Greenplum 对JSON的支持
Greenplum 对JSON的支持
源文章:http://www.postgresqltutorial.com/postgresql-json/
Greenplum 对JSON的支持
Greenplum 对JSON的支持 1
1 JSON概述 2
2 JSON常用运算符与函数 2
2.1 JSON常用运算符 2
2.2 JSON常用的创建函数 3
2.3 JSON处理函数 4
3 JSON 运算符常用实例 5
3.1 单组JSON解析 5
3.2 多组JSON解析 5
3.3 复杂的JSON解析 6
3.3.1 多个JSON子集的解析 6
3.3.2 获取JSON子集的数据 6
3.3.3 获取一个JSON集合的子元素 6
4 JSON 创建函数的使用 7
4.1 创建int类型的JSON格式数据 7
4.2 把行的数据转化为JSON类型的数据 7
5 JSON处理函数的使用 8
5.1 获取JSON中的数据 8
5.2 获取JSON中的数据(去除双引号) 8
5.3 获取JSON数据中的KEY的值 9
6 查询JSON数据的方式 9
6.1 创建支持JSON数据的表 9
6.1.1 创建表的SQL 9
6.1.2 插入数据SQL 10
6.1.3 获取JSON数据的KEY值 10
6.2 获取JSON结构中的数据 11
6.3 按照条件查询数据 12
6.4 集合函数查询JSON数据 13
6.5 使用默认的函数查找数据 14
6.5.1 JSON_EACH 函数的使用 14
6.5.2 JSON_OBJECT_KEYS 函数的使用 14
6.6 把查询数据转化为JSON 15
6.6.1 查看原始数据 15
6.6.2 把查询的数据转化为JSON 16
6.6.2.1 把字段的名字作为JSON对象 16
6.6.2.2 使用默认的JSON字段名字 17
1 JSON概述
JSON作为结构化的数据,目前越来越受到开发者的爱戴,它简单灵活易于理解。是作为储存数据的一种比较使用的一种格式,greenplum从5.0开始便很好的支持了JSON数据。
参考资料:https://hashrocket.com/blog/posts/faster-json-generation-with-postgresql#how-to
Greenplum官网介绍:https://gpdb.docs.pivotal.io/530/admin_guide/query/topics/json-data.html
2 JSON常用运算符与函数
2.1 JSON常用运算符
| Operator |
Right Operand Type |
Description |
Example |
Example Result |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -> |
int |
Get JSON array element (indexed from zero). |
'[{"a":"foo"},{"b":"bar"},{"c":"baz"}]'::json->2 |
{"c":"baz"} |
| -> |
text |
Get JSON object field by key. |
'{"a": {"b":"foo"}}'::json->'a' |
{"b":"foo"} |
| ->> |
int |
Get JSON array element as text. |
'[1,2,3]'::json->>2 |
3 |
| ->> |
text |
Get JSON object field as text. |
'{"a":1,"b":2}'::json->>'b' |
2 |
| #> |
text[] |
Get JSON object at specified path. |
'{"a": {"b":{"c": "foo"}}}'::json#>'{a,b}' |
{"c": "foo"} |
| #>> |
text[] |
Get JSON object at specified path as text. |
'{"a":[1,2,3],"b":[4,5,6]}'::json#>>'{a,2}' |
3 |
2.2 JSON常用的创建函数
array_to_json(anyarray [, pretty_bool])
row_to_json(record [, pretty_bool])
2.3 JSON处理函数
json_each(json)
json_each_text(json)
json_extract_path(from_json json, VARIADIC path_elems text[])
json_extract_path_text(from_json json, VARIADIC path_elems text[])
json_object_keys(json)
json_populate_record(base anyelement, from_json json)
json_populate_recordset(base anyelement, from_json json)
json_array_elements(json)
3 JSON 运算符常用实例
3.1 单组JSON解析
select '{"a":1}'::json ->>'a' as jsondata;
3.2 多组JSON解析
select '{"a":1,"b":2}'::json->>'b' as jsondata;
3.3 复杂的JSON解析
3.3.1 多个JSON子集的解析
select '[{"a":"foo"},{"b":"bar"},{"c":"baz"}]'::json->2 as jsondata;
注意以上结果查询的坐标是从0开始的,查询条件必须是索引
3.3.2 获取JSON子集的数据
select '{"a": {"b":{"c": "foo"}}}'::json#>'{a,b}' as jsondata;
注意#>'{a,b}的使用,表示一层一层的查询
3.3.3 获取一个JSON集合的子元素
select '{"a":[1,2,3],"b":[4,5,6]}'::json#>>'{a,2}' as jsondata;
注意这个JSON写的格式,以及获取的顺序
4 JSON 创建函数的使用
4.1 创建int类型的JSON格式数据
select array_to_json('{{1,5},{99,100}}'::int[]) as jsondata;
注意int数组的json数据已经把原本的格式转换了。
4.2 把行的数据转化为JSON类型的数据
select row_to_json(row(1,2,'foo')) as jsondata;
注意查看以上的结果可以看出row是行的数据,结果中f1,f2,f3是默认的字段的名,在后面将会介绍怎样获取字段名转化为JSON。
5 JSON处理函数的使用
5.1 获取JSON中的数据
select * from json_each('{"a":"foo", "b":"bar"}');
以上结果只显示出了key与value的值,如果只需要这部分的数据导出来更好。
5.2 获取JSON中的数据(去除双引号)
select * from json_each_text('{"a":"foo", "b":"bar"}')
可以注意到与上一个比较value的值去除了双引,这个数据是比较使用的。
5.3 获取JSON数据中的KEY的值
select * from json_object_keys('{"f1":"abc","f2":{"f3":"a", "f4":"b"}}') as jsondata;
只把数据的key的值获取出来了,注意别名的使用,必须放在数据的后面,不知道为啥?
经过测试竟然没有json_object_values的方法。
6 查询JSON数据的方式
6.1 创建支持JSON数据的表
6.1.1 创建表的SQL
创建带有主键的表
CREATE TABLE test_json (
ID serial NOT NULL PRIMARY KEY,
info json NOT NULL
);
6.1.2 插入数据SQL
INSERT INTO test_json (info)
VALUES
(
'{ "customer": "John Doe", "items": {"product": "Beer","qty": 6}}'
),
(
'{ "customer": "Lily Bush", "items": {"product": "Diaper","qty": 24}}'
),
(
'{ "customer": "Josh William", "items": {"product": "Toy Car","qty": 1}}'
),
(
'{ "customer": "Mary Clark", "items": {"product": "Toy Train","qty": 2}}'
);
6.1.3 获取JSON数据的KEY值
SELECT info -> 'customer' AS customer FROM test_json;
以上数据只把制定KEY的VALUE获取出来,注意使用-> 是不把双引号去掉的。
SELECT info ->> 'customer' AS customer FROM test_json;
使用->> 就可以把双引去掉了。
6.2 获取JSON结构中的数据
SELECT
info -> 'items' ->> 'product' AS product
FROM
test_json
ORDER BY
product;
SQL中可以->与->>一起使用,区别就是结果有无双引的问题。
6.3 按照条件查询数据
SELECT
info ->> 'customer' AS customer
FROM
test_json
WHERE
info -> 'items' ->> 'product' = 'Diaper'
查询条件也可以作为解析的对象。
也可以写成以下的形式
SELECT
info ->> 'customer' AS customer,
info -> 'items' ->> 'product' AS product
FROM
test_json
WHERE
CAST (
info -> 'items' ->> 'qty' AS INTEGER
) = 2
info -> 'items' ->> 'qty' AS INTEGER 是获取json集合中元素是qty的数据 转化为INTEGER,
case() 是把数值转化为int4类型
6.4 集合函数查询JSON数据
SELECT
MIN(CAST( info -> 'items' ->> 'qty' AS INTEGER)),
MAX (CAST (info -> 'items' ->> 'qty' AS INTEGER)),
SUM (CAST (info -> 'items' ->> 'qty' AS INTEGER)),
AVG (CAST (info -> 'items' ->> 'qty' AS INTEGER))
FROM
test_json
6.5 使用默认的函数查找数据
6.5.1 JSON_EACH 函数的使用
SELECT
json_each(info)
FROM
test_json;
json_each 函数把含有key与value的数据全部取了出来,如果一行有多个key与value则会把分行显示出来。
6.5.2 JSON_OBJECT_KEYS 函数的使用
SELECT
json_object_keys (info->'items') as jsondata
FROM
test_json;
6.6 把查询数据转化为JSON
6.6.1 查看原始数据
select * from test_json_date;
6.6.2 把查询的数据转化为JSON
6.6.2.1 把字段的名字作为JSON对象
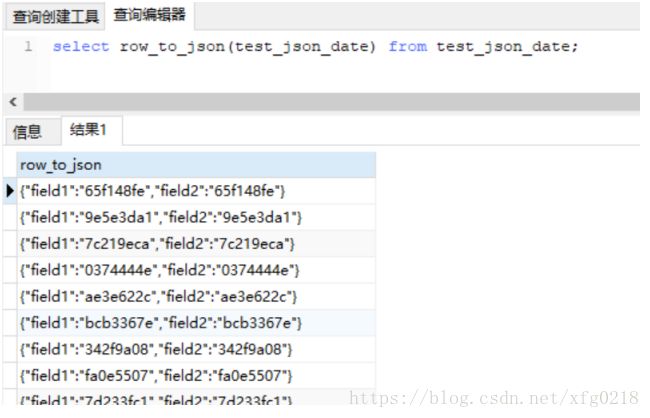
select row_to_json(test_json_date) from test_json_date;
test_json_date 是表的名字,row_to_json() 里面的也是表里面的名字
6.6.2.2 使用默认的JSON字段名字
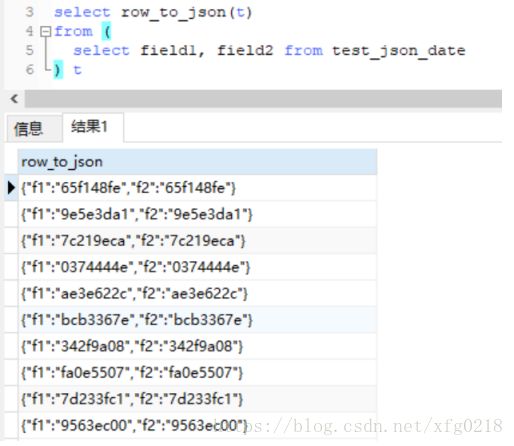
select row_to_json(row(field1, field2)) from test_json_date;
可以看出已使用默认的字段作为JSON的对象了。
或写成以下形式