你凭什么说Spring会导致MyBatis的一级缓存失效!
一、概述
最近老是听说Spring和MyBtis集成后,一级缓存就不可用了!
我就纳闷了,为什么一级缓存不可用呢?这难道是Spring的BUG?这引起了我极大的兴趣,因为Spring作为一个极其优秀的项目管理框架,它居然也有BUG,我要一探究竟,满足我的好奇心!
二、真的没走缓存
为了帮助我查看源码,我把MyBatis和Spring集成后写了如下代码:
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext;
@Before
public void init(){
annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
}
@Test
public void selectTest(){
TestMapper bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(TestMapper.class);
List<User> users = bean.selectUser("周六");
System.out.println(users);
List<User> users1 = bean.selectUser("周六");
System.out.println(users == users1);
}
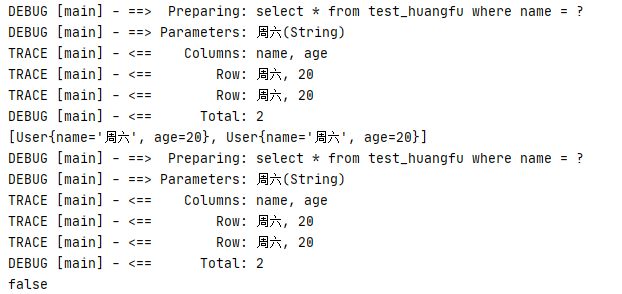
讲道理,以上代码在常规的环境下,是一定会走一级缓存的,因为他满足一级缓存命中的条件,即同一个SqlSession、 StatementId相同,参数相同、分页条件相同、查询语句相同、环境名称相同 六大命中规则,所以理论上,一级缓存是一定会命中的!但是事实上日志如下:
他居然没有走缓存,而是去查询了两遍数据库,一级缓存华丽丽的的失效了,可是这道理是为什么呢?
三、失效的原因
Spring作为一个顶级项目管理框架,对于如此明显的BUG,他不可能发现不了,及时真的发现不了,那么github上使用者也不可能不提BUG,于是,我打断点调试调试,看下源码就是是如何来操作的!
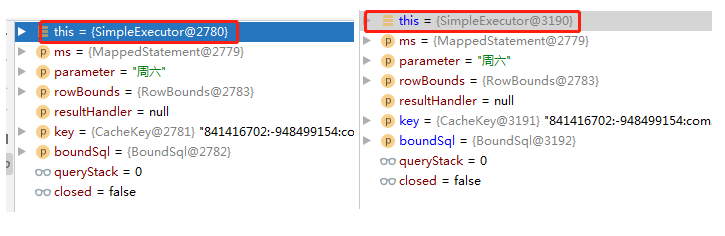
从哪里下手呢?刚刚我们说过一级缓存的命中规则,2,3,4,5,6条规则一定是一样的,因为我只是单纯的复制了两遍查询,代码上没有变动,所以他的查询语句、参数之类的条件一定是相同的,那么最可能出现的条件就是第一条:同一个SqlSession,难道说Spring集成MyBatis后,每一次查询都是用了不同的SqlSession? 以前看过我文章的都应该知道,我之前分析过一篇关于MyBatis设计模式的文章,关于门面模式中说到过:每一个SqlSession都会有一个唯一的执行器(Executor)与之对应,所以说如果想验证是不是同一个SqlSession,只需要验证两次使用的执行器是不是一个就OK了,说做就做,我在BaseExecutor#query方法上断点,结果如下:
果然不出我所料,两次查询走的根本不是一个执行器,那么也就一定不是一个SqlSession,这下只掉原因了,但是为什么呢?
四、罪魁祸首
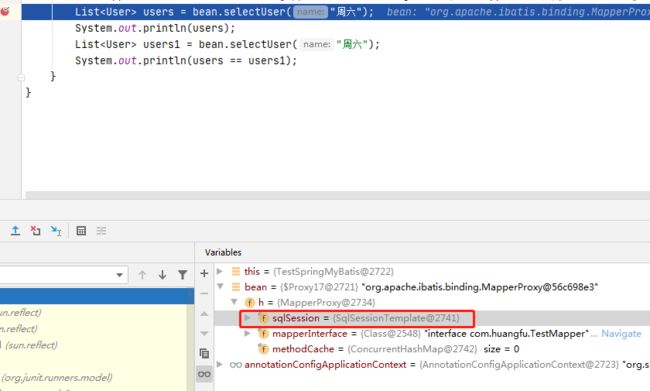
通过上图的断点我们可以看出来,正常情况下,我们的Mapper代理里面所包含的应该是DefaultSqlSession对象,但是通过整合Spring后我们发现,我们的SqlSession对象被偷梁换柱了,换成了SqlSessionTemplate类,我们进入到这个类中:
public class SqlSessionTemplate implements SqlSession, DisposableBean {...}
发现这个类也继承了SqlSession接口,那就好办了,那么查询的方法一定是经过Select方法来实现的,我们进入到他的selectList方法,看下他的实现逻辑:
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.sqlSessionProxy.selectList(statement, parameter);
}
我们发现,这个方法内部内部的查询似乎又交给了一层代理,由这一层代理去真正执行的查询操作,我们似乎快找到原因了:
public SqlSessionTemplate(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
... 忽略不必要的代码...
this.sqlSessionProxy = (SqlSession) newProxyInstance(SqlSessionFactory.class.getClassLoader(),
new Class[] { SqlSession.class }, new SqlSessionInterceptor());
}
果不其然,这个对象在初始化的时候,将这个代理对象也连带着初始化了,这个正是使用的JDK的动态代理来实现的,熟悉动态代理的同学可能会知道,JDK动态代理的精髓也就是InvocationHandler的子类,也就是SqlSessionInterceptor,我们进入到里面看一下他的实现:
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//获取SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
//反射调用真正的处理方法
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
//提交数据
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
//返回查询的数据
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
//。。。。忽略不必要代码
} finally {
if (sqlSession != null) {
//关闭SqlSession的连接
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
}
既然SqlSession不一致,那么肯定是在获取SqlSession的时候,里面实现了一些逻辑,从而造成了 SqlSession的不一致,我们进入到getSqlSession方法中:
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
//...忽略不必要代码....
//从ThreadLocal变量里面获取当前的SqlSession的处理器
SqlSessionHolder holder =
(SqlSessionHolder)TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
//如果事务同步管理器处于活动状态则从SqlSessionHolder获取Session
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
//如果SqlSessionHolder中获取的SqlSession为空,则新建一个SqlSession
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
//若事务同步管理器处于活动状态则将SqlSession设置到SqlSessionHolder中保存起来,以便下次使用
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
原来如此,原来并不是说Spring使MyBatis的一级缓存失效了,而是因为Spring只有在开启了事务之后,在同一个事务里的SqlSession会被缓存起来,同一个事务中,多次查询是可以命中缓存的!我们回到SqlSessionInterceptor#invoke方法里面,他在关闭的SqlSession的时候同样对 是否开启事务做了处理,我们看closeSqlSession方法的源码:
public static void closeSqlSession(SqlSession session, SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory) {
//........忽略不必要的代码
SqlSessionHolder holder =
(SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
//查看事务同步管理器是否存在 session
if ((holder != null) && (holder.getSqlSession() == session)) {
holder.released();
} else {
//如果不存在就将该Session关闭掉
session.close();
}
}
那么,既然导致一级缓存失效的罪魁祸首我们找到了,如何解决呢?
五、解决方案
为什么一级缓存失效,因为两次查询没有使用同一个事物,那么我们加上同一个事物,看看情况如何:
@Test
public void selectTest(){
TestMapper bean = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(TestMapper.class);
//添加事务
DataSourceTransactionManager dataSourceTransactionManager =
annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(DataSourceTransactionManager.class);
TransactionStatus transaction =
dataSourceTransactionManager.getTransaction(new DefaultTransactionDefinition());
List<User> users = bean.selectUser("周六");
System.out.println(users);
List<User> users1 = bean.selectUser("周六");
System.out.println(users == users1);
}
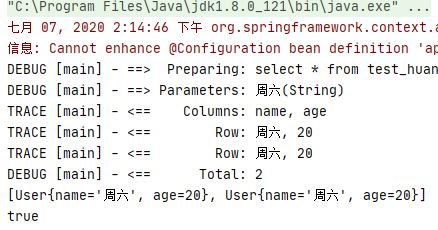
我们这个时候来看一下结果:
果然不出我所料,一级缓存又被成功的使用上了。
古人云:耳听为虚,眼见为实!只有真正的经历过,才知道哪些是真,哪些是假!这一次调试源码,不光让我对Spring整合MyBatis有了一个整体的认知,更是让我对动态代理有了一个更加深入的了解,后续我会整理一下,分享出来!
才疏学浅,如果文章中理解有误,欢迎大佬们私聊指正!欢迎关注作者的公众号,一起进步,一起学习!