MTCNN网络 前期XML转text,通过读取text,计算negative、positive、part
1.XML转成Text
前几天自己看github大神的代码,然后跟着复原了一遍MTCNN,因为想跑跑自己的数据集,所以就拿了YOLO2中一段代码,修改一下, 开始自己制作MTCNN前期的数据集。
目标检测目前是万变不离其宗,都需要前期的标注。但是如果要改变神经网络形式提高检测精度,那么前期的标注处理就变的非常多样化。
数据标注这一块我就不多叙述了。先上一张我标注的图片给大家养养眼。
1.1标注的好的图片
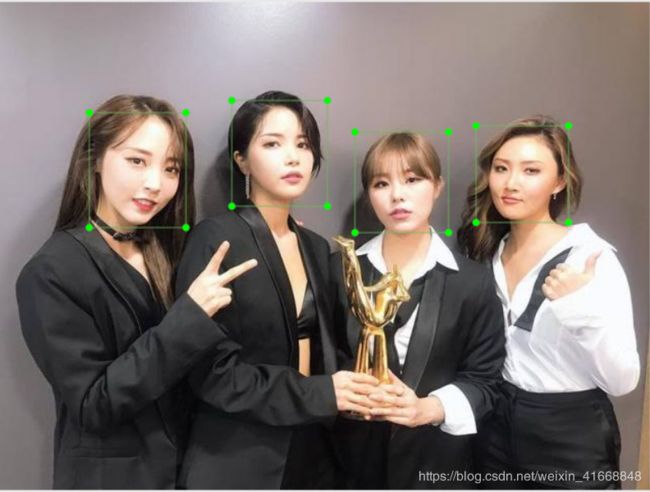

这是我标注的图片
保存后的XML格式为
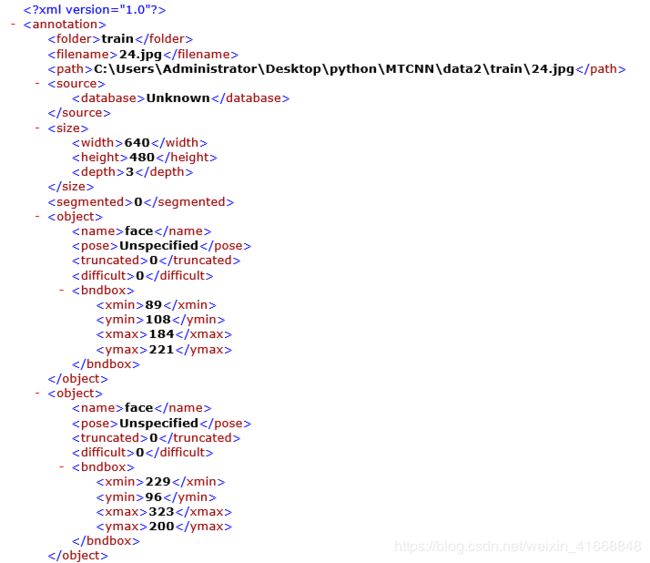
这是我截取的一部分
annot ----->保存的是xml文件
train ------->保存的是原图
到这里我们就开始从xml文件中读取x1,x2,y1,y2 放入text文件中。以便计算IOU
这段代码是yolo2中读取xml文件,yolo2读取xml中有 [w,h,x1,y1,x2,y2,class]
但是MTCNN读取XML内容不需要这么多,只需要 [地址、x1,y1,x2,y2]
所以我修改了一下。注释掉了 获取label 只获取XML中的 [path,x1,y1,x2,y2]
当然该代码也可以联级,省略中间的Text 文本,直接调用去计算IOU
import os, glob
import numpy as np
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def parse_annotation(img_dir, ann_dir):
"""
parse annotation and save is into numpy array
img_dir: image path( 训练集图片路径)
ann_dir: annotation xml file path (训练集xml路径)
labels: ('sugarweet','weed')
"""
imgs_info = [] # 存储所以图片信息的容器列表
max_boxes = 0 # 计算所有图片中,目标在一张中出现最多数量
# os.listdir() 方法用于返回指定的文件夹包含的文件或文件夹的名字的列表
for ann in os.listdir(ann_dir):
tree = ET.parse(os.path.join(ann_dir, ann)) # 分析指定XML文件
img_info = dict() # 为标签xml文件创建一个内容存放的容器
img_info['object'] = []
boxes_counter = 0
for elem in tree.iter(): # 遍历xml所有的标签(annotation)
if 'filename' in elem.tag: # 若filename在annotation标签内
img_info['filename'] = os.path.join(img_dir, elem.text)
if 'width' in elem.tag:
img_info['width'] = int(elem.text)
# assert img_info['width'] == 512
if 'height' in elem.tag:
img_info['height'] = int(elem.text)
# assert img_info['width'] == 512
# 读取目标框的信息
if 'object' in elem.tag or 'part' in elem.tag:
# x1-y1-x2-y2-label
object_info = [0, 0, 0, 0]
# print(str(object_info))
boxes_counter += 1
for attr in list(elem): # 遍历object标签下的内容
# add image info into object_info
# if 'name' in attr.tag:
# label = labels.index(attr.text) + 1 # 累计类别数量
#
# object_info[4] = label
if 'bndbox' in attr.tag:
for pos in list(attr): # 在bndbox中遍历
if 'xmin' in pos.tag:
object_info[0] = int(pos.text)
if 'ymin' in pos.tag:
object_info[1] = int(pos.text)
if 'xmax' in pos.tag:
object_info[2] = int(pos.text)
if 'ymax' in pos.tag:
object_info[3] = int(pos.text)
img_info['object'].append(object_info)
imgs_info.append(img_info) # filename,w/h/box_info
# (N,5) = (max_objects_num,5) 5 is x-y-w-h-label
if boxes_counter > max_boxes:
max_boxes = boxes_counter
# 转化为矩阵:[b,max_things,5]
boxes = np.zeros([len(imgs_info), max_boxes, 4])
imgs = [] # 存储filename文件名地址
for i, img_info in enumerate(imgs_info):
# [N,5] N: boxes number
img_boxes = np.array(img_info['object'])
# 使用每张图片的 x1-y1-x2,y2 l填充[b,max_things,4]
boxes[i, :img_boxes.shape[0]] = img_boxes
imgs.append(img_info['filename'])
#这是就是保存 [path、x1,y1,x2,y2] 的过程。
wirt = out_file = open('label.txt', 'w')
for i in range(len(imgs)):
path = imgs[i]
wirt.write("\n"+ str(path))
for box in boxes[i]:
ine = " " + str(box[0]) + " " + str(box[2]) \
+ " " + str(box[1]) + " " + str(box[3])
wirt.write(ine)
return imgs, boxes
img_path = "data2/train" # 图片地址
ann_path = "data2/annot" # xml地址
# labels = ("23") # 类别
imgs, boxes = parse_annotation(img_path, ann_path)
我们制作的label.txt文本已经出现了。
因为我只是举例子,所以我用了2张图片做演示。
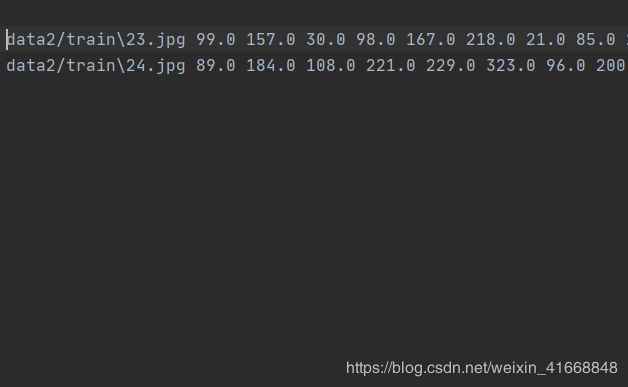
注意!!!
看到该文本第一行是空白了没有,这是因为换行造成的,这个需要处理一下。不然会因为换行符问题造成读取遗漏。然后爆BUG。
处理代码
# 读取label.txt
with open(anno_file, 'r') as f:
annotations = f.readlines()
#删除第一行
del annotations[0]
2.计算IOU
我们开始利用Text文本里面的 [path、x1,y1,x2,y2] ,计算IOU、保存:negative、positive、part
import sys
import numpy as np
import cv2
import os
import numpy.random as npr
stdsize = 12
anno_file = "label.txt"
# im_dir = "samples"
pos_save_dir = str(stdsize) + "/positive"
part_save_dir = str(stdsize) + "/part"
neg_save_dir = str(stdsize) + '/negative'
save_dir = "./" + str(stdsize)
def IoU(box, boxes):
"""Compute IoU between detect box and gt boxes
Parameters:
----------
box: numpy array , shape (5, ): x1, y1, x2, y2, score
input box
boxes: numpy array, shape (n, 4): x1, y1, x2, y2
input ground truth boxes
Returns:
-------
ovr: numpy.array, shape (n, )
IoU
"""
box_area = (box[2] - box[0] + 1) * (box[3] - box[1] + 1)
area = (boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0] + 1) * (boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1] + 1)
# boxes[:, 0]代表取boxes这个nx4矩阵所有行的第一个数据
xx1 = np.maximum(box[0], boxes[:, 0])
# print(xx1)
yy1 = np.maximum(box[1], boxes[:, 1])
xx2 = np.minimum(box[2], boxes[:, 2])
yy2 = np.minimum(box[3], boxes[:, 3])
# compute the width and height of the bounding box
w = np.maximum(0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
ovr = inter / (box_area + area - inter)
return ovr
# 生成一系列文件夹用于存储三类样本
def mkr(dr):
if not os.path.exists(dr):
os.mkdir(dr)
mkr(save_dir)
mkr(pos_save_dir)
mkr(part_save_dir)
mkr(neg_save_dir)
# 生成一系列txt文档用于存储Positive,Negative,Part三类数据的信息
f1 = open(os.path.join(save_dir, 'pos_' + str(stdsize) + '.txt'), 'w')
f2 = open(os.path.join(save_dir, 'neg_' + str(stdsize) + '.txt'), 'w')
f3 = open(os.path.join(save_dir, 'part_' + str(stdsize) + '.txt'), 'w')
# 读取label.txt 并处理第一行的空白
with open(anno_file, 'r') as f:
annotations = f.readlines()
del annotations[0]
num = len(annotations)
print("%d pics in total" % num)
p_idx = 0 # positive
n_idx = 0 # negative
d_idx = 0 # dont care
idx = 0
box_idx = 0
for annotation in annotations:
annotation = annotation.strip().split(' ')
print(annotation)
im_path = annotation[0]
#bbox = list((map(float, annotation[1:])))
bbox = annotation[1:]
boxes = np.array(bbox, dtype=np.float32).reshape(-1, 4)
img = cv2.imread(im_path)
idx += 1
if idx % 100 == 0:
print(idx, "images done")
height, width, channel = img.shape
# print(img.shape)
neg_num = 0
while neg_num < 50:
# 生成随机数,对每张数据集中的图像进行切割,生成一系列小的图像
size = npr.randint(40, min(width, height) / 2)
nx = npr.randint(0, width - size)
ny = npr.randint(0, height - size)
crop_box = np.array([nx, ny, nx + size, ny + size])
# print(crop_box)
# 计算小的图像与标注产生的检测框之间的IoU
Iou = IoU(crop_box, boxes)
# print(Iou)
cropped_im = img[ny : ny + size, nx : nx + size, :]
resized_im = cv2.resize(cropped_im, (stdsize, stdsize), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
if np.max(Iou) < 0.3:
# Iou with all gts must below 0.3
save_file = os.path.join(neg_save_dir, "%s.jpg"%n_idx)
f2.write(str(stdsize)+"/negative/%s"%n_idx + ' 0\n')
cv2.imwrite(save_file, resized_im)
n_idx += 1
neg_num += 1
for box in boxes:
# box (x_left, y_top, x_right, y_bottom)
x1, y1, x2, y2 = box
w = x2 - x1 + 1
h = y2 - y1 + 1
# max(w, h) < 40:参数40表示忽略的最小的脸的大小
# in case the ground truth boxes of small faces are not accurate
if max(w, h) < 40 or x1 < 0 or y1 < 0:
continue
# generate positive examples and part faces
for i in range(20):
print(i)
size = npr.randint(int(min(w, h) * 0.8), np.ceil(1.25 * max(w, h)))
# delta here is the offset of box center
delta_x = npr.randint(-w * 0.2, w * 0.2)
delta_y = npr.randint(-h * 0.2, h * 0.2)
nx1 = max(x1 + w / 2 + delta_x - size / 2, 0)
ny1 = max(y1 + h / 2 + delta_y - size / 2, 0)
nx2 = nx1 + size
ny2 = ny1 + size
if nx2 > width or ny2 > height:
continue
crop_box = np.array([nx1, ny1, nx2, ny2])
offset_x1 = (x1 - nx1) / float(size)
offset_y1 = (y1 - ny1) / float(size)
offset_x2 = (x2 - nx2) / float(size)
offset_y2 = (y2 - ny2) / float(size)
cropped_im = img[int(ny1) : int(ny2), int(nx1) : int(nx2), :]
resized_im = cv2.resize(cropped_im, (stdsize, stdsize), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
box_ = box.reshape(1, -1)
if IoU(crop_box, box_) >= 0.65:
save_file = os.path.join(pos_save_dir, "%s.jpg"%p_idx)
f1.write(str(stdsize)+"/positive/%s"%p_idx + ' 1 %.2f %.2f %.2f %.2f\n'%(offset_x1, offset_y1, offset_x2, offset_y2))
cv2.imwrite(save_file, resized_im)
p_idx += 1
elif IoU(crop_box, box_) >= 0.4:
save_file = os.path.join(part_save_dir, "%s.jpg"%d_idx)
f3.write(str(stdsize)+"/part/%s"%d_idx + ' -1 %.2f %.2f %.2f %.2f\n'%(offset_x1, offset_y1, offset_x2, offset_y2))
cv2.imwrite(save_file, resized_im)
d_idx += 1
box_idx += 1
print ("%s images done, pos: %s part: %s neg: %s"%(idx, p_idx, d_idx, n_idx))
f1.close()
f2.close()
f3.close()