linux系统之根文件系统树制作
前言: 很早就在linux下做过了uboot移植,linux内核移植以及文件系统的制作,一直没有来得及总结,现在好好把之前做过的东西整理一下,主要是为了备忘。现在总结一下根文件系统树制作的流程。
1.根文件系统简介
文件系统是对一个存储设备上的数据和元数据进行组织的机制。这种机制有利于用户和操作系统的交互。根文件系统它包含系统引导以及其他文件系统所能挂载的必要文件。
根文件系统,是Linux内核启动时挂载(mount)的第一个文件系统,这也是它和其他普通文件系统的不同之处,根文件系统同样具有普通文件系统的存储数据文件的功能。
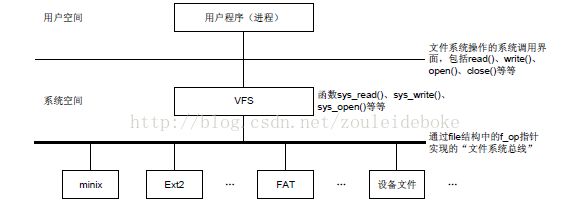
Linux又支持多种文件系统,包括ext2、ext3、vfat、ntfs、iso9660、jffs、romfs和nfs等,为了对各类文件系统 进行统一管理,Linux引入了虚拟文件系统VFS(Virtual File System),通过VFS屏蔽下层文件系统之间的差异。下图是VFS、内核、文件系统的层次结构:
在这里要明白,Linux内核和文件系统是相互独立的,在嵌入式中移植的内核下载到开发板上,是没有办法真正的启动Linux操作系统的,会出现无法加载文件系统的错误。
Linux启动时,第一个必须挂载的是根文件系统;若系统不能从指定设备上挂载根文件系统,则系统会出错而退出启动。成功之后可以自动或手动挂载其他的文件系统。因此,一个系统中可以同时存在不同的文件系统。
在 Linux 中将一个文件系统与一个存储设备关联起来的过程称为挂载(mount)。使用 mount 命令将一个文件系统附着到当前文件系统层次结构中(根)。在执行挂装时,要提供文件系统类型、文件系统和一个挂装点。根文件系统被挂载到根目录下“/”上后,在根目录下就有根文件系统的各个目录,文件:/bin /sbin /mnt等,再将其他分区挂接到/mnt目录上,/mnt目录下就有这个分区的各个目录,文件。
2.根文件系统树制作
[zoulei@CentOS opt]$ cd rootfs
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ ls
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ mkdir-p {apps,bin,data,dev,info,proc,root,sbin,sys,tmp,var,etc/{,init.d,dropbear},mnt/{,usb,sdc,nfs,dev},usr/{,bin,sbin,lib,share},lib/{,modules/{,3.0.0}}}
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ tree -L 3
.
|-- apps # 挂载Application所在分区用的目录
|-- bin
|-- data # 挂载data分区所在的目录
|-- dev
|-- etc
| |-- dropbear # dropbear ssh server依赖的文件
| `-- init.d #系统启动初始化脚本
|-- info #挂载info分区所在的目录
|-- lib #动态库所存放的目录
| `-- modules # insmod时,依赖/lib/modules/内核版本目录
| `-- 3.0.0 #我们将Linux驱动放到该目录下,目录名对应内核版本号
|-- mnt #设备在运行时的一些挂载点
| |-- dev #保留备用
| |-- nfs # NFS挂载点
| |-- sdc # SD卡挂载点
| `-- usb # U盘挂载点
|-- proc # proc文件挂载点
|-- root # root用户目录
|-- sbin
|-- sys # sys文件系统挂载点
|-- tmp # tmpfs文件系统挂载点
|-- usr
| |-- bin
| |-- lib #用户程序动态库放到这里
| |-- sbin
| `-- share
`-- var
27 directories, 0 files
上面的一些目录,可以先不用关系它的用途,今后对文件系统进行扩展时在介绍。
3.dev目录下创建设备文件
因为内核挂载完文件系统后,init进程需要用到/dev/console和/dev/null这两个设备文件来调用mdev构建dev,所以必须在制作文件系统时静态创建这两个设备文件,否则在系统启动时将提示:
Waring:unable to open an initial console:
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$sudo mknod -m666 dev/null c 1 3
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ sudo mknod -m666 dev/console c 5 1
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ sudo mknod -m666 dev/ttyS0 c 4 64
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ sudo mknod -m666 dev/ttySAC0 c 4 64
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ sudo mknod dev/mtdblock0 b 31 0
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ sudo mknod dev/mtdblock1 b 31 1
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ sudo mknod dev/mtdblock2 b 31 2
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$sudo mknod dev/mtdblock3 b 31 3
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ sudo mknod dev/mtdblock4 b 31 4
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ sudo mknod dev/mtdblock5 b 31 5
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$sudo mknod dev/mtdblock6 b 31 6
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ sudo mknod dev/mtdblock7 b 31 7
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ sudo mknod dev/mtdblock8 b 31 8
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ sudo mknod dev/mtdblock9 b 31 9
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ ls -l dev/
总用量 0
crw-rw-rw- 1 root root 5, 1 12月 25 2016 console
brw-r--r-- 1 root root 31, 0 12月 25 2016 mtdblock0
brw-r--r-- 1 root root 31, 1 12月 25 2016 mtdblock1
brw-r--r-- 1 root root 31, 2 12月 25 2016 mtdblock2
brw-r--r-- 1 root root 31, 3 12月 25 2016 mtdblock3
brw-r--r-- 1 root root 31, 4 12月 25 2016 mtdblock4
brw-r--r-- 1 root root 31, 5 12月 25 2016 mtdblock5
brw-r--r-- 1 root root 31, 6 12月 25 2016 mtdblock6
brw-r--r-- 1 root root 31, 7 12月 25 2016 mtdblock7
brw-r--r-- 1 root root 31, 8 12月 25 2016 mtdblock8
brw-r--r-- 1 root root 31, 9 12月 25 2016 mtdblock9
crw-rw-rw- 1 root root 1, 3 12月 25 2016 null
crw-rw-rw- 1 root root 4, 64 12月 25 2016 ttyS0
crw-rw-rw- 1 root root 4, 64 12月 25 2016 ttySAC0
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$
4.var目录下创建符号连接文件
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ ln -s /tmp var/lock
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ ln -s /tmp var/log
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ ln -s /tmp var/run
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ ln -s /tmp var/tmp
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ ls -l var/
总用量 0
lrwxrwxrwx 1 zoulei zoulei 4 12月 25 2016 lock -> /tmp
lrwxrwxrwx 1 zoulei zoulei 4 12月 25 2016 log -> /tmp
lrwxrwxrwx 1 zoulei zoulei 4 12月 25 2016 run -> /tmp
lrwxrwxrwx 1 zoulei zoulei 4 12月 25 2016 tmp -> /tmp
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$
5.拷贝交叉编译器中的动态库到相应目录下
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ cp -af /opt/buildroot-2012.08/arm920t/usr/arm-linux/sysroot/lib/*so* lib/
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ cp -af /opt/buildroot-2012.08/arm920t/usr/arm-linux/lib/*so* lib/
这里防止出错,最好用这个脚本来拷贝
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ cd etc/
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ ls
dropbear fs.conf fstab group hostname hosts init.d inittab issue mdev.conf passwd profile protocols shadow TZ
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ vim inittab
# /etc/inittab
#
# Copyright (C) 2017 zoulei
#
# Note: BusyBox init doesn't support runlevels. The runlevels field is
# completely ignored by BusyBox init. If you want runlevels, use sysvinit.
#
# Format for each entry: :::
#
# id == tty to run on, or empty for /dev/console.
# If specified, then /dev/$id device must exist
# runlevels == ignored, busybox doesn't support it
# action == one of sysinit, respawn, askfirst, wait, and once
# process == program to run
# Startup the system
# mount all the file systems specified in /etc/fstab
::sysinit:/bin/mount -a
#Use mdev as hotplug to auto mount USB storage or SD card
::sysinit:/bin/echo /sbin/mdev > /proc/sys/kernel/hotplug
#Use mdev to auto generate the device node in /dev path
::sysinit:/sbin/mdev -s
#make shm, pts support
::sysinit:/bin/mkdir -p /dev/pts
::sysinit:/bin/mkdir -p /dev/shm
::sysinit:/bin/mount -t devpts devpts /dev/pts
#Mount our apps/info partition
null::wait:/bin/mount -o sync,noatime,ro -t jffs2 /dev/mtdblock6 /apps
null::wait:/bin/mount -o sync,noatime,ro -t jffs2 /dev/mtdblock7 /info
#Set hostname
null::sysinit:/bin/hostname -F /etc/hostname
#Enable console logon
null::respawn:/sbin/getty -L ttyS0 115200 vt100
# now run any rc scripts
null::wait:/etc/init.d/rcS
# system daemon
null::respawn:/sbin/syslogd -n
null::respawn:/sbin/klogd -n
# Stuff to do before rebooting
null::shutdown:/bin/umount /apps
null::shutdown:/bin/umount /info
null::shutdown:/bin/killall klogd
null::shutdown:/bin/killall syslogd
null::shutdown:/bin/umount -a -r
#null::shutdown:/sbin/swapoff -a [zoulei@CentOS etc]$ vim init.d/rcS
#!/bin/sh
# Copyright (C) 2017 zoulei121
# Start all init scripts in /etc/init.d
# executing them in numerical order.
#
for i in /etc/init.d/S??* ; do
$i
done
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ vim init.d/S01_network
#!/bin/sh
ifconfig eth0 192.168.1.111 netmask 255.255.255.0 up
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ vim init.d/S99_rcsApp
opyright (C) 2017 zoulei121
#
# Start all init scripts in /apps/etc/init.d
# executing them in numerical order.
#
if (test -d /apps/etc/init.d)
then
for i in /apps/etc/init.d/S??* ; do
$i
done
fi
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ chmod 777 init.d/*
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ ll init.d/
total 12
-rwxrwxrwx 1 lingyun trainning 222 Apr 26 13:27 rcS
-rwxrwxrwx 1 lingyun trainning 64 Apr 26 13:33 S01_network
-rwxrwxrwx 1 lingyun trainning 248 Apr 26 13:37 S99_rcsApp
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$
10.创建fstab文件
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ vim fstab
# /etc/fstab: static file system information.
# Copyright (C) 2017 zoulei121
#
#
#devpts /dev/pts devpts defaults 0 0
#/dev/root / ext2 rw,noauto 0 1
proc /proc proc defaults 0 0
tmpfs /tmp tmpfs defaults 0 0
tmpfs /dev tmpfs defaults 0 0
sysfs /sys sysfs defaults 0 0 [zoulei@CentOS etc]$echo "root" > hostname
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ echo "127.0.0.1 localhost" >> hosts
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ echo "MST7MDT" >> TZ
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ echo "Copyright (C) 2017 zoulei121
12.创建profile文件
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ vim profile
# /etc/profile: system-wide .profile file for the Bourne shells.
export PATH=\
/bin:\
/sbin:\
/usr/bin:\
/usr/sbin:\
/usr/local/bin:\
/apps/bin:\
/apps/tools:\
/apps/tslib/bin\
# If running interactively, then:
if [ "$PS1" ]; then
if [ "$BASH" ]; then
export PS1="[\u@\h \W]\\$ "
alias ll='/bin/ls --color=tty -laFh'
alias ls='/bin/ls --color=tty -F'
export LS_COLORS='no=00:fi=00:di=01;34:ln=01;36:pi=40;33:so=01;35:do=01;35:bd=40;33;01:cd=40;33;01:or=40;31;01:ex=01;
32:*.tar=01;31:*.tgz=01;31:*.arj=01;31:*.taz=01;31:*.lzh=01;31:*.zip=01;31:*.z=01;31:*.Z=01;31:*.gz=01;31:*.bz2=01;31:*.deb=0
1;31:*.rpm=01;31:*.jar=01;31:*.jpg=01;35:*.jpeg=01;35:*.png=01;35:*.gif=01;35:*.bmp=01;35:*.pbm=01;35:*.pgm=01;35:*.ppm=01;35
:*.tga=01;35:*.xbm=01;35:*.xpm=01;35:*.tif=01;35:*.tiff=01;35:*.mpg=01;35:*.mpeg=01;35:*.avi=01;35:*.fli=01;35:*.gl=01;35:*.d
l=01;35:*.xcf=01;35:*.xwd=01;35:';
else
if [ "`id -u`" -eq 0 ]; then
export PS1='>: '
else
export PS1='>: '
fi
fi
# System Setting
set -o vi
alias ll='ls -l'
export USER=`id -un`
export LOGNAME=$USER
export HOSTNAME=`/bin/hostname`
export HISTSIZE=1000
export HISTFILESIZE=1000
export PAGER='/bin/more '
export EDITOR='/bin/vi'
export INPUTRC=/etc/inputrc
export DMALLOC_OPTIONS=debug=0x34f47d83,inter=100,log=logfile
export VAR1=
export VAR2=
export VAR3=
export VAR4=
export VAR5=
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=/lib:/usr/lib/
# QT Extendded 4.4.3 Setting
export QTDIR=/apps/qt-extended-4.4.3
export QWS_MOUSE_PROTO='TSLIB:/dev/event0'
export QWS_DISPLAY='LinuxFB:/dev/fb0'
export QWS_DISPLAY='LinuxFB:mmWidth240:mmHeight320:0'
export QWS_SIZE='240x320'
export QT_PLUGIN_PATH=$QTDIR/plugins/
export QT_QWS_FONTDIR=$QTDIR/lib/fonts
export PATH=$QTDIR/bin:$PATH
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:$QTDIR/lib
# Touch Scree tslib Setting
export TSLIB_ROOT=/apps/tslib
export TSLIB_CONFFILE=$TSLIB_ROOT/etc/ts.conf
export TSLIB_CALIBFILE=$TSLIB_ROOT/etc/pointercal
export TSLIB_TSDEVICE=/dev/event0
export TSLIB_CONSOLEDEVICE=none
export TSLIB_FBDEVICE=/dev/fb0
fi;
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ vim protocols
# /etc/protocols:
# # $Id: protocols,v 1.1.1.1 2001/09/12 19:03:24 andersee Exp $
# #
# # Internet (IP) protocols
# #
# # from: @(#)protocols 5.1 (Berkeley) 4/17/89
# #
# # Updated for NetBSD based on RFC 1340, Assigned Numbers (July 1992).
#
# ip 0 IP # internet protocol, pseudo protocol number
# icmp 1 ICMP # internet control message protocol
# igmp 2 IGMP # Internet Group Management
# ggp 3 GGP # gateway-gateway protocol
# ipencap 4 IP-ENCAP # IP encapsulated in IP (officially ``IP'')
# st 5 ST # ST datagram mode
# tcp 6 TCP # transmission control protocol
# egp 8 EGP # exterior gateway protocol
# pup 12 PUP # PARC universal packet protocol
# udp 17 UDP # user datagram protocol
# hmp 20 HMP # host monitoring protocol
# xns-idp 22 XNS-IDP # Xerox NS IDP
# rdp 27 RDP # "reliable datagram" protocol
# iso-tp4 29 ISO-TP4 # ISO Transport Protocol class 4
# xtp 36 XTP # Xpress Tranfer Protocol
# ddp 37 DDP # Datagram Delivery Protocol
# idpr-cmtp 39 IDPR-CMTP # IDPR Control Message Transport
# rspf 73 RSPF #Radio Shortest Path First.
# vmtp 81 VMTP # Versatile Message Transport
# ospf 89 OSPFIGP # Open Shortest Path First IGP
# ipip 94 IPIP # Yet Another IP encapsulation
# encap 98 ENCAP # Yet Another IP encapsulation
mdev会在/etc目录下找mdev的配置文件: mdev.conf. 如果该文件不存在,那么在执行mdev –s这个命令时,会提示找不到mdev.conf,这时我们可以建一个空的mdev.conf文件解决这个问题。下面创建使用mdev自动挂载u盘和SD卡的配置/etc/mdev.conf。
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ vim mdev.conf
sd[a-z][0-9] 0:0 0777 @(mount /dev/$MDEV /mnt/usb)
sd[a-z] 0:0 0777 $(umount /mnt/usb)
#ub[a-z][0-9] 0:0 0777 @(mount /dev/$MDEV /mnt/usb)
#ub[a-z] 0:0 0777 $(umount /mnt/usb)
mmcblk[0-9]p[0-9] 0:0 0777 @(mount /dev/$MDEV /mnt/sdc)
mmcblk[0-9] 0:0 0777 $(umount /mnt/sdc)
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ vim group
root:x:0:root**********************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
注意:
它的格式如下:
groupname:password:gid:members
第一个字段为用户组名称。
第二个字段为用户组密码,当为x时密码是映射到/etc/gshadow中的,是非逆的。
第三个字段为GID,及组号,为正整数或0,0被付于了root用户组;系统通常会预留一些较靠前的GID给系统虚拟用户之用,每个系统预留的GID都不同,Fedora预留了500个,所以我们添加新用户组时是从500开始的。GID的范围由/etc/login.defs中的GID_MIN和GID_MAX决定第四个字段为用户列表,每个用户间用逗号分隔。
这里的password代表组口令,很少用到。它可使原先不在这个群组中的用户可以通过newgrp命令暂时继承该组的权限,使用 newgrp命令时会新开一个shell。口令的加密方式和passwd文件中的口令一样,所以如果需设置组口令,要用passwd程序虚设一个用户,再把该用户password节中的加密口令拷贝到/etc/group文件中。members列代表组成员,我们可把需加入该组的用户以逗号分隔添加到这里即可。同一组的成员可继承该组所拥有的权限。
***********************************************************************************************************************************************************************************16.创建用户passwd文件
[zoulei@CentOS etc]$ vim passwd
root:x:0:0:root:/:/bin/sh
注意:
它的格式如下:
username:password:uid:gid:gecos:homedir:shell
第一个字段为登录名
第二个字段为口令,一般被映射到shadow文件中
第三个字段为UID
第四个字段为GID
第五个字段为用户名全称,gecos是通用电子计算机操作系统的缩写,是Bell实验室中的一台大型主机。
第六个字段为用户根目录
第七个字段为用户所用SHELL的类型。
Unix系统最初是用明文保存密码的,后来由于安全的考虑,采用crypt()算法加密密码并存放在/etc/passwd文件。现在,由于计算机处理能力的提高,使密码破解变得越来越容易。/etc/passwd文件是所有合法用户都可访问的,大家都可互相看到密码的加密字符串,这给系统带来很大的安全威胁。现代的Unix系统使用影子密码系统,它把密码从/etc/pa sswd文件中分离出来,真正的密码保存在/etc/shadow文件中,shadow文件只能由超级用户访问。这样入侵者就不能获得加密密码串,用于破解。使用shadow密码文件后,/etc/passwd文件中所有帐户的password域的内容为"x",如果password域的内容为"*",则该帐号被停用。使用passwd这个程序可修改用户的密。
*****************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************17.创建密码映射shadow文件 [zoulei@CentOS etc]$ vim shadow
root::0:0:99999:7::: #显示的是加密后的字符串******************************************************************************************************************************************************
该文件我们可以在Linux系统上使用passwd命令修改root口令来获取:
[zoulei@localhost ~]$ passwd root
Changing password for user root.
New UNIX password:
Retype new UNIX password:
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
[zoulei@localhost ~]$ cat /etc/shadow | grep root
root:$1$jGZIHmtT$y8ZXoPllK12/wl51kMw4e/:0:0:99999:7:::
当然,在设置为嵌入式平台上的root口令后,最好把系统上的root命令恢复到原始密码。
他的格式如下:
username:password:last_change:min_change:max_change:warm:failed_expire:expiration:reserved
第一字段:用户名(也被称为登录名),在/etc/shadow中,用户名和/etc/passwd 是相同的,这样就把passwd 和shadow中用的用户记录联系在一起;这个字段是非空的;
第二字段:密码(已被加密),这个字段是非空的;
第三字段:上次修改口令的时间;这个时间是从1970年01月01日算起到最近一次修改口令的时间间隔(天数),您可以通过passwd 来修改用户的密码,然后查看/etc/shadow中此字段的变化;
第四字段:两次修改口令间隔最少的天数;如果这个字段的值为空,帐号永久可用;
第五字段:两次修改口令间隔最多的天数;如果这个字段的值为空,帐号永久可用;
第六字段:提前多少天警告用户口令将过期;如果这个字段的值为空,帐号永久可用;
第七字段:在口令过期之后多少天禁用此用户;如果这个字段的值为空,帐号永久可用;
第八字段:用户过期日期;此字段指定了用户作废的天数(从1970年的1月1日开始的天数),如果这个字段的值为空,帐号永久可用;
第九字段:保留字段,目前为空,以备将来发展之用;
这里我们设置为不用密码登陆,将password格式的内容清空:
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ vim etc/shadow
root::0:0:99999:7:::
18.在文件系统中安装busybox[zoulei@CentOS opt]$ ls
buildroot-2012.08 buildroot-install.sh busybox-1.20.2 mtd-utiles
buildroot-2012.02.tar.bz2 buildroot-2012.08-arm920t.config build_ubifs.sh busybox-1.20.2.tar.bz2 rootfs
[zoulei@CentOS opt]$ tar xjf busybox-1.20.2.tar.bz2
[zoulei@CentOS busybox-1.20.2]$ cd
[zoulei@CentOS busybox-1.20.2]$ vim Makefile
#修改CROSS_COMPILER为:
CROSS_COMPILE ?= /opt/buildroot-2012.08/arm920t/usr/bin/arm-linux-
******************************************************************************************************************************************************************
注意:这里的路径选择你的交叉编译器所在的路径。********************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
[zoulei@CentOS busybox-1.20.2]$ vt100
[zoulei@CentOS busybox-1.20.2]$ sudo make menuconfig
#选择:
Busybox Settings --->
General Configuration --->
[*] Don't use /usr
Installation Options ("make install" behavior) --->
What kind of applet links to install (as soft-links) --->
(/home/zoulei/opt/rootfs) BusyBox installation prefix
#其他选项结合和自己的需求定制[zoulei@CentOS busybox-1.20.2]$ file busybox
busybox: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, ARM, version 1 (SYSV), statically linked, stripped
[zoulei@CentOS busybox-1.20.2]$ sudo make install
....
../rootfs/sbin/udhcpc -> ../bin/busybox
../rootfs/sbin/udhcpd -> ../bin/busybox
../rootfs/sbin/vconfig -> ../bin/busybox
../rootfs/sbin/zcip -> ../bin/busybox
打印内容省略......
--------------------------------------------------
You will probably need to make your busybox binary
setuid root to ensure all configured applets will
work properly.
--------------------------------------------------
[zoulei@CentOS busybox-1.20.2]$
[zoulei@CentOS busybox-1.20.2]$ ls ../rootfs
apps bin data dev etc info lib linuxrc mnt proc root sbin sys tmp usr var
19.移植dropbear
首先编译生成PC版的,在制作密钥时用到。
[zoulei@CentOS ~]$ wget http://matt.ucc.asn.au/dropbear/releases/dropbear-0.53.1.tar.bz2
[zoulei@CentOS ~]$ tar -xjf dropbear-0.53.1.tar.bz2
[zoulei@CentOS ~]$ cd dropbear-0.53.1
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$ ./configure && make
生成的文件:
dropbear: ssh2 server
dropbearkey: 密钥生成器
dropbearconvert: 可以转换openssh的密钥
dbclient: ssh2 client
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$ ./dropbearkey -t rsa -f /opt/rootfs/etc/dropbear/dropbear_rsa_host_key
Will output 1024 bit rsa secret key to '/opt/rootfs/etc/dropbear/dropbear_rsa_host_key'
Generating key, this may take a while...
Public key portion is:
ssh-rsa AAAAB3NzaC1yc2EAAAADAQABAAAAgwChXpm6ogojmWy7GTZloJDdSIFq7pd49P3dh2I8Ap/7Cr9KRWlfQb0rchkFv1h62736FyX28S1jo7HpES9Rjp7MinG66pyzFjOfrsruzkeheo7YBrk8GPeSdEm65O3gPlJzReyMY3r020fwVIGaMf7+bPBuMsYY1g+8OcgeEygYCExz [email protected]
Fingerprint: md5 ed:a6:c9:6d:6e:85:f6:10:b2:3c:49:90:52:be:9b:19
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$ ./dropbearkey -t dss -f /opt/rootfs/etc/dropbear/dropbear_dss_host_key
Will output 1024 bit dss secret key to '/opt/rootfs/etc/dropbear/dropbear_dss_host_key'
Generating key, this may take a while...
Public key portion is:
ssh-dss AAAAB3NzaC1kc3MAAACBAOa5XsTcByi4cdnhJ44Uro/athrTzv68+yeizFejzQM+K1e4ung/2SfAIZW/ms41HSSMhO6Siv/oOGz3cPnw8NKkWHWTP6pQmyZlvl2zNdrbDwiPGQ17rb5THoVDbXwn54c/aMR27mj+DBJ4+SDpL08wfs6k2JaelQIpBYWbFJ+rAAAAFQCgrFTR2dqbRdrk+lhaxnU7L8ADiQAAAIEAwUThj2irqMRCuItsKN+hYKmydUAtAL47ys+GBYMxKH36cLBovm19+2gaBTKsdBJbBs7j/7/xrFLPypAQmN3MukeSQvIUGQ0qzqPEcwtOdDtqOzi2//f4Cb3JUQd+JVXYj0lYGjRMZGuGzUlk6zoVoY8SEdGpQgRtI5Zi/M1H5YEAAACAMYxm7p6mBeA/SD5uESAgfPgF87h0ZIdC2cONVG0Ay/TJvOJC2ioNyQEL+UinNEV5+cA4tv5huA8zryp/jBgHVtxUQu168KlzSzo8397Rsy5Lhg7zgRGZYhLNEBzypHQjX8bpEve76GgHSbZ+9aj+zznpvAmKwonqZNLic2/HTMc=
Fingerprint: md5 96:f3:31:04:8b:a6:1b:a5:cc:37:e5:08:9c:18:98:cd
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$ chmod 666 /opt/rootfs/etc/dropbear/dropbear_*
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$
20.编译ARM版本的
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$ make distclean
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$ ./configure CC=/opt/buildroot-2012.08/arm920t/usr/bin/arm-linux-gcc --build=i686 --host=arm-linux --disable-zlib
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$ make
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$ file dropbear
dropbear: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, ARM, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked (uses shared libs), not stripped
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$ file dbclient
dbclient: ELF 32-bit LSB executable, ARM, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked (uses shared libs), not stripped
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$ mv dbclient ssh
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$arm-linux-strip dropbear
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$ arm-linux-strip ssh
[zoulei@CentOS dropbear-0.53.1]$ cp dropbear ssh /opt/rootfs/usr/sbin/
21.在文件系统中创建启动脚本[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ vim etc/init.d/S04_dropbear
#!/bin/sh
/usr/sbin/dropbear[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ chmod 777 etc/init.d/S04_dropbear
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$ ls
apps bin data dev etc info lib linuxrc mnt proc root sbin sys tmp usr var
[zoulei@CentOS rootfs]$
这样就制作好了根文件系统树,接下来我们就可以移植各种文件系统了。。
当然在做这个文件系统树过程中遇到了很多问题,在我另外一篇博客有总结,请参考:点击打开链接