四、union-find算法
- union-find算法
- 动态连通性
- 可能的应用
- 代码
- 实现
- quick-find算法用一个ID代表类别
- quick-union算法
- 加权quick-union算法
- 最优算法 路径压缩的加权quick-union算法
union-find算法
动态连通性
问题总结:就是输入一个整数对代表两个融点(也就是对象,融点是术语),如果两个融点未连通,则将它们连在一起(调用union方法,下面黑色的部分),并打印;如果两个融点已经连通则处理下一对数据(下图灰色的部分,什么也不干)。过程如下:
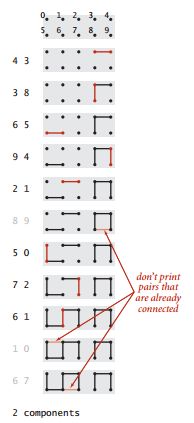
设计一个数据结构来保存程序已知的所有整数对的足够多的信息,并用它们来判断一个新对象是否相连。这个问题也称为动态连通性问题
可能的应用:
- 网络(计算机之间的连接)
- 变量名的等价性
- 数学集合
这里使用网络方面的术语,将对象称为融点,将整数对称为连接,将等价类称为连通分量 或者简称分量。假设用0到N-1的整数表示N个融点
代码
定义的API :
先给出最终代码,后面会讨论一步一步怎么优化的:
public class UF {
private int[] parent; // parent[i] = parent of i
private byte[] rank; // rank[i] = rank of subtree rooted at i (never more than 31)
private int count; // number of components
public UF(int N) {
if (N < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException();
count = N;
parent = new int[N];
rank = new byte[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 0;
}
}
public int find(int p) {
validate(p);
while (p != parent[p]) {
parent[p] = parent[parent[p]]; // path compression by halving
p = parent[p];
}
return p;
}
public int count() {
return count;
}
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
// make root of smaller rank point to root of larger rank
if (rank[rootP] < rank[rootQ]) parent[rootP] = rootQ;
else if (rank[rootP] > rank[rootQ]) parent[rootQ] = rootP;
else {
parent[rootQ] = rootP;
rank[rootP]++;
}
count--;
}
private void validate(int p) {
int N = parent.length;
if (p < 0 || p >= N) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (N-1));
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = StdIn.readInt();
UF uf = new UF(N);
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
int p = StdIn.readInt();
int q = StdIn.readInt();
if (uf.connected(p, q)) continue;
uf.union(p, q);
StdOut.println(p + " " + q);
}
StdOut.println(uf.count() + " components");
}
}成本模型(优劣性怎么比): 在研究union-find 的API的各种算法时,我们统计的是数组的访问次数(访问任意数组元素的次数,无论读写)
实现
quick-find算法:用一个ID代表类别
public class QuickFindUF {
private int[] id; // id[i] = component identifier of i
private int count; // number of components
public QuickFindUF(int N) {
count = N;
id = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
id[i] = i;
}
public int count() {
return count;
}
public int find(int p) {
validate(p);
return id[p];
}
private void validate(int p) {
int N = id.length;
if (p < 0 || p >= N) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (N-1));
}
}
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
validate(p);
validate(q);
return id[p] == id[q];
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int pID = id[p]; // needed for correctness
int qID = id[q]; // to reduce the number of array accesses
// p and q are already in the same component
if (pID == qID) return;
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++)
if (id[i] == pID) id[i] = qID;
count--;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = StdIn.readInt();
QuickFindUF uf = new QuickFindUF(N);
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
int p = StdIn.readInt();
int q = StdIn.readInt();
if (uf.connected(p, q)) continue;
uf.union(p, q);
StdOut.println(p + " " + q);
}
StdOut.println(uf.count() + " components");
}
}算法分析:find很快,union很慢要扫描整个数组

上图中的connected的方法描述不对,可能是老版本的
quick-find 算法的运行时间对于最终只得到少数连通分量的一般应用是平方级别的
quick-union算法
每个触电所对应的id[] 元素都是同一个分量中的另一个触点的名称(也可能是它自己)——称之为链接
每个连通分量是通过链来连接的,find返回父类(也就是类的代表,父类初始化为自己)(说白了就是树,具体看代码)
public class QuickUnionUF {
private int[] parent; // parent[i] = parent of i
private int count; // number of components
public QuickUnionUF(int N) {
parent = new int[N];
count = N;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
}
}
public int count() {
return count;
}
public int find(int p) {
validate(p);
while (p != parent[p])
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
// validate that p is a valid index
private void validate(int p) {
int N = parent.length;
if (p < 0 || p >= N) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (N-1));
}
}
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
count--;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int N = StdIn.readInt();
QuickUnionUF uf = new QuickUnionUF(N);
while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
int p = StdIn.readInt();
int q = StdIn.readInt();
if (uf.connected(p, q)) continue;
uf.union(p, q);
StdOut.println(p + " " + q);
}
StdOut.println(uf.count() + " components");
}
}森林的表示
上面的表示形式也称为森林,一棵树就是一个类别

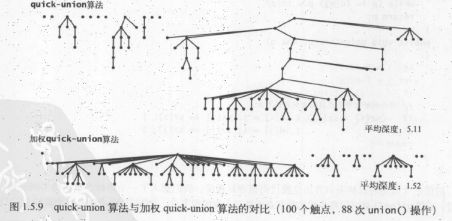
quick-union 算法比quick-find算法更快,因为他不需要为每对输入遍历整个数组,最好线性,最坏平方级别,quick-union算是一种改进
加权quick-union算法
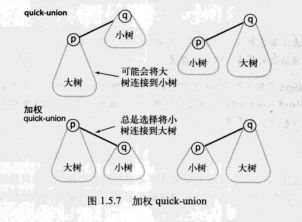
我们只需要简单地修改quick-union算法就能保证像这样的糟糕情况不在出现(下图中所示,大树接到小树上了,不利于find)。
将会记录每一棵树的代销并总是将较小的数连接到较大的数上(树的深度对find的影响很大)
public class WeightedQuickUnionUF {
private int[] parent; // parent[i] = parent of i
private int[] size; // size[i] = number of sites in subtree rooted at i
private int count; // number of components
public WeightedQuickUnionUF(int N) {
count = N;
parent = new int[N];
size = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
size[i] = 1;
}
}
public int count() {
return count;
}
public int find(int p) {
validate(p);
while (p != parent[p])
p = parent[p];
return p;
}
// validate that p is a valid index
private void validate(int p) {
int N = parent.length;
if (p < 0 || p >= N) {
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("index " + p + " is not between 0 and " + (N-1));
}
}
public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
return find(p) == find(q);
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int rootP = find(p);
int rootQ = find(q);
if (rootP == rootQ) return;
// make smaller root point to larger one
if (size[rootP] < size[rootQ]) {
parent[rootP] = rootQ;
size[rootQ] += size[rootP];
}
else {
parent[rootQ] = rootP;
size[rootP] += size[rootQ];
}
count--;
}
}归并两个含有 2n 个节点的树时,由此树的高度增加到了 n+1 ,因此,加权quick-union能够保证对数级别的性能。


最优算法: 路径压缩的加权quick-union算法
理想情况下,我们希望每个节点都直接连接到它的根节点上(形成一个完全扁平的树,使find更快,单又不同于quick-find的做法),但我们又不想像quick-find算法那样通过大量的连接修改做到这一点。所以在检查节点的同时将它们直接链到根节点上。rank越大,合并的次数越多,数也越大((1, 1)(2, 2)(4, 4)合并的轨迹都是这样,rank越大,显然树也越大)
但是,最坏情况下不保证是常数级别。代码就是一开始给出的最终代码
