10分钟学会NIO技术
NIO的概述
NIO是New I/O的简称,与旧式基于流的I/O相对,从名字上来看,它表示新的一套I/O标准。它是从JDK1.4中被纳入到JDK中的。
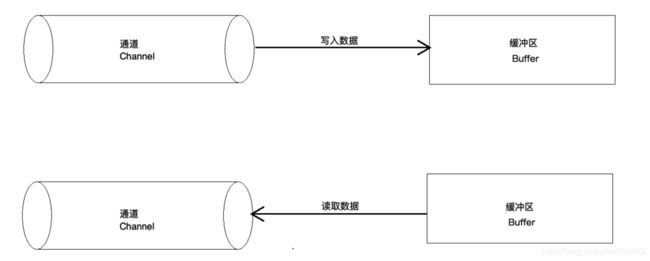
与旧式的IO流相比,NIO是基于Block的,它以块为单位来处理数据,最为重要的两个组件是缓冲区Buffer和通道Channel。缓冲区是一块连续的内存块,是NIO读写数据的载体;通道表示缓冲数据的源头和目的地,它用于向缓冲区读取或者写入数据,是访问缓冲区的接口。
Buffer的基本原理
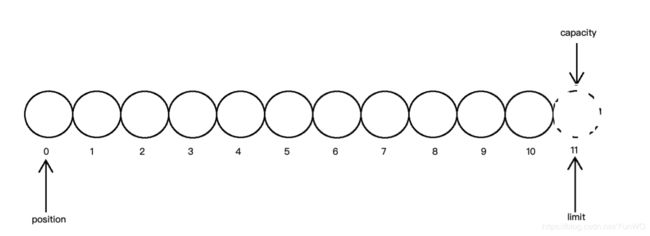
Buffer中最重要的3个参数:位置(position)、容量(capacity)、上限(limit)。他们3者的含义如下
位置(position): 表示当前缓冲区的位置,从position位置之后开始读写数据。
容量(capacity): 表示缓冲区的最大容量
上限(limit): 表示缓冲区的实际上限,它总是小于或等于容量
缓冲区的容量(capacity)是不变的,而位置(position)和上限(limit)和以根据实际需要而变化。也就是说,可以通过改变当前位置和上限来操作缓冲区内任意位置的数据。
Buffer的常用方法
NIO提供一系列方法来操作Buffer的位置(position)和上限(limit),以及向缓冲区读写数据。
put() //向缓冲区position位置添加数据。并且position往后移动,不能超过limit上限。
get() //读取当前position位置的数据。并且position往后移动,不能超过limit上限。
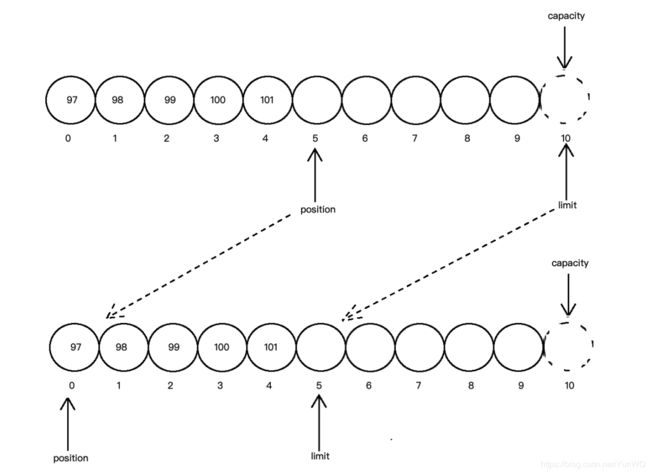
flip() //将limit置位为当前position位置,再讲position设置为0
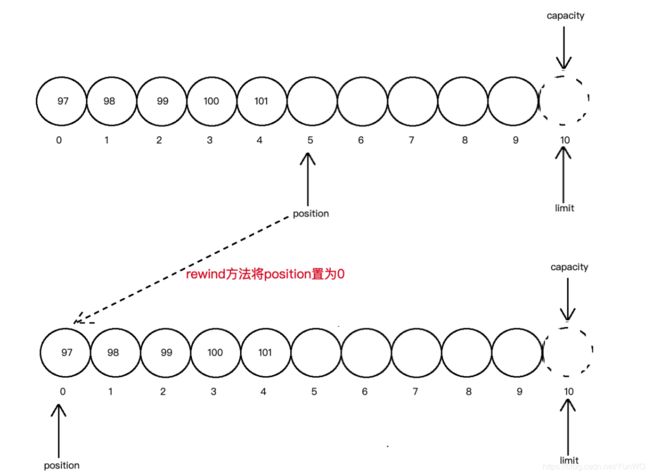
rewind() //仅将当前position位置设置为0
remaining //获取缓冲区中当前position位置和limit上限之间的元素数(有效的元素数)
hasRemaining() //判断当前缓冲区是否存在有效的元素数
mark() //在当前position位置打一个标记
reset() //将当前position位置恢复到mark标记的位置。
duplicate() //复制缓冲区
创建缓冲区
//创建一个容量为10的缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer1=ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
//创建一个包裹数据的缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer2 = ByteBuffer.wrap("abcde".getBytes());
获取/设置缓冲区参数
//创建一个容量为10的缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
System.out.println("位置:"+byteBuffer.position()); //0
System.out.println("上限:"+byteBuffer.limit()); //10
System.out.println("容量:"+byteBuffer.capacity());//10
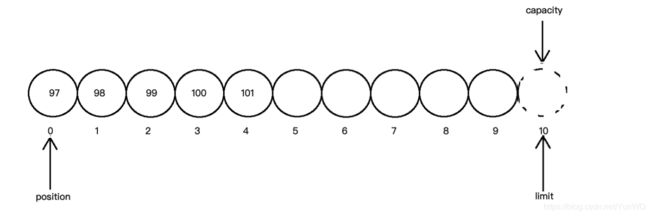
添加数据到缓冲区
//创建一个容量为10的缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
//添加数据到缓冲区
byteBuffer.put("abcde".getBytes());
System.out.println("position位置:"+byteBuffer.position()); //5
System.out.println("limit上限:"+byteBuffer.limit()); //10
System.out.println("capacity容量:"+byteBuffer.capacity()); //10
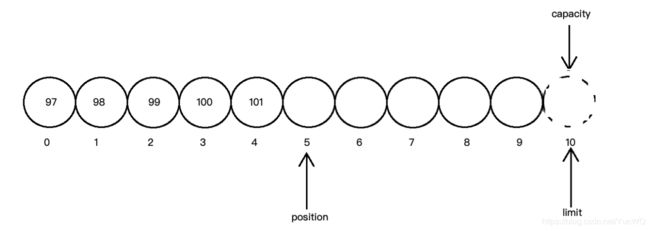
rewind重置缓冲区
rewind函数将position置为0位置,并清除标记。
//创建一个容量为10的缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
//添加数据到缓冲区
byteBuffer.put("abcde".getBytes());
System.out.println("position位置:"+byteBuffer.position()); //5
System.out.println("limit上限:"+byteBuffer.limit()); //10
System.out.println("capacity容量:"+byteBuffer.capacity()); //10
System.out.println("------------");
//重置缓冲区
byteBuffer.rewind();
System.out.println("position位置:"+byteBuffer.position()); //0
System.out.println("limit上限:"+byteBuffer.limit()); //10
System.out.println("capacity容量:"+byteBuffer.capacity());//10
flip重置缓冲区
flip函数现将limit设置为position位置,再将position置为0位置,并清除mar标记。
//创建一个容量为10的缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
//添加数据到缓冲区
byteBuffer.put("abcde".getBytes());
System.out.println("position位置:"+byteBuffer.position()); //5
System.out.println("limit上限:"+byteBuffer.limit()); //10
System.out.println("capacity容量:"+byteBuffer.capacity()); //10
System.out.println("------------");
//重置缓冲区
byteBuffer.flip();
System.out.println("position位置:"+byteBuffer.position()); //0
System.out.println("limit上限:"+byteBuffer.limit()); //5
System.out.println("capacity容量:"+byteBuffer.capacity());//10
clear清空缓冲区
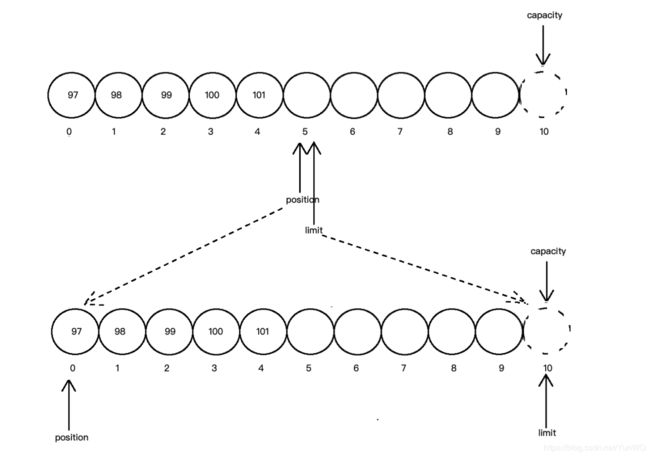
clear方法也将position置为0,同时将limit置为capacity的大小,并清除mark标记。
//创建一个容量为10的缓冲区
ByteBuffer byteBuffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
//设置上限为5
byteBuffer.limit(5);
//添加数据到缓冲区
byteBuffer.put("abcde".getBytes());
System.out.println("position位置:"+byteBuffer.position()); //5
System.out.println("limit上限:"+byteBuffer.limit()); //5
System.out.println("capacity容量:"+byteBuffer.capacity()); //10
System.out.println("------------");
//重置缓冲区
byteBuffer.clear();
System.out.println("position位置:"+byteBuffer.position()); //0
System.out.println("limit上限:"+byteBuffer.limit()); //10
System.out.println("capacity容量:"+byteBuffer.capacity());//10
标记和恢复
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10);
//添加数据到缓冲区
buffer.put("abcde".getBytes());
//打一个标记
buffer.mark();
System.out.println("标记位置:"+buffer.position()); //5
//再添加5个字节数据到缓冲区
buffer.put("fijkl".getBytes());
System.out.println("当前位置:"+buffer.position()); //10
//将position恢复到mark标记位置
buffer.reset();
System.out.println("恢复标记位置:"+buffer.position());//5
FileChannel通道
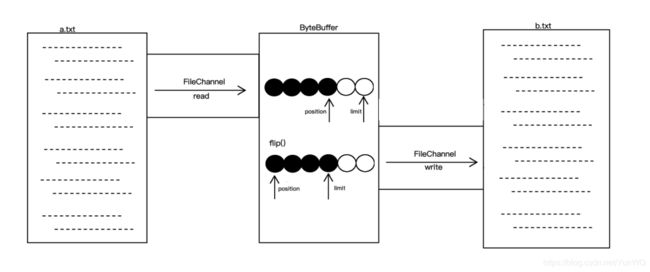
FileChannel是用于操作文件的通道,可以用于读取和写入文件中的数据。
//创建读取文件通道
FileChannel fisChannel = new FileInputStream("day05/src/a.txt").getChannel();
//创建写入文件的通道
FileChannel fosChannel = new FileOutputStream("day05/src/b.txt").getChannel();
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(2);
while (fisChannel.read(buffer)!=-1){
System.out.println("position:"+buffer.position()); //0
System.out.println("limit:"+buffer.limit());//2
//重置缓冲区(为输出buffer数据做准备)
buffer.flip();
fosChannel.write(buffer);
//重置缓冲区(为输入buffer数据做准备)
buffer.clear();
}
//关闭通道
fisChannel.close();
fosChannel.close();
SocketChannel通道
下面代码使用SocketChannel通道上传文件到服务器
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建通道
SocketChannel socketChannel = SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 10000));
//创建缓冲区
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//读取本地文件数据到缓冲区
FileChannel fisChannel = new FileInputStream("day05/src/a.txt").getChannel();
while (fisChannel.read(buffer)!=-1){
buffer.flip(); //为写入数据做准备
socketChannel.write(buffer);
buffer.clear(); //为读取数据做准备
}
//关闭本地通道
fisChannel.close();
//socketChannel.shutdownOutput();
//读取服务端回写的数据
buffer.clear();
int len = socketChannel.read(buffer);
System.out.println(new String(buffer.array(), 0, len));
//关闭socket通道
socketChannel.close();
}
}
ServerSocketChannel通道
下面代码使用ServerSocketChannel通道接收文件并保存到服务器
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.创建ServerSocketChannel通道
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2.绑定端口号
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(10000));
//3.设置非阻塞
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
System.out.println("服务器已开启");
while (true) {
//4.获取客户端通道,如果有客户端连接返回客户端通道,否则返回null
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
if(socketChannel!=null){
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//创建本地通道,用于往文件中写数据
UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();
FileChannel fosChannel=new FileOutputStream("day05/src/"+uuid+".txt").getChannel();
ByteBuffer buffer=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (socketChannel.read(buffer)>0){
buffer.flip(); //准备把缓冲区数据输出
fosChannel.write(buffer);
buffer.clear();//准备读取数据到缓冲区
}
fosChannel.close();
//回写数据到客户端
ByteBuffer resultBuffer=ByteBuffer.wrap("上传文件成功".getBytes());
socketChannel.write(resultBuffer);
//关闭客户端通道
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
}
NIO Selector选择器
Selector 一般称 为选择器 ,当然你也可以翻译为 多路复用器 。它是Java NIO核心组件中的一个,用于检查一个或多个NIO Channel(通道)的状态是否处于可读、可写。如此可以实现单线程管理多个channels,也就是可以管理多个网络链接。
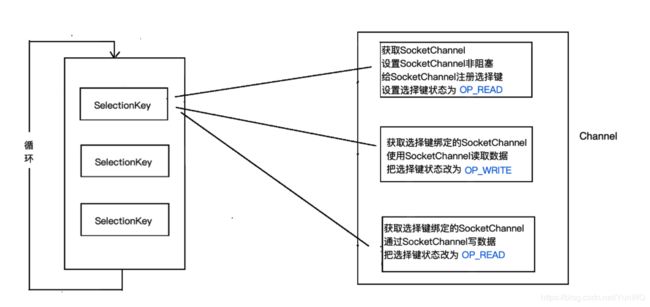
使用Selector的服务器模板代码
有了模板代码我们在编写程序时,大多数时间都是在模板代码中添加相应的业务代码
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 8080));
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
while(true) {
int readyNum = selector.select();
if (readyNum == 0) {
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectedKeys.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
if(key.isAcceptable()) {
// 接受连接
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
// 通道可读
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
// 通道可写
}
it.remove();
}
}
NIO Selector服务端
按照上面的模板代码,改写接收文件的服务端。
public class Server {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
ServerSocketChannel ssc = ServerSocketChannel.open();
ssc.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 10000));
ssc.configureBlocking(false);
Selector selector = Selector.open();
ssc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
FileChannel fosChannel=null;
while (true) {
int readyNum = selector.select();
System.out.println(readyNum);
if (readyNum == 0) {
continue;
}
Set<SelectionKey> selectedKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> it = selectedKeys.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
SocketChannel socketChannel1=null;
SocketChannel socketChannel2=null;
if (key.isAcceptable()) {
System.out.println("isAcceptable");
// 创建新的连接,并且把连接注册到selector上,而且,
// 声明这个channel只对读操作感兴趣。
socketChannel1 = ssc.accept();
socketChannel1.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel1.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();
fosChannel=new FileOutputStream("day05/src/"+uuid+".txt").getChannel();
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
System.out.println("isReadable");
// 通道可读
socketChannel2 = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
//创建本地通道,用于往文件中写数据
ByteBuffer readBuff=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while (socketChannel2.read(readBuff)>0){
readBuff.flip(); //准备把缓冲区数据输出
fosChannel.write(readBuff);
readBuff.clear();//准备读取数据到缓冲区
}
fosChannel.close();
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
} else if (key.isWritable()) {
System.out.println("isWritable");
// 通道可写
ByteBuffer writeBuff=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
writeBuff.put("上传成功".getBytes());
writeBuff.flip();
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
socketChannel.write(writeBuff);
key.interestOps(SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
it.remove();
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
//e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
}
}
}