遗传算法Python实现
遗传算法的基本概念
- 初始时,预备一个 population,可以是随机产生的。
- 对每个 candidate 进行 估值 (evaluation),即是让这个 candidate 在人工的世界里生存。 例如我们测试它在所需的功能的表现如何。 那计分的方法叫 objective function 「目的函数」。
- 选取表现最好的 N 个 candidates,进行 变种 mutation 或 重组 recombination。 变种是作用在单个 candidate 上的,重组则需要一对 candidates。 那就涉及到我们怎样将设计空间的元素表示为「基因」,于是有所谓 表述 (representation) 的问题。 这编码是要由研究者设计的。
- 在评分的时候,可以容许那些 candidates 在环境中互相合作亦同时竞争,那叫 cooperative evolution。 我觉得 Genifer 有需要用这方法,因为在知识库中的每个知识片段,是要和其他知识互相作用,那逻辑系统才能推导出有意思的结果。
待求解的问题
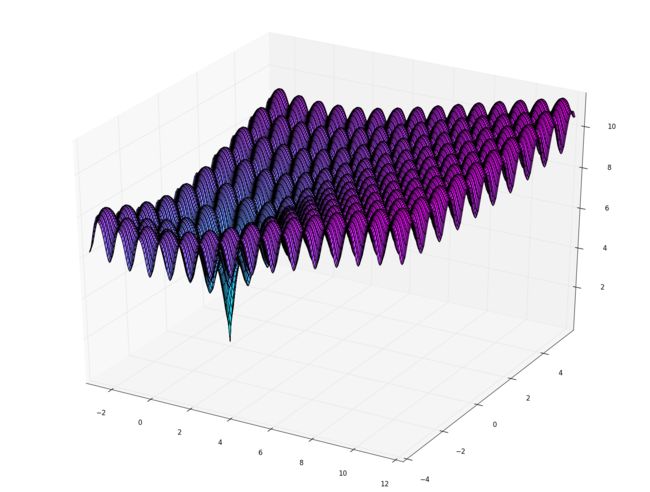
寻找最优解的函数表达式为
f(x,y)=−20e−0.2x2+y22−ecos2πx+cos2πy2+20+e f(x,y)=-20e^{-0.2\sqrt{\frac{x^2+y^2}{2}}}-e^{\frac{\cos2\pi x+\cos2\pi y}{2}}+20+e f(x,y)=−20e−0.22x2+y2−e2cos2πx+cos2πy+20+e
该函数的最小值为
f(0,0)=0f(0,0)=0f(0,0)=0
作图源码
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
import numpy as np
fig = figure()
ax = Axes3D(fig)
X = np.arange(-3.0, 12.1, 0.08)
Y = np.arange(-4.1, 5.8, 0.08)
X, Y = np.meshgrid(X, Y)
Z = -20*np.exp(-0.2*np.sqrt(np.sqrt((X**2+Y**2)/2)))+20+np.e-np.exp((np.cos(2*np.pi*X)+np.sin(2*np.pi*Y))/2)
ax.plot_surface(X, Y, Z, rstride=1, cstride=1, cmap='cool')
##一个变量的二进制串位数的确定
包括断点的区间[a,b][a,b][a,b],精度ppp,共有NNN个数,则N=⌈a−bp⌉+1N=\lceil\frac{a-b}{p}\rceil+1N=⌈pa−b⌉+1。用mmm表示二进制位数,分析:
当N=4N=4N=4时,m=2m=2m=2,
当N=5N=5N=5时,m=3m=3m=3。
观察得 2m−1<N≤2m2^{m-1}<N\leq 2^m2m−1<N≤2m,故有log2N≤m<log2(N+1)\log_2 N\leq m< \log_2(N+1)log2N≤m<log2(N+1),
在程序中可表示为m=⌈log2N⌉=⌈log2(⌈a−bp⌉+1)⌉ m = \lceil\log_2 N\rceil = \left\lceil\log_2 (\lceil\frac{a-b}{p}\rceil+1)\right\rceil m=⌈log2N⌉=⌈log2(⌈pa−b⌉+1)⌉
程序代码
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 函数定义
def func(x):
y = -20*np.exp(-0.2*np.sqrt(np.sqrt((x[0]**2+x[1]**2)/2)))-np.exp((np.cos(2*np.pi*x[0])+np.cos(2*np.pi*x[1]))/2)+20+np.e
return y
#适应度计算
def getfitness(pop2):
pop = trans2to10(pop2)
fitness = 20*np.exp(-0.2*np.sqrt(np.sqrt((pop[:,0]**2+pop[:,1]**2)/2)))+np.exp((np.cos(2*np.pi*pop[:,0])+np.cos(2*np.pi*pop[:,1]))/2)
return fitness
def getcumsumrate(fitness):
cumsumrate = fitness.cumsum()/sum(fitness)
return cumsumrate
#根据参数(本例有两个参数)的取值范围和精度要求获得基因的个数
def getbitlength(range =((-3,12.1,0.0001),(-4.1,5.8,0.0001))):
N1 = np.ceil((range[0][1]-range[0][0])/range[0][2])+1
bitlength1 = np.int(np.ceil(np.log2(N1)))
N2 = np.ceil((range[1][1]-range[1][0])/range[1][2])+1
bitlength2 = np.int(np.ceil(np.log2(N2)))
return bitlength1,bitlength2
def getpop2(bitlength=(18,17),sizepop=20):
pop2 = np.random.rand(sizepop,sum(bitlength))
pop2[pop2>0.5] = 1
pop2[pop2<=0.5] = 0
return pop2
# 解码
def to2_10(binlist):
val = 0
pow = 1
for i in range(len(binlist))[::-1]:
val += binlist[i]*pow
pow *= 2
return val
def trans2to10(pop2,leninfo = (18,17),rang = ((-3,12.1,0.0001),(-4.1,5.8,0.0001))):
row,column = pop2.shape
pop10 = np.zeros((row,2))
for i in range(row):
pop10[i][0] = rang[0][2]*to2_10(pop2[i][:leninfo[0]])+rang[0][0]
pop10[i][1] = rang[1][2]*to2_10(pop2[i][leninfo[0]:])+rang[1][0]
return pop10
def getselectpair(cumsumrate):#用转盘算法根据累积概率选择两个个体
while True:
flag = cumsumrate-np.random.rand() #rand() [0,1)
sel0 = 0
while flag[sel0]<0 :
sel0 += 1
flag = cumsumrate-np.random.rand() #rand() [0,1)
sel1 = 0
while flag[sel1]<0 :
sel1 += 1
if sel0 != sel1:
break
return [sel0,sel1]
sizepop = 50 #种群规模
genermax = 100 #迭代次数
ratecross = 0.70 #染色体交配率
ratemutation = 0.12 #基因突变率
leninfo = getbitlength()
pop2 = getpop2(sizepop=sizepop)
fitnesslog = []
while genermax > 0:
genermax -= 1
pop2new = np.zeros(pop2.shape)
fitness = getfitness(pop2)
fitnesslog.append([max(fitness),mean(fitness)])
cumsumrate = getcumsumrate(fitness)
for i in range(0,sizepop,2):
selectpair = getselectpair(cumsumrate)
pop2new[i,:] = pop2[selectpair[0]].copy()
pop2new[i+1,:] = pop2[selectpair[1]].copy()
rand2 = np.random.rand(2)
if rand2[0]<=ratecross:#交叉操作,对应变量1
crossbit0 = np.int(np.random.rand()*leninfo[0])
pop2new[i,crossbit0:leninfo[0]],pop2new[i+1,crossbit0:leninfo[0]]=pop2new[i+1,crossbit0:leninfo[0]],pop2new[i,crossbit0:leninfo[0]]
if rand2[1]<=ratecross:#交叉操作,对应变量2
crossbit1 = np.int(np.random.rand()*leninfo[1])+leninfo[0]
pop2new[i,crossbit1:],pop2new[i+1,crossbit1:]=pop2new[i+1,crossbit1:],pop2new[i,crossbit1:]
rand4 = np.random.rand(4)
if rand4[0] < ratemutation:
mutationbit = np.int(rand4[1]*sum(leninfo))
pop2new[i,mutationbit] = np.abs(pop2new[i,mutationbit]-1)
if rand4[2] < ratemutation:
mutationbit = np.int(rand4[3]*sum(leninfo))
pop2new[i+1,mutationbit] = np.abs(pop2new[i+1,mutationbit]-1)
pop2 = pop2new
fitnesslog = np.array(fitnesslog)
bestlog = np.zeros(fitnesslog.shape[0])
bestlog[0] = fitnesslog[0,0]
for i in range(1,fitnesslog.shape[0]):
if(fitnesslog[i,0])>bestlog[i-1]:
bestlog[i]=fitnesslog[i,0]
else:
bestlog[i]=bestlog[i-1]
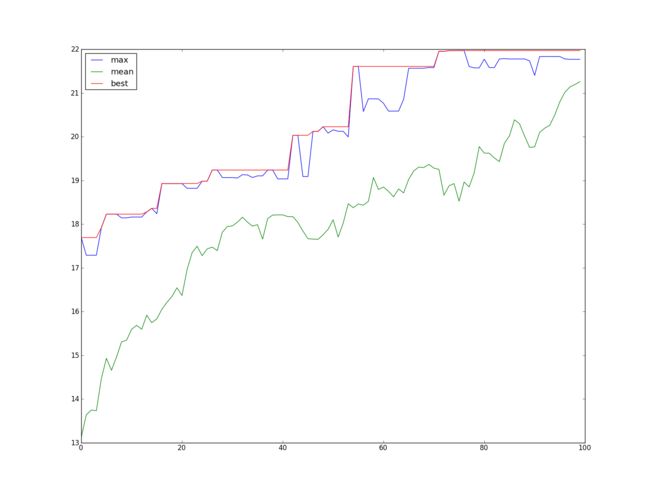
plt.plot(fitnesslog[:,0])
plt.plot(fitnesslog[:,1])
plt.plot(bestlog)
plt.legend(('max','mean','best'),loc='best')
进一步阅读
- HELLO,遗传算法!,地址http://garfileo.is-programmer.com/2011/2/19/hello-ga.24563.html
python面向对象实现的遗传算法,有源代码