LeetCode - Top 100 Liked Questions
771. Jewels and Stones
You're given strings J representing the types of stones that are jewels, and S representing the stones you have. Each character in S is a type of stone you have. You want to know how many of the stones you have are also jewels.
The letters in J are guaranteed distinct, and all characters in J and S are letters. Letters are case sensitive, so "a" is considered a different type of stone from "A".
第一次的思路:把S转换成数组,遍历是否在J里存在
My Solution: Runtime: 60 ms, faster than 100.00% , Memory Usage: 34 MB, less than 62.96%
/**
* @param {string} J
* @param {string} S
* @return {number}
*/
var numJewelsInStones = function(J, S) {
let result = 0
S.split('').forEach((item, index) => {
if (J.indexOf(item) != -1) {
result = result + 1
}
})
return result
};大佬思路:ES6,字符串 includes直接判断,解决indexOf的两个弊端(1.语义化;2.不能判断是否有NaN的元素)
伪数组转数组:
ES5: Array.prototype.slice.call(object)
ES6: [...object]; Array.from(object)
sample 60 ms submission
/**
* @param {string} J
* @param {string} S
* @return {number}
*/
var numJewelsInStones = function(J, S) {
var count = 0;
for(var i = 0; i < S.length; i++){
if(J.includes(S[i])){
count ++;
}
}
return count
};sample 33576 kb submission
const numJewelsInStones = (J, S) => S.split('').filter(char => J.indexOf(char) !== -1).length;461. Hamming Distance
The Hamming distance between two integers is the number of positions at which the corresponding bits are different.
Given two integers x and y, calculate the Hamming distance.
Note:
0 ≤ x, y < 231.
第一次的思路:通过异或得到的字符串转数组,再用reduce累加位数为1的值
My Solution: Runtime: 60 ms, faster than 90.50%, Memory Usage: 33.8 MB, less than 31.33%
/**
* @param {number} x
* @param {number} y
* @return {number}
*/
var hammingDistance = function(x, y) {
return (x^y).toString(2).split('').reduce((x, y) => parseInt(x) + parseInt(y))
};大佬思路:用while与1移位累加出结果
sample 56 ms submission
/**
* @param {number} x
* @param {number} y
* @return {number}
*/
//time is O(logn) and space is O(1)
var hammingDistance = function(x, y) {
let ans = 0
let t = x ^ y
while(t){
ans = ans + (t & 1)
t = t >> 1
}
return ans
};sample 33580 kb submission
/**
* @param {number} x
* @param {number} y
* @return {number}
*/
var hammingDistance = function(x, y) {
var count = 0;
while (x > 0 || y > 0) {
if (x%2 != y%2) count++;
x = Math.floor(x / 2);
y = Math.floor(y / 2);
}
return count;
};总结:1.二进制与十进制的相互转换;2.异或;3.reduce
减少用到不需要的变量名,用其他循环代替for,用位运算代替加,可以减少时间;
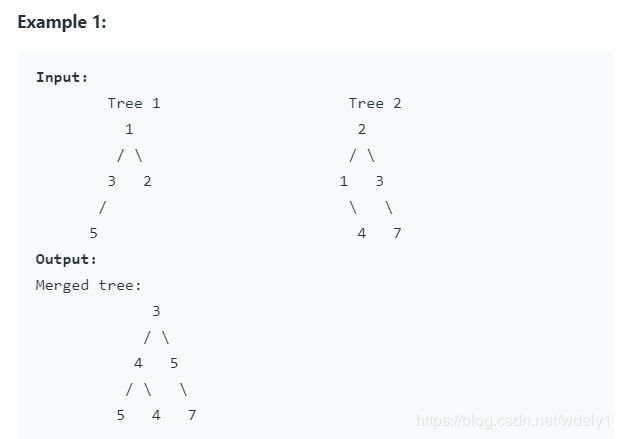
617. Merge Two Binary Trees
Given two binary trees and imagine that when you put one of them to cover the other, some nodes of the two trees are overlapped while the others are not.
You need to merge them into a new binary tree. The merge rule is that if two nodes overlap, then sum node values up as the new value of the merged node. Otherwise, the NOT null node will be used as the node of new tree.
第一次的思路:递归合并左右孩子节点
My Solution: Runtime: 104 ms, faster than 49.30%, Memory Usage: 40.1 MB, less than 75.76%
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} t1
* @param {TreeNode} t2
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var mergeTrees = function(t1, t2) {
if (t1 == null || t2 == null) return t1 == null ? t2 : t1
if (t1 !== null && t2 !== null) {
t1.val = t1.val + t2.val
t1.left = mergeTrees(t1.left, t2.left)
t1.right = mergeTrees(t1.right, t2.right)
}
return t1
};sample 96 ms submission
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} t1
* @param {TreeNode} t2
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var mergeTrees = function(t1, t2) {
if(t1==null){
return t2;
}
if(t2==null){
return t1;
}
t1.val += t2.val;
t1.left = mergeTrees(t1.left, t2.left);
t1.right = mergeTrees(t1.right, t2.right);
return t1;
};sample 39996 kb submission
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} t1
* @param {TreeNode} t2
* @return {TreeNode}
*/
var mergeTrees = function(tree1, tree2) {
if(tree1 && tree2) {
tree1.val += tree2.val
tree1.left = mergeTrees(tree1.left, tree2.left);
tree1.right = mergeTrees(tree1.right, tree2.right);
}
return tree1 || tree2;
};448. Find All Numbers Disappeared in an Array
Given an array of integers where 1 ≤ a[i] ≤ n (n = size of array), some elements appear twice and others appear once.
Find all the elements of [1, n] inclusive that do not appear in this array.
Could you do it without extra space and in O(n) runtime? You may assume the returned list does not count as extra space.
第一次的思路:先去重,再遍历数组,存在则出栈,不存在则入栈
My Solution: Runtime: 4656 ms, faster than 21.64%, Memory Usage: 51.1 MB, less than 12.33%
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findDisappearedNumbers = function(nums) {
let result = Array.from(new Set(nums))
nums.forEach((e, i) => {
if (result.includes(i+1)) {
result.splice(result.indexOf(i+1), 1)
} else {
result.push(i+1)
}
})
return result
};大佬思路:用hashmap的思想,把数组的值-1作为新下标,去找到对应的值*-1,剩下为正数的值,则为消失值对应的位置,再根据下标+1,则为消失的值
sample 100 ms submission
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findDisappearedNumbers = function(nums) {
const result = [];
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i += 1) {
if (nums[Math.abs(nums[i]) - 1] > 0) {
nums[Math.abs(nums[i]) - 1] *= -1;
}
}
for(let i = 0; i < nums.length; i += 1) {
if (nums[i] > 0) {
result.push(i + 1);
}
}
return result;
};sample 41980 kb submission
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number[]}
*/
var findDisappearedNumbers = function(nums) {
let output = [];
let length = nums.length;
let i = 1;
while (i < length+1) {
let flag = false;
for (let j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
if (i === nums[j]) {
flag = true;
}
}
if (!flag) {
output.push(i);
}
i++;
}
return output;
};169. Majority Element
Given an array of size n, find the majority element. The majority element is the element that appears more than ⌊ n/2 ⌋ times.
You may assume that the array is non-empty and the majority element always exist in the array.
第一次的思路:先按照升序排序,再循环记录每个值出现的次数,最后筛出次数最多的一项
My Solution: Runtime: 88 ms, faster than 20.27%, Memory Usage: 8.1 MB, less than 16.50%
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var majorityElement = function(nums) {
nums = nums.sort()
let last = nums[0]
let time = []
let n = 0
nums.forEach((e, i) => {
if (last != e || i == nums.length -1) {
if(i == nums.length -1) n = n + 1
time.push({
value: last,
time: n
})
n = 1
last = e
} else {
n = n + 1
}
})
return time.find(i => i.time > Math.floor(nums.length/2)).value
};大佬思路:遍历数组,记录最大值及出现的次数count,若下一个值不等于新值,则count-1,若减后count = 0,则最大值=新值,count = 1;若下一个值等于新值,则count++。最后的num则为结果
sample 60 ms submission
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var majorityElement = function(nums) {
const len = nums.length;
if (!len) { return null; }
let num = nums[0];
let count = 1;
for (let i = 1; i < len; i++) {
let curr = nums[i];
if (num !== curr) {
count--;
if (count <= 0) {
num = curr;
count = 1;
}
} else {
count++;
}
}
return num;
};sample 36976 kb submission
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var majorityElement = function(nums) {
[major, count] = [undefined, 0];
let n = nums.length;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (count > ~~ ((n + 1) / 2)) { return major; }
if (major == undefined) {
major = nums[i];
count = 1;
} else if (count == 0) {
major = nums[i];
count = 1;
}
else if (nums[i] === major) {
count++;
} else {
count--;
}
}
return major;
};70. Climbing Stairs
You are climbing a stair case. It takes n steps to reach to the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Note: Given n will be a positive integer.
第一次的思路:斐波那契数列,用递归得到新值
Time Limit Exceeded
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var climbStairs = function(n) {
if (n > 2) {
return climbStairs(n-1) + climbStairs(n-2)
} else if (n == 2) {
return 2
} else if (n == 1) {
return 1
} else {
return 0
}
};不使用递归,直接使用数组的方式:最重要的是递归的思考方式,而不是写出递归的代码,递归确实影响效率。
My Solution: 56 ms, faster than 99.66%, Memory Usage: 33.7 MB, less than 58.26%
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var climbStairs = function(n) {
let arr = [0,1,2]
for (let i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
arr[i] = arr[i-1] + arr[i-2]
}
return arr[n]
};大佬思路:直接存上一次的前两个数,连数组都省了
sample 52 ms submission
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var climbStairs = function(n) {
// dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2]
if(n <= 2) return n;
let a = 1, b = 2;
for(let i = 2; i < n; i++) {
let tmp = a + b;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
return b;
};sample 33472 kb submission
/**
* @param {number} n
* @return {number}
*/
var climbStairs = function(n) {
let memo = {}
let stairs = (n, memo = {}) => {
if (memo[n]) {return memo[n]};
if (n < 4) {return n};
memo[n] = stairs(n-1, memo) + stairs(n-2,memo);
return memo[n]
}
return stairs(n, memo)
}53. Maximum Subarray
Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum and return its sum.
第一次的思路:并没有在短时间内写出来
大佬思路:(动态规划法)largestSum存之前的和,contiguousSum存当前的和;当前最大和=contiguousSum或contiguousSum+nums[i];每轮比较largestSum和contiguousSum
sample 60 ms submission
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var maxSubArray = function(nums) {
var largestSum = nums[0];
var contiguousSum = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
contiguousSum = Math.max(nums[i], contiguousSum + nums[i]);
if (contiguousSum > largestSum) {
largestSum = contiguousSum;
}
}
return largestSum;
};sample 34632 kb submission
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var maxSubArray = function(nums) {
let total = nums[0]
let currentSum = 0;
nums.forEach(num => {
if (currentSum > 0) {
currentSum = currentSum + num;
} else {
currentSum = num;
}
total = Math.max(currentSum, total)
})
return total
};kadane算法
算法描述:(跟我第一次想的很相似,但是没有记录下来过程中最大的值)
- 遍历该数组, 在遍历过程中, 将遍历到的元素依次累加起来, 当累加结果小于或等于0时, 从下一个元素开始,重新开始累加。
- 累加过程中, 要用一个变量(max_so_far)记录所获得过的最大值。
- 一次遍历之后, 变量 max_so_far 中存储的即为最大子片段的和值。
/** * @param {number[]} nums * @return {number} */ var maxSubArray = function(nums) { let sum = 0; let result = 0; for (let i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) { sum = sum + nums[i] if (sum < 0) { sum = 0 } if (result < sum) { result = sum } } return result; };
287. Find the Duplicate Number
Given an array nums containing n + 1 integers where each integer is between 1 and n (inclusive), prove that at least one duplicate number must exist. Assume that there is only one duplicate number, find the duplicate one.
第一次的思路:先去重,再遍历找出对应的值,然后出栈,剩下的那个值就为重复值
My Solution: Runtime:72 ms, faster than 61.43%, Memory Usage: 38.8 MB, less than 6.35%
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var findDuplicate = function(nums) {
let arr = [...new Set(nums)]
arr.forEach((item, index) => {
nums.splice(nums.indexOf(item), 1)
})
return nums[0]
};大佬思路:用对象的键值对,先遍历一遍数组,key为值,value为出现的次数,最后再遍历一次,找出value>1的值
sample 56 ms submission
/**
* @param {number[]} nums
* @return {number}
*/
var findDuplicate = function(nums) {
let obj = {}
for (let i = 0; i 1) return keys[j]
};