls != null ? windowDecls : new SqlNodeList(pos)); this.orderBy = orderBy; this.offset = offset; this.fetch = fetch; }
>>validate the sql query
SqlValidatorImpl验证sqlNode
public SqlNode validate(SqlNode topNode) { SqlValidatorScope scope = new EmptyScope(this); scope = new CatalogScope(scope, ImmutableList.of("CATALOG")); final SqlNode topNode2 = validateScopedExpression(topNode, scope); final RelDataType type = getValidatedNodeType(topNode2); Util.discard(type); return topNode2; }
>>transform to a relational tree
SqlToRelConverter.java
/** * Converts an unvalidated query's parse tree into a relational expression. * * @param query Query to convert * @param needsValidation Whether to validate the query before converting; *falseif the query has already been * validated. * @param top Whether the query is top-level, say if its result * will become a JDBC result set;falseif * the query will be part of a view. */ public RelRoot convertQuery( SqlNode query, final boolean needsValidation, final boolean top) { if (needsValidation) { query = validator.validate(query); } RelMetadataQuery.THREAD_PROVIDERS.set( JaninoRelMetadataProvider.of(cluster.getMetadataProvider())); RelNode result = convertQueryRecursive(query, top, null).rel; if (top) { if (isStream(query)) { result = new LogicalDelta(cluster, result.getTraitSet(), result); } } RelCollation collation = RelCollations.EMPTY; if (!query.isA(SqlKind.DML)) { if (isOrdered(query)) { collation = requiredCollation(result); } } checkConvertedType(query, result); if (SQL2REL_LOGGER.isDebugEnabled()) { SQL2REL_LOGGER.debug( RelOptUtil.dumpPlan("Plan after converting SqlNode to RelNode", result, SqlExplainFormat.TEXT, SqlExplainLevel.EXPPLAN_ATTRIBUTES)); } final RelDataType validatedRowType = validator.getValidatedNodeType(query); return RelRoot.of(result, validatedRowType, query.getKind()) .withCollation(collation); }
(2)update
代码实现
override def sqlUpdate(stmt: String): Unit = { sqlUpdate(stmt, this.queryConfig) } override def sqlUpdate(stmt: String, config: QueryConfig): Unit = { val planner = getFlinkPlanner // parse the sql query val parsed = planner.parse(stmt) parsed match { case insert: SqlInsert => // validate the SQL query val query = insert.getSource val validatedQuery = planner.validate(query) // get query result as Table val queryResult = new TableImpl(this, new PlannerQueryOperation(planner.rel(validatedQuery).rel)) // get name of sink table val targetTablePath = insert.getTargetTable.asInstanceOf[SqlIdentifier].names // insert query result into sink table insertInto(queryResult, config, targetTablePath.asScala:_*) case _ => throw new TableException( "Unsupported SQL query! sqlUpdate() only accepts SQL statements of type INSERT.") } }
步骤类似,不再赘述。
3. 总结
Flink Table API&SQL 为流式数据和静态数据的关系查询保留统一的接口,而且利用了Calcite的查询优化框架和SQL parser。该设计是基于Flink已构建好的API构建的,DataStream API 提供低延时高吞吐的流处理能力而且就有exactly-once语义而且可以基于event-time进行处理。而且DataSet拥有稳定高效的内存算子和流水线式的数据交换。Flink的core API和引擎的所有改进都会自动应用到Table API和SQL上。
参考资料:
【1】http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-29038263-id-5765791.html