java1.7集合源码赏析系列:HashTable、ConcurrentHashMap、HashMap差异分析
HashTable与ConcurrentHashMap均可实现HashMap的功能,对外提供了键值对存储的数据结构。但是在内部结构及实现上有何区别,性能上的差异到底在哪里又是如何导致的,让我们从源码的角度上来进行分析。
1. 声明的区别
//hashtable的声明
public class Hashtable<K,V>
extends Dictionary<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
//ConcurrentHashMap的声明
public class ConcurrentHashMap<K, V> extends AbstractMap<K, V>
implements ConcurrentMap<K, V>, Serializable
//hashmap的声明
public class HashMap<K,V>
extends AbstractMap<K,V>
implements Map<K,V>, Cloneable, SerializableHashtable继承了Dictionary类,实现了Map接口,提供了clone方法。
ConcurrentHashMap继承了AbstractMap类,实现了ConcurrentMap接口。
HashMap继承了AbstractMap类,实现了Map接口,提供了clone方法。
三者之间最大的差别在于实现了不同的接口ConcurrentMap和Map。
再看看ConcurrentMap。
//ConcurrentMap的声明
public interface ConcurrentMap<K, V> extends Map<K, V> 小结:在一定的程度上可以理解为Hashtable在提供的方法上与HashMap并无不同,ConcurrentHashMap则提供了更多的方法,或者说功能更加强大。
2.方法的区别
从最为常用的方法来看,即get和put。
//依然是方法声明,实现代码略去
//HashMap
public V get(Object key){
}
public V put(K key, V value) {
}
//Hashtable
public synchronized V get(Object key){
}
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
}
//ConcurrentHashMap
public V get(Object key) {
}
public V put(K key, V value){
}
小结:ConcurrentHashMap与HashMap没有区别。HashTable则在方法级别上加入了同步锁synchronized,并且读写都有。由此可以看出HashTable虽然解决了线程安全的问题,但是性能却是急剧下降的。
3.数据结构的区别
//HashTable的数据存储在Entry数组中,每个Entry元素是一个单向链表。
private transient Entry[] table;
//Entry的属性
private static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
int hash;
final K key;
V value;
Entry next;
}
//HashMap的数据存储在Entry数组中,每个Entry元素是一个单向链表。
transient Entry[] table = (Entry[]) EMPTY_TABLE;
//Entry的属性
static class Entry<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final K key;
V value;
Entry next;
int hash;
}
//ConcurrentHashMap使用一个Segment数组存放数据,每一个Segment元素又维护着一个HashEntry链表数组
final Segment[] segments;
//Segment的属性
transient volatile HashEntry[] table;
//HashEntry的属性
static final class HashEntry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V value;
volatile HashEntry next;
} 小结:HashMap的数据结构与HashTable一致,ConcurrentHashMap则是维护着多个HashMap。
4.数据操作的区别
//HashTable
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
//HashTable不允许空值,虽然Hashtable没有对key为空做处理,但是如果key是null时会抛空指针
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry tab[] = table;
int hash = hash(key);
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
V old = e.value;
e.value = value;
return old;
}
}
modCount++;
if (count >= threshold) {
// Rehash the table if the threshold is exceeded
rehash();
tab = table;
hash = hash(key);
index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
}
// Creates the new entry.
Entry e = tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
return null;
} //HashMap
public V put(K key, V value) {
if (table == EMPTY_TABLE) {
inflateTable(threshold);
}
if (key == null)
return putForNullKey(value);
int hash = hash(key);
int i = indexFor(hash, table.length);
for (Entry e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) {
Object k;
if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) {
V oldValue = e.value;
e.value = value;
e.recordAccess(this);
return oldValue;
}
}
modCount++;
addEntry(hash, key, value, i);
return null;
} hashmap和hashtable的put操作是一样的,此处不再做讲解,传送门java1.7集合源码赏析系列:HashMap
//ConcurrentHashMap
//值不能为空,key为空时会抛空指针
public V put(K key, V value) {
Segment s;
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//第一次hash
int hash = hash(key);
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;
if ((s = (Segment)UNSAFE.getObject // nonvolatile; recheck
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null) // in ensureSegment
s = ensureSegment(j);
//取到对应的segment再put
return s.put(key, hash, value, false);
}
//segment的put方法
//这里的操作与hashmap类似,不同的是在put里面有了锁
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
HashEntry node = tryLock() ? null :
scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);
V oldValue;
try {
HashEntry[] tab = table;
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
HashEntry first = entryAt(tab, index);
for (HashEntry e = first;;) {
if (e != null) {
K k;
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.value = value;
++modCount;
}
break;
}
e = e.next;
}
else {
if (node != null)
node.setNext(first);
else
node = new HashEntry(hash, key, value, first);
int c = count + 1;
if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
rehash(node);
else
setEntryAt(tab, index, node);
++modCount;
count = c;
oldValue = null;
break;
}
}
} finally {
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
} 小结:Hashtable、ConcurrentHashMap的key和value都不能为空,HashMap的key和value都可以为空。Hashtable和HashMap的put操作是一样的,ConcurrentHashMap则略微复杂点。
ConcurrentHashMap的结构图:
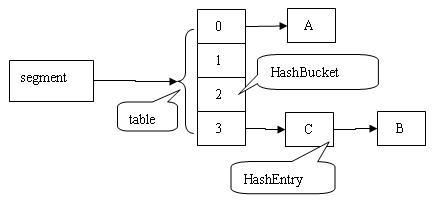
HashMap和Hashtable的结构是一样的segment元素中存储的就是HashMap的结构,此处不再赘述。
总结:1.HashTable与HashMap结构一样,Hashtable是串行操作,多线程情况下慢于HashMap。
2.ConcurrentHashMap通过再hash的方式将数据划分成更细粒度的HashMap,在细粒度上控制并发,因此多线程情况下快于Hashtable。而它的读操作又是支持并发的,因此性能是远远超于Hashtable的。
3.多线程情况下建议使用ConcurrentHashMap
4.使用HashMap,数据量较大的情况下,建议1)初始化指定初始容量,如果在业务确定的情况下,考虑也初始化加载因子。2)对key的hashcode需做深入考虑,避免雪崩效应,方法有string、整型、或者重写。