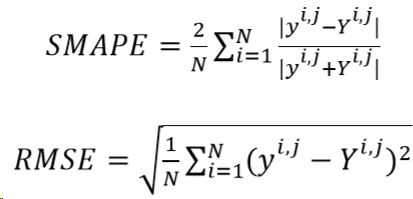【论文阅读】Deep Inferential Spatial-Temporal Network for Forecasting Air Pollution Concentrations
摘要:
Deep Inferential Spatial-Temporal Network以解决空间和时间方面的非线性相关问题。使用inferential predictor、 spatial predictor和temporal predictor进行了48小时天气预报,主要研究数据来源于北京地区35个站点和格网气象数据
目前的主要问题:
1、多因子问题 multiple factors could affect air pollutants and we are not able to capture all of them
2、污染物的聚集情况受污染物种类、地理位置等影响 the trends of air pollution concentrations are complicated
3、站点的数量以及地理分布的限制 the number of monitoring stations is limited in a city due to huge land usage, expensive maintenance fee and necessary human labor
主要贡献:
1、使用混合模型处理limited data以预测未来的PM2.5浓度,模型包括inferential predictor、 spatial predictor和temporal predictor
2、inferential predictor用于处理稀疏的空气污染数据,在没有数据的区域进行插值处理
3、基于 inferential prediction的CNN模型得到区域特征
4、在 temporal predictor上使用了注意力机制
5、大尺度的空气质量和气象数据
Related Work
环境学家使用 classical dispersion models,但是不精确也不普适;数据驱动的方法如时间序列模型忽略了其他的features;
在deep learning 引入之后,CNN LSTM等成为热点
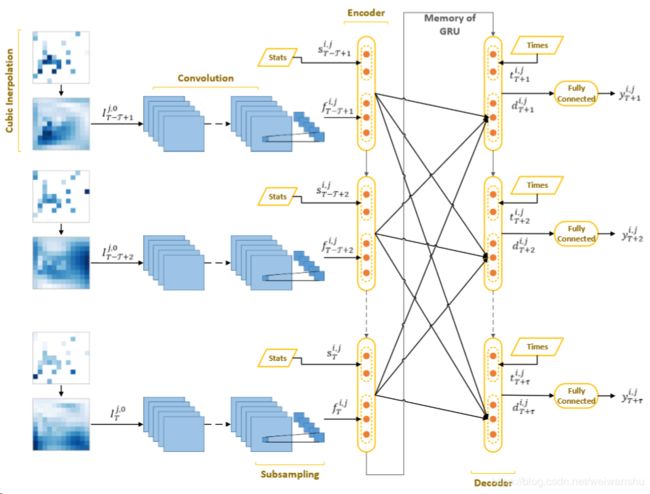
概念和方法
Grid——用经纬划分格网、格网内air pollutions 和 meteorological features相同。格网内有站点的就使用站点读数,没有站点的就使用cubic interpolation进行插值
需要解决的问题是已知所有格网 ?小时的空气污染指标 ? 的时间序列 ?? 以及气象的历史数据 ??,![]()
求得格网 ? 的空气污染指标 ? 未来 ? 时刻的数据??,? = ![]()
主要方法
Inferential Predictor: Cubic Interpolation Spatial Predictor: CNN
Temporal Predictor: Sequence-to-sequence with Simplified Attention
实验数据
1、air pollution monitoring station and mereological station data of Beijing, China between January 1, 2017 and May 31, 2018
2、divided Beijing into 11 × 12 regions based on 0.1-degree of longitude and latitude coordinates. The size of each region is about 10 ?? × 10 ??
3、 DIST-Net is designed to predict the future 48 h of target air pollution (e.g., pm2.5, pm10 or O3) at target location based on the air pollution and mereological data of the previous 72 hours.
Loss Function
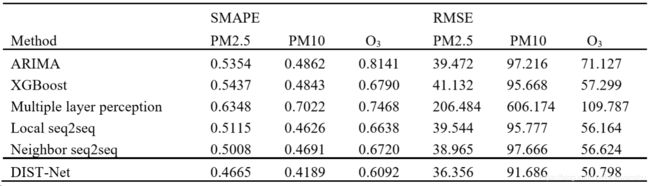
结果