如何使用Kotlin Scope 方法及takeIf/takeUnless
如何使用Kotlin Scope 方法及takeIf/takeUnless
文章目录
- 如何使用Kotlin Scope 方法及takeIf/takeUnless
- 5个scope方法 +2个方法
- 什么是 *scope functions*?
- **scope方法的区别**
- let示例 (上下文对象it, 返回值lambda的结果)
- apply示例 (上下文对象this,可省略, 返回上下文对象)
- also示例 (上下文对象it, 返回上下文对象)
- run示例 (上下文对象this,可省略, 返回lambda结果)
- kotlin.run示例 (无上下文, 返回值是lambda的记过)
- with示例 (上下文对象this,可省略, 返回lambda 结果)
- run 与 let对比 (上下文对象不同)
- :star2:scope 方法的选择:star2:
- :warning:注意
- null check
- `takeIf` and `takeUnless`
- 参考
StardardKt类提供以下几个常用的方法
5个scope方法 +2个方法
- let
- run
- apply
- also
- with
- takeIf/takeUnless ( StardardKt)
什么是 scope functions?
The Kotlin standard library contains several functions whose sole purpose is to execute a block of code within the context of an object. When you call such a function on an object with a lambda expression provided, it forms a temporary scope. In this scope, you can access the object without its name. Such functions are called scope functions.
简单理解,在上下文对象范围 (大括号) 内,可以不用对象的名字,直接调用
scope方法的区别
- 上下文对象引用方式(this or it)
- 返回值 (上下文对象 或者 lambda结果)
let示例 (上下文对象it, 返回值lambda的结果)
Person("Alice", 20, "Amsterdam").let {
println(it)
it.moveTo("London")
it.incrementAge()
println(it) // 这里是Unit
}
正常写
val alice = Person("Alice", 20, "Amsterdam")
println(alice)
alice.moveTo("London")
alice.incrementAge()
println(alice)
The scope functions do not introduce any new technical capabilities, but they can make your code,more concise and readable.
scope functions 使得代码更加简洁易读
apply示例 (上下文对象this,可省略, 返回上下文对象)
val adam = Person("Adam").apply {
age = 20 // same as this.age = 20 or adam.age = 20
city = "London"
}
println(adam)
这是不是比设计模式中builder模式更加简单,创建对象更加简洁
also示例 (上下文对象it, 返回上下文对象)
fun getRandomInt(): Int {
return Random.nextInt(100).also {
writeToLog("getRandomInt() generated value $it")
}
}
val i = getRandomInt()
做额外操作,如日志,埋点
run示例 (上下文对象this,可省略, 返回lambda结果)
val numbers = mutableListOf("one", "two", "three")
val countEndsWithE = numbers.run {
add("four")
add("five")
count { it.endsWith("e") } //返回count计数的结果
}
println("There are $countEndsWithE elements that end with e.")
run is useful when your lambda contains both the object initialization and the computation of the return value.
同时进行对象初始化和返回计算结果时推荐使用
kotlin.run示例 (无上下文, 返回值是lambda的记过)
val hexNumberRegex = run {
val digits = "0-9"
val hexDigits = "A-Fa-f"
val sign = "+-"
Regex("[$sign]?[$digits$hexDigits]+")
}
for (match in hexNumberRegex.findAll("+1234 -FFFF not-a-number")) {
println(match.value)
}
将相同功能代码聚在一起
with示例 (上下文对象this,可省略, 返回lambda 结果)
val numbers = mutableListOf("one", "two", "three")
with(numbers) {
println("'with' is called with argument $this")
println("It contains $size elements")
}
官网建议不要返回lambda 结果,即返回Unit
run 与 let对比 (上下文对象不同)
val service = MultiportService("https://example.kotlinlang.org", 80)
val result = service.run {
port = 8080
query(prepareRequest() + " to port $port")
}
// the same code written with let() function:
val letResult = service.let {
it.port = 8080
it.query(it.prepareRequest() + " to port ${it.port}")
}
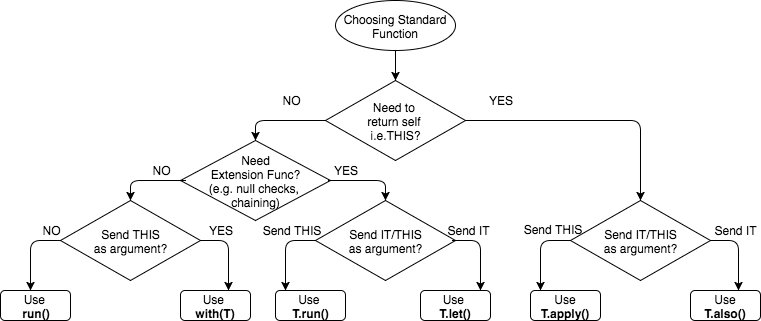
scope 方法的选择
官网的不同方法差异
| 方法 | 引用对象 | 返回值 | 是否扩展函数 |
|---|---|---|---|
let |
it |
Lambda 结果 | Yes |
run |
this |
Lambda 结果 | Yes |
kotlin.run |
- | Lambda 结果 | No: 调用不需要上下文对象 |
with |
this |
Lambda 结果 | No: 上下文对象作为参数 |
apply |
this |
上下文对象 | Yes |
also |
it |
上下文对象 | Yes |
简化成下图
简单调用总结
- let
- 非空对象执行lambda
- lambda表示作为变量
- apply
- 对象初始化
- run
- 对象初始化并计算结果
- kotlin.run
- 表达式语句
- also
- 附加操作
- with
- Grouping function calls on an object (分组方法调用? 比较少用,不是很清楚,一般都用run代替)
⚠️注意
- 虽然scope 方法使得代码更加简洁,但不要过度使用,这样会使代码可读性降低,甚至会导致错误
- 避免嵌套使用,如果嵌套请注意上下文对象是this 还是 it
- ⚠️外部有相同名字的变量时, run ,apply中this不能省略,否者会使用外部的变量
null check
//都用过?.let
obj?.let{
}
//其实?.run 也行,省略上下文,但是注意不要跟局部或者成员变量的属性搞混了
obj?.run{
}
其实可以混用,但是为了可读性,限制使用场景
takeIf and takeUnless
这两的扩展也是stardartKt里的,官方kotlon-docs也放在scope funciton 里介绍的存在的目的就是更好的进行链式调用 (checks of the object state in call chains)
val number = Random.nextInt(100)
val evenOrNull = number.takeIf { it % 2 == 0 }
val oddOrNull = number.takeUnless { it % 2 == 0 }
println("even: $evenOrNull, odd: $oddOrNull")
一般是由都是搭配elvis表示式使用
//变量
val showName = name.takeIf{ it.isNullOrEmpty()} ?: "default"
//代码块 , 可以取代 if else , 一链到底是不是很爽
name.takeIf{ it.isNullOrEmpty()}
?.let {
//满足条件时执行
} ?:kotlin.run {
//不满足条件时执行
}
以上是个人的使用经验,如有问题或者更好的,欢迎留言.
参考
Using Scoped Functions in Kotlin - let, run, with, also, apply
kotlin-docs scope-functions