分页实现方法的性能比较
我们先给出几种主要的分页方法和核心语句,然后直接给出结论,有兴趣的读者可以看看后面的数据
几种常用存储过程分页方法
TopN方法
select Top(@PageSize) from TableName where ID Not IN
(Select Top ((@PageIndex-1)*@PageSize) ID from Table Name where .... order by ... )
where .... order by ...
临时表
declare @indextable table(id int identity(1,1),nid int,PostUserName nvarchar(50))
declare @PageLowerBound int
declare @PageUpperBound int
set @PageLowerBound=(@pageindex-1)*@pagesize--下限
set @PageUpperBound=@PageLowerBound+@pagesize--上限
set rowcount @PageUpperBound
insert into @indextable(nid,PostUserName) select ReplyID,PostUserName from TableName order by ......
select * from TableName p,@indextable t where p.ID=t.nid
and t.id>@PageLowerBound and t.id<=@PageUpperBound order by t.id
CTE--2005新语法,类似临时表,但是生命周期稍微不同,这里只是他的一个运用
with cte_temp--定义零时表,PageIndex是一个计算字段,储存了搜索结果的页号
As (ceiling((Row_Number() over(order by .... )-1)/@pagesize as int) as PageIndex,* from TableName where.....)
select * from cte_temp where pageindex=@pageindex-1;
结论:
TopN在小页数下最快,如果在10页以下,可以考虑用它,CTE和临时表时间很稳定,CTE消耗的时间比临时表多,但是不会引起tempdb的暴涨和IO增加
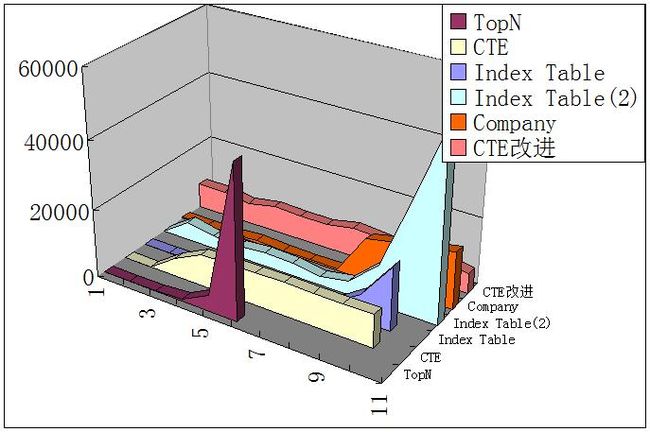
性能比较
试验环境:win2003server,Sqlserver2005,库大小2,567,245行,没有where子句,试验时每页大小50,页码作为变量
取0,3,10,31,100,316,1000,3162...页,也就是10的指数,试验结果如下
| 页数 | TopN | CTE | 临时表(有缓存) | 临时表(无缓存) |
公司正在使用的存储过程 | CTE改进 |
| 1 | 3 | 12 | 10 | 101 | 457 | 7302 |
| 3 | 15 | 7 | 79 | 5524 | 464 | 7191 |
| 10 | 127 | 5504 | 88 | 3801 | 464 | 6116 |
| 32 | 588 | 9672 | 122 | 3601 | 976 | 7602 |
| 100 | 4680 | 9738 | 166 | 4235 | 486 | 7151 |
| 316 | 45271 | 9764 | 323 | 3867 | 522 | 7255 |
| 1000 | Null | 9806 | 869 | 2578 | 635 | 8948 |
| 3162 | Null | 9822 | 2485 | 4110 | 12460 | 8210 |
| 10000 | Null | 9754 | 7812 | 11926 | 14250 | 7359 |
| 31623 | Null | 9775 | 18729 | 33218 | 15249 | 7511 |
| 100000 | Null | Null | 31538 | 55569 | 17139 | 6124 |
数据解释和分析
临时表分为有没有缓存两种时间,CTE就是上面的方法,CTE改进只是把选入CTE临时表的列数减少了,只选取了页号和主键,Null表示时间无法计算(时间太长),数据单位是毫秒.
从上面的数据可以看到,TopN在前32页都是有优势的,但是页数增大后,性能降低很快,CTE改进比CTE有所进步,平均进步两秒左右,但是还是比临时表慢,但是考虑临时表会增大日志文件的大小,引起大量IO,CTE也就有他自己的优势,公司现在正在使用的存储过程效率不错,但是在页码靠后的情况下性能会降低