第四届蓝桥杯真题总结
第一题
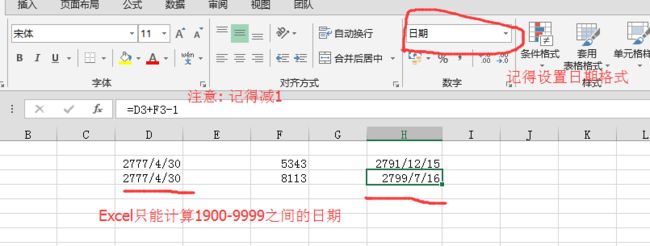
题目标题: 高斯日记 大数学家高斯有个好习惯:无论如何都要记日记。 他的日记有个与众不同的地方,他从不注明年月日,而是用一个整数代替,比如:4210 后来人们知道,那个整数就是日期,它表示那一天是高斯出生后的第几天。这或许也是个好习惯,它时时刻刻提醒着主人:日子又过去一天,还有多少时光可以用于浪费呢? 高斯出生于:1777年4月30日。 在高斯发现的一个重要定理的日记上标注着:5343,因此可算出那天是:1791年12月15日。 高斯获得博士学位的那天日记上标着:8113 请你算出高斯获得博士学位的年月日。 提交答案的格式是:yyyy-mm-dd, 例如:1980-03-21 请严格按照格式,通过浏览器提交答案。 注意:只提交这个日期,不要写其它附加内容,比如:说明性的文字。
#include
using namespace std;
int year = 1777, month = 4, day = 30;
bool IsEndofMonth();
void AddDay(int days);
void IncDay();
bool IsLeapYear();
bool IsLeapYear()
{
return (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || (year % 400 == 0);
}
bool IsEndofMonth()
{
switch(month)
{
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11: return day == 30;
case 2:
if (IsLeapYear())
return day == 29;
else
return day == 28;
default:
return day == 31;
}
}
void IncDay() //增加一天
{
if(IsEndofMonth()) //增加天数,记得要判断是否是年末,月末
{
if(month == 12)
{
day = 1; month = 1; year++;
}
else { //已经是IsEndMonth
day = 1; month++;
}
}
else {
day++;
}
}
void AddDay(int days)
{
for (int i = 1; i < days; i++) //增加多少天 days - 1
{
IncDay();
}
}
int main()
{
// AddDay(5343);
AddDay(8113);
cout << year << "-" << month << "-" << day << endl;
return 0;
}
第二题
标题: 马虎的算式 小明是个急性子,上小学的时候经常把老师写在黑板上的题目抄错了。 有一次,老师出的题目是:36 x 495 = ? 他却给抄成了:396 x 45 = ? 但结果却很戏剧性,他的答案竟然是对的!! 因为 36 * 495 = 396 * 45 = 17820 类似这样的巧合情况可能还有很多,比如:27 * 594 = 297 * 54 假设 a b c d e 代表1~9不同的5个数字(注意是各不相同的数字,且不含0) 能满足形如: ab * cde = adb * ce 这样的算式一共有多少种呢?
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10000000;
int num[] = {1, 2, 3,4, 5,6,7,8,9};
int flag[maxn];
void solve()
{
int ans = 0;
do {
int a = num[0]*10 + num[1];
int b = num[2]*100 + num[3]*10 + num[4];
int a_2 = num[0]*100 + num[3]*10 + num[1];
int b_2 = num[2]*10 + num[4];
if (a*b == a_2*b_2) {
ans++;
}
} while (next_permutation(num, num + 9));
// 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
//从6这里全排列时,前面不变,相当于 之前的排列*4*3*2*1,所以答案需要最后除以他们
cout << ans/4/3/2/1 << endl;
}
void solve2()
{
int ans = 0;
for (int a = 1; a <= 9; a++)
{
for (int b = 1; b <= 9; b++)
{
if (a == b) continue;
for (int c = 1; c <= 9; c++)
{
if (a == c || b == c) continue;
for (int d = 1; d <= 9; d++)
{
if (a == d || b == d || c == d) continue;
for (int e = 1; e <= 9; e++)
{
if (a == e || b == e || c == e || d == e) continue;
int n1 = a*10 + b;
int n2 = c*100 + d*10 + e;
int n3 = a*100 + d*10 + b;
int n4 = c*10 + e;
if (n1*n2 == n3*n4) {
ans++;
}
}
}
}
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main()
{
solve();
solve2();
return 0;
}
两种答案算出来都是:142。注:这种题目,如果不确定,可以用两种方法来比较一下!!
第三题:
题目标题: 第39级台阶 小明刚刚看完电影《第39级台阶》,离开电影院的时候,他数了数礼堂前的台阶数,恰好是39级! 站在台阶前,他突然又想着一个问题: 如果我每一步只能迈上1个或2个台阶。先迈左脚,然后左右交替,最后一步是迈右脚,也就是说一共要走偶数步。那么,上完39级台阶,有多少种不同的上法呢? 请你利用计算机的优势,帮助小明寻找答案。
题解:虽然是简单递归,但是还是得多练习。。这种题目要先找递归结束条件,然后就是递归项。题目说了,上完39级台阶,且最后要有走偶数步。。可以认为,递归项是:(当前走的步数,剩余的台阶数)。递归结束条件是:剩余台阶 < 0, 显然直接return;当前走的步数%2==0 && 剩余台阶为0,则方案数+1;
#include#include ; }#include #include using namespace std; int ans; void dfs(int cur, int rest) { if (rest < 0) { return; } if (rest == 0 && cur % 2 == 0) { ans++; return; } dfs(cur + 1, rest - 1); dfs(cur + 1, rest - 2); } void solve() { dfs(0, 39); cout << ans << endl; } int main() { solve(); return 0
第四题:
回头写,咸鱼只能写个水题,心塞塞..........
第五题:
题目标题:前缀判断
如下的代码判断 needle_start指向的串是否为haystack_start指向的串的前缀,如不是,则返回NULL。
比如:"abcd1234" 就包含了 "abc" 为前缀
char* prefix(char* haystack_start, char* needle_start)
{
char* haystack = haystack_start;
char* needle = needle_start;
while(*haystack && *needle){
if(______________________________) return NULL; //填空位置
}
if(*needle) return NULL;
return haystack_start;
}
请分析代码逻辑,并推测划线处的代码,通过网页提交。
if(*needle++ != *haystack++) return NULL; //填空位置
第六题:
标题:三部排序
一般的排序有许多经典算法,如快速排序、希尔排序等。
但实际应用时,经常会或多或少有一些特殊的要求。我们没必要套用那些经典算法,可以根据实际情况建立更好的解法。
比如,对一个整型数组中的数字进行分类排序:
使得负数都靠左端,正数都靠右端,0在中部。注意问题的特点是:负数区域和正数区域内并不要求有序。可以利用这个特点通过1次线性扫描就结束战斗!!
以下的程序实现了该目标。
其中x指向待排序的整型数组,len是数组的长度。
void sort3p(int* x, int len)
{
int p = 0;
int left = 0;
int right = len-1;
while(p<=right){
if(x[p]<0){
int t = x[left];
x[left] = x[p];
x[p] = t;
left++;
p++;
}
else if(x[p]>0){
int t = x[right];
x[right] = x[p];
x[p] = t;
right--;
}
else{
__________________________; //填空位置
}
}
}
}
答案:p++;
第七题:错误票据
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100000 + 50;
int N;
int num[maxn];
void solve()
{
int cnt = 0;
string line;
int a;
getchar();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
getline(cin, line);
istringstream in(line);
while (in >> a) {
num[cnt++] = a;
}
}
sort(num, num + cnt);
int m = 0, n = 0;
int flag_m = 0, flag_n = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cnt - 1; i++) {
if (num[i + 1] - num[i] > 1 && !flag_m) {
m = num[i] + 1;
flag_m = 1;
}
if ((num[i] == num[i + 1]) && !flag_n) {
n = num[i];
flag_n = 1;
}
if (flag_m && flag_n) {
break;
}
}
printf("%d %d\n", m, n);
}
int main()
{
cin >> N;
solve();
return 0;
}
第八题:
#include
#include
#include <string>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000 + 20;
void solve()
{
int init[maxn],
over[maxn];
string in, ov;
int ans = 0;
cin >> in;
cin >> ov;
for (unsigned i = 0; i < in.length(); i++) {
if (in[i] == '*') {
init[i] = 1;
}
else {
init[i] = 0;
}
if (ov[i] == '*') {
over[i] = 1;
}
else {
over[i] = 0;
}
}
for (unsigned i = 0; i < in.size() - 1; i++)
{
if (init[i] != over[i]) {
init[i] = over[i];
init[i+1] = !init[i+1];
ans++;
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main()
{
solve();
return 0;
}
第九题:标题:带分数
100 可以表示为带分数的形式:100 = 3 + 69258 / 714
还可以表示为:100 = 82 + 3546 / 197
注意特征:带分数中,数字1~9分别出现且只出现一次(不包含0)。
类似这样的带分数,100 有 11 种表示法。
题目要求:
从标准输入读入一个正整数N (N<1000*1000)
程序输出该数字用数码1~9不重复不遗漏地组成带分数表示的全部种数。
注意:不要求输出每个表示,只统计有多少表示法!
例如:
用户输入:
100
程序输出:
11
再例如:
用户输入:
105
程序输出:
6
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
int num[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9},
N, ans;
int getSum(int lh, int rh)
{
int sum = 0;
for (int i = lh; i <= rh; i++)
{
sum = sum * 10 + num[i];
}
return sum;
}
void check()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 9; i++)
{
int a = getSum(0, i);
if (a > N) continue;
for (int j = i + 1; j < 8; j++)
{
int b = getSum(i + 1, j);
int c = getSum(j + 1, 8);
if (b >= c && b % c == 0 && (a + b/c == N)) {
ans++;
}
}
}
}
void solve()
{
cin >> N;
do {
check();
} while(next_permutation(num, num + 9));
printf("%d\n", ans);
}
int main()
{
solve();
return 0;
}
第十题:连号区间数
#include
#include
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 50000 + 100;
int N;
int Pi[maxn];
void solve()
{
cin >> N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
scanf("%d", &Pi[i]);
}
int ans = N;
int max1, min1;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
max1 = min1 = Pi[i];
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++)
{
if (max1 < Pi[j]) {
max1 = Pi[j];
}
if (min1 > Pi[j]) {
min1 = Pi[j];
}
if (max1 - min1 == j - i)
{
ans++;
}
}
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main()
{
solve();
return 0;
}
posted @
2018-03-13 23:44 douzujun 阅读(
...) 评论(
...) 编辑 收藏