【Java】整数反转引发的一个问题
整数反转引发的一个问题
- 问题引入
- 整数反转
- 踩坑之路
- Too Young Too Simple
- 填坑永远在路上
- 函数说明
- 其他相关函数
- 常见异常
- 恍然大悟
- 正解
- 代码:
- 完整代码
- 参考
问题引入
整数反转
给出一个 32 位的有符号整数,你需要将这个整数中每位上的数字进行反转。
示例 1:
输入: 123
输出: 321
示例 2:
输入: -123
输出: -321
示例 3:
输入: 120
输出: 21
注意:假设我们的环境只能存储得下 32 位的有符号整数,则其数值范围为 [−231, 231 − 1]。请根据这个假设,如果反转后整数溢出那么就返回 0。
踩坑之路
Too Young Too Simple
思路:使用一个StringBuffer从数字的尾部开始倒着追加数字字符。最后用Integer.parseInt()函数将String转换成整数,同时还可以去掉0。代码如下:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReverseNum {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(reverse(num));
}
private static int reverse(int x) {
String numStr = String.valueOf(x);
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
String res = "";
if (numStr.charAt(0) == '-') {
for (int i = numStr.length() - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
stringBuffer.append(numStr.charAt(i));
}
res = "-" + stringBuffer.toString();
} else {
for (int i = numStr.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
stringBuffer.append(numStr.charAt(i));
}
res = stringBuffer.toString();
}
return Integer.parseInt(res);
}
}
然而:当输入1234560789,出现了如下异常:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.NumberFormatException: For input string: "9870654321"
at java.base/java.lang.NumberFormatException.forInputString(NumberFormatException.java:68)
at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:652)
at java.base/java.lang.Integer.parseInt(Integer.java:770)
at com.me.ReverseNum.reverse(ReverseNum.java:27)
at com.me.ReverseNum.main(ReverseNum.java:9)
填坑永远在路上
根据异常,我们定位到Integer.parseInt()函数上,打开该函数的源码,如下:
public static int parseInt(String s) throws NumberFormatException {
return parseInt(s,10);
}
继续往下看:
/**
* Parses the string argument as a signed integer in the radix
* specified by the second argument. The characters in the string
* must all be digits of the specified radix (as determined by
* whether {@link java.lang.Character#digit(char, int)} returns a
* nonnegative value), except that the first character may be an
* ASCII minus sign {@code '-'} ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}) to
* indicate a negative value or an ASCII plus sign {@code '+'}
* ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) to indicate a positive value. The
* resulting integer value is returned.
*
* An exception of type {@code NumberFormatException} is
* thrown if any of the following situations occurs:
*
* - The first argument is {@code null} or is a string of
* length zero.
*
*
- The radix is either smaller than
* {@link java.lang.Character#MIN_RADIX} or
* larger than {@link java.lang.Character#MAX_RADIX}.
*
*
- Any character of the string is not a digit of the specified
* radix, except that the first character may be a minus sign
* {@code '-'} ({@code '\u005Cu002D'}) or plus sign
* {@code '+'} ({@code '\u005Cu002B'}) provided that the
* string is longer than length 1.
*
*
- The value represented by the string is not a value of type
* {@code int}.
*
*
* Examples:
*
* parseInt("0", 10) returns 0
* parseInt("473", 10) returns 473
* parseInt("+42", 10) returns 42
* parseInt("-0", 10) returns 0
* parseInt("-FF", 16) returns -255
* parseInt("1100110", 2) returns 102
* parseInt("2147483647", 10) returns 2147483647
* parseInt("-2147483648", 10) returns -2147483648
* parseInt("2147483648", 10) throws a NumberFormatException
* parseInt("99", 8) throws a NumberFormatException
* parseInt("Kona", 10) throws a NumberFormatException
* parseInt("Kona", 27) returns 411787
*
*
* @param s the {@code String} containing the integer
* representation to be parsed
* @param radix the radix to be used while parsing {@code s}.
* @return the integer represented by the string argument in the
* specified radix.
* @throws NumberFormatException if the {@code String}
* does not contain a parsable {@code int}.
*/
public static int parseInt(String s, int radix)
throws NumberFormatException
{
/*
* WARNING: This method may be invoked early during VM initialization
* before IntegerCache is initialized. Care must be taken to not use
* the valueOf method.
*/
if (s == null) { // 如果接受的字符串为空, 就报空字符串的异常
throw new NumberFormatException("null");
}
if (radix < Character.MIN_RADIX) { // 判断基数是不是符合要求
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" less than Character.MIN_RADIX");
}
if (radix > Character.MAX_RADIX) { // 判断基数是不是符合要求
throw new NumberFormatException("radix " + radix +
" greater than Character.MAX_RADIX");
}
boolean negative = false; // 判断符号
int i = 0, len = s.length(); // 设置初始位置和字符串的长度
int limit = -Integer.MAX_VALUE;
if (len > 0) { // 字符串的长度必须大于零
char firstChar = s.charAt(0); // 获得字符串的第一个字符
if (firstChar < '0') { // Possible leading "+" or "-"
if (firstChar == '-') {
negative = true;
limit = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
} else if (firstChar != '+') { // 如果不为+的话就报错
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s, radix);
}
// 字符串的长度为1但是又不是数字, 那肯定就出错了
if (len == 1) { // Cannot have lone "+" or "-"
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s, radix);
}
i++;
}
int multmin = limit / radix;
int result = 0;
/*
* 下面的过程其实很好理解, 以8进制的"534"为例
* * (-5*8-3)*8-4 = -348, 根据符号位判断返回的是348
*/
while (i < len) {
// Accumulating negatively avoids surprises near MAX_VALUE
// 除了前面的判断这里的也有点复杂, 因为要考虑到各种进位
// 这个将i位置上的字符根据基数转为实际的值, A->11
int digit = Character.digit(s.charAt(i++), radix);
if (digit < 0 || result < multmin) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s, radix);
}
result *= radix;
if (result < limit + digit) {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s, radix);
}
result -= digit;
}
return negative ? result : -result; // 根据符号位来判断返回哪一个
} else {
throw NumberFormatException.forInputString(s, radix);
}
}
函数说明
Integer.parseInt(String s):方法用于将字符串参数作为有符号的十进制整数进行解析。
如果方法有两个参数, 使用第二个参数指定的基数,将字符串参数解析为有符号的整数。
- parseInt(String s): 返回用十进制参数表示的整数值。
- parseInt(String s, int radix):使用指定基数的字符串参数表示的整数 (基数可以是 10, 2, 8, 或 16 等进制数)
其他相关函数
**Integer.valueof(String s):**把字符串s解析成Integer对象类型,返回的integer 可以调用对象中的方法。
**StringUtils.defaultIfBlank(T str, T defaultStr):**如果字符串为空白符就返回默认字符串defaultStr。可以以string的类型比较数值大小
Integer.parseInt(s)与Integer.valueOf(s)的区别:
Integer.parseInt(s) 多次解析同一个字符串得到的int基本类型数据是相等的,可以直接通过“==" 进行判断是值是否相等。基本类型不含equals方法。
Integer.parseInt(s) == Integer.parseInt(s)
Integer.valueOf(s) 多次解析相同的一个字符串时,得到的是Integer类型的对象,得到的对象有时是同一个对象,有时是不同的对象,要根据把s字符串解析的整数值的大小进行决定:
- 如果s字符串对应的整数值在 -128~127之间,则解析出的Integer类型的对象是同一个对象;
- 如果s字符串对应的整数值不在-128~127之间,则解析出的Integer类型的对象不是同一个对象。
不管对象是否相等,对象中的value值是相等的。
Integer.parseInt(s) == Integer.parseInt(s)
Integer.parseInt(s).equals(Integer.parseInt(s))
equals是比较的两个对象value值是否相等;
“==”是比较两个对象是否相等。
JDK源码中,由于在-128~127之间的整数值用的比较频繁,当每次要创建一个value值在-128~127之间的Integer对象时,直接从缓存中拿到这个对象,所以value值相同的Integer对象都是对应缓存中同一个对象。-128~127之外的整数值用的不是太频繁,每次创建value值相同的Integer对象时,都是重新创建一个对象,所以创建的对象不是同一个对象。
常见异常
看完了源码,大概知道了什么情况下会出现异常:
- 如下4种情况会抛 NumberFormatException 异常
- 第一个字符串参数s为null、或长度为0的字符串
- 第二个基数参数radix小于MIN_RADIX=2、或大于MAX_RADIX=36
- 字符串s的任何数字都不是指定基数的字符(数字/字母),除如下2种情况:
①第一个字符可以为减号-
②加号+且长度大于1第一个字符可以为减号-、或加号+且长度大于1 - 字符串s的值不是int型
- 常见的 NumberFormatException 异常
- s为空串、空,如:parseInt("")
- s中包括空格,如:parseInt("23 ")
- 10进制时,s中包括字符串,如:parseInt(“a32”)
- s不以-、+、数字开头、或包含字符串
- s超出int允许的范围[-2147483648,2147483647],对应到2进制数字:"-10000000000000000000000000000000" (32位数字)~ “1111111111111111111111111111111”(31位数字)
- 其他转换基数radix时,超出表示范围
恍然大悟
看到这里,我们就知道了为什么输入1234560789就会出现NumberFormatException 异常,因为这个数值已经超出了int所允许的范围,因此,会抛出异常。
那么问题来了,如何解决?
正解
采用计算的方式,不再使用字符追加的方式。以12345为例,先拿到5,再拿到4,之后是3,2,1,我们按这样的顺序就可以反向拼接处一个数字了,也就能达到反转的效果。怎么拿末尾数字呢?用取模运算就可以。
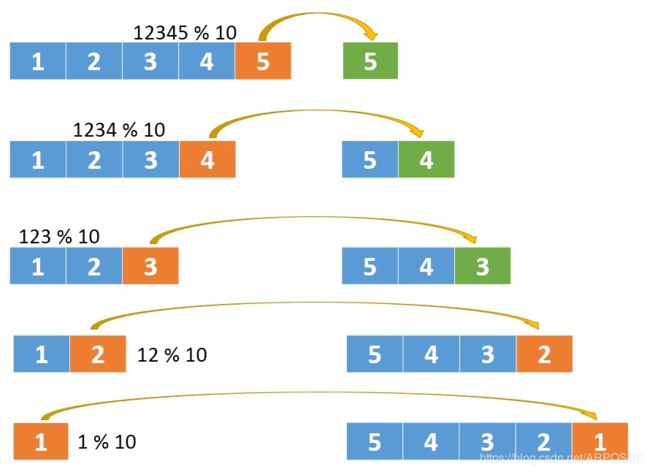
过程说明:
1、将12345 % 10 得到5,之后将12345 / 10
2、将1234 % 10 得到4,再将1234 / 10
3、将123 % 10 得到3,再将123 / 10
4、将12 % 10 得到2,再将12 / 10
5、将1 % 10 得到1,再将1 / 10
这么看起来,一个循环就搞定了,循环的判断条件是x>0
但这样做忽略了负数。
循环的判断条件应该是while(x!=0),无论正数还是负数,按照上面不断的/10这样的操作,最后都会变成0,所以判断终止条件就是!=0
有了取模和除法操作,对于像12300这样的数字,也可以完美的解决掉了。
看起来这道题就这么解决了,但请注意,题目上还有这么一句
假设我们的环境只能存储得下 32 位的有符号整数,则其数值范围为 [−2^31, 2^31 − 1]。
也就是说我们不能用long存储最终结果,而且有些数字可能是合法范围内的数字,但是反转过来就超过范围了。假设有1147483649这个数字,它是小于最大的32位整数2147483647的,但是将这个数字反转过来后就变成了9463847411,这就比最大的32位整数还要大了,这样的数字是没法存到int里面的,所以肯定要返回0(溢出了)。
甚至,我们还需要提前判断
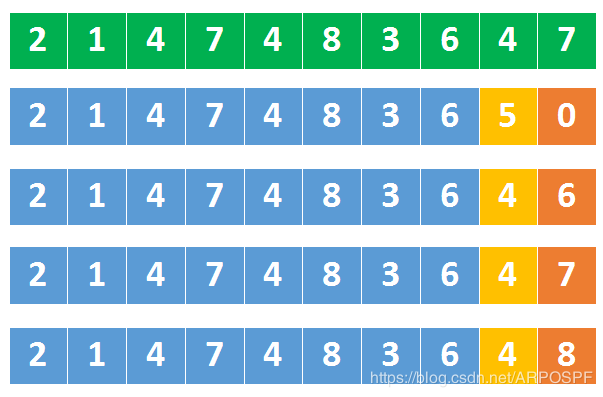
上图中,绿色的是最大32位整数
第二排数字中,橘子的是5,它是大于上面同位置的4,这就意味着5后跟任何数字,都会比最大32位整数都大。
所以,我们到【最大数的1/10】时,就要开始判断了
如果某个数字大于 214748364那后面就不用再判断了,肯定溢出了。
如果某个数字等于 214748364呢,这对应到上图中第三、第四、第五排的数字,需要要跟最大数的末尾数字比较,如果这个数字比7还大,说明溢出了。
对于负数也是一样的
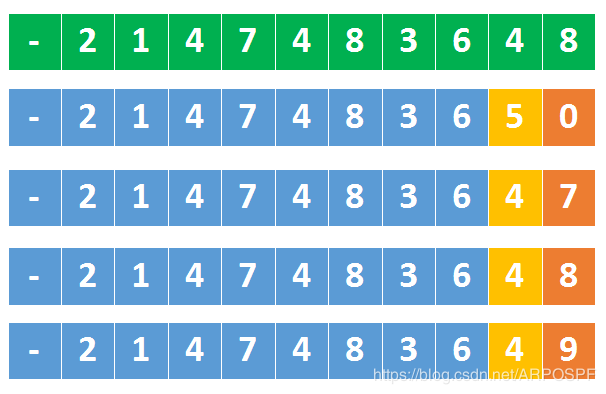
上图中绿色部分是最小的32位整数,同样是在【最小数的 1/10】时开始判断
如果某个数字小于 -214748364说明溢出了
如果某个数字等于 -214748364,还需要跟最小数的末尾比较,即看它是否小于8
代码:
public static int reverse(int x) {
int res = 0;
while (x != 0) {
// 每次取末尾数字
int tmp = x % 10;
// 判断是否大于最大32位整数
if (res > 214748364 || (res == 214748364 && tmp > 7)) {
return 0;
}
// 判断是否小于最小32位整数
if (res < -214748364 || (res == -214748364 && tmp < -8)) {
return 0;
}
res = res * 10 + tmp;
x = x / 10;
}
return res;
}
完整代码
package com.me;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ReverseNum {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int num = sc.nextInt();
// System.out.println(reverse0(num));
System.out.println(reverse1(num));
System.out.println(reverse2(num));
System.out.println(reverse3(num));
}
public static int reverse0(int x) {
String numStr = String.valueOf(x);
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
String res = "";
if (numStr.charAt(0) == '-') {
for (int i = numStr.length() - 1; i >= 1; i--) {
stringBuffer.append(numStr.charAt(i));
}
res = "-" + stringBuffer.toString();
} else {
for (int i = numStr.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
stringBuffer.append(numStr.charAt(i));
}
res = stringBuffer.toString();
}
return Integer.parseInt(res);
}
public static int reverse1(int x) {
int res = 0;
while (x != 0) {
// 每次取末尾数字
int tmp = x % 10;
// 判断是否大于最大32位整数
if (res > 214748364 || (res == 214748364 && tmp > 7)) {
return 0;
}
// 判断是否小于最小32位整数
if (res < -214748364 || (res == -214748364 && tmp < -8)) {
return 0;
}
res = res * 10 + tmp;
x = x / 10;
}
return res;
}
public static int reverse2(int x) {
int res = 0;
while (x != 0) {
int t = x % 10;
int newRes = res * 10 + t;
//如果数字溢出,直接返回0
if ((newRes - t) / 10 != res)
return 0;
res = newRes;
x = x / 10;
}
return res;
}
public static int reverse3(int x) {
long res = 0;
while (x != 0) {
res = res * 10 + x % 10;
x /= 10;
}
return (int) res == res ? (int) res : 0;
}
}
参考
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-integer/solution/tu-wen-xiang-jie-javadai-ma-de-2chong-shi-xian-fan/
- https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-integer/solution/tu-jie-7-zheng-shu-fan-zhuan-by-wang_ni_ma/
- https://blog.csdn.net/bingleihenshang/article/details/84838150