POJ2559 Largest Rectangle in a Histogram【单调栈】
Largest Rectangle in a Histogram
| Time Limit: 1000MS | Memory Limit: 65536K | |
| Total Submissions: 29417 | Accepted: 9502 |
Description
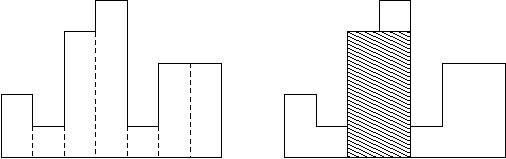
A histogram is a polygon composed of a sequence of rectangles aligned at a common base line. The rectangles have equal widths but may have different heights. For example, the figure on the left shows the histogram that consists of rectangles with the heights 2, 1, 4, 5, 1, 3, 3, measured in units where 1 is the width of the rectangles:
Usually, histograms are used to represent discrete distributions, e.g., the frequencies of characters in texts. Note that the order of the rectangles, i.e., their heights, is important. Calculate the area of the largest rectangle in a histogram that is aligned at the common base line, too. The figure on the right shows the largest aligned rectangle for the depicted histogram.
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case describes a histogram and starts with an integer n, denoting the number of rectangles it is composed of. You may assume that 1<=n<=100000. Then follow n integers h1,...,hn, where 0<=hi<=1000000000. These numbers denote the heights of the rectangles of the histogram in left-to-right order. The width of each rectangle is 1. A zero follows the input for the last test case.
Output
For each test case output on a single line the area of the largest rectangle in the specified histogram. Remember that this rectangle must be aligned at the common base line.
Sample Input
7 2 1 4 5 1 3 3
4 1000 1000 1000 1000
0Sample Output
8
4000Hint
Huge input, scanf is recommended.
Source
Ulm Local 2003
题意
题目给一个由几个相连接的矩形组成的多边形,计算多边形包含的最大的矩形的面积。
思路
单调栈,枚举每个矩形的高,以此矩形的高h为基准,计算向左、向后扩展的最大距离x,答案就是最大的 h*x。使用单调栈求这个距离,实际上就是求以某个数为最小值的最大区间。
C++代码
#include
#include
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N=100010;
//l[i]表示矩形i向左扩展的最大距离,st模拟栈,栈中存放矩形的编号,h[i]表示矩阵的高度
int l[N],st[N],h[N];
int main()
{
int n,top;
while(scanf("%d",&n)&&n)
{
ll ans=0;
top=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&h[i]);
l[i]=i;//记录编号为i的矩形向左能扩展到的位置
}
h[n+1]=-1;//添加一个最小值,这样就能保证把栈中的元素都清空
//维护一个递增栈,栈中存放矩阵的编号
for(int i=1;i<=n+1;i++)
{
//如果栈非空,或者 h[栈顶元素]大于 h[i]如果直接加进去就破坏了
//递增的性质,因此要退栈,直至为空或 h[栈顶元素]<=h[i]
while(top>0&&h[st[top]]>h[i])
{
//以当前栈顶元素的高为基准,向左向右扩展的区间为
//[l[ st[top] ] ,i),因此以它的高为基准的最大面积为以下表达式
ll temp=(ll)(i-l[st[top]])*h[st[top]];//强制类型转换,防止溢出
ans=max(ans,temp);
//由于 h[ st[top] ] > h[i],因此st[top]向左能扩展到的地方,i也能扩展到
l[i]=l[st[top]];
top--;
}
if(top>0&&h[st[top]]==h[i]) l[i]=l[st[top]];//高度相等时,i可向左扩展
st[++top]=i;//压入这个元素
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
}
return 0;
}