day01-网络爬虫
网络爬虫
- 1.课程计划
- 2.网络爬虫
- 2.1.爬虫入门程序
- 2.1.1.环境准备
- 2.1.2.环境准备
- 2.1.3.加入log4j.properties
- 2.1.4.编写代码
- 3.网络爬虫
- 3.1.网络爬虫介绍
- 3.2.为什么学网络爬虫
- 4.HttpClient
- 4.1.GET请求
- 4.2.带参数的GET请求
- 4.3.POST请求
- 4.4.带参数的POST请求
- 4.5.连接池
- 4.6.请求参数
- 5.Jsoup
- 5.1.jsoup介绍
- 5.2.jsoup解析
- 5.2.1.解析url
- 5.2.2.解析字符串
- 5.2.3.解析文件
- 5.2.4.使用dom方式遍历文档
- 5.2.5.使用选择器语法查找元素
- 5.2.6.Selector选择器概述
- 5.2.7.Selector选择器组合使用
- 6.爬虫案例
- 6.1.需求分析
- 6.1.1.SPU和SKU
- 6.2.开发准备
- 6.2.1.数据库表分析
- 6.2.2.添加依赖
- 6.2.3.添加配置文件
- 6.3.代码实现
- 6.3.1.编写pojo
- 6.3.2.编写dao
- 6.3.3.编写Service
- 6.3.4.编写引导类
- 6.3.5.封装HttpClient
- 6.3.6.实现数据抓取
1.课程计划
1.入门程序
2.网络爬虫介绍
3.HttpClient抓取数据
4.Jsoup解析数据
5.爬虫案例
2.网络爬虫
网络爬虫(Web crawler),是一种按照一定的规则,自动地抓取万维网信息的程序或者脚本
2.1.爬虫入门程序
2.1.1.环境准备
- JDK1.8
- IntelliJ IDEA
- IDEA自带的Maven
2.1.2.环境准备
创建Maven工程itcast-crawler-first并给pom.xml加入依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- HttpClient -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
<version>4.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 日志 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
<version>1.7.25</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
2.1.3.加入log4j.properties
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG,A1
log4j.logger.cn.itcast = DEBUG
log4j.appender.A1=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.A1.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.A1.layout.ConversionPattern=%-d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss,SSS} [%t] [%c]-[%p] %m%n
2.1.4.编写代码
编写最简单的爬虫,抓取传智播客首页:http://www.itcast.cn/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://www.itcast.cn/");
CloseableHttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8");
System.out.println(content);
}
}
测试结果:可以获取到页面数据
3.网络爬虫
3.1.网络爬虫介绍
在大数据时代,信息的采集是一项重要的工作,而互联网中的数据是海量的,如果单纯靠人力进行信息采集,不仅低效繁琐,搜集的成本也会提高。如何自动高效地获取互联网中我们感兴趣的信息并为我们所用是一个重要的问题,而爬虫技术就是为了解决这些问题而生的。
网络爬虫(Web crawler)也叫做网络机器人,可以代替人们自动地在互联网中进行数据信息的采集与整理。它是一种按照一定的规则,自动地抓取万维网信息的程序或者脚本,可以自动采集所有其能够访问到的页面内容,以获取相关数据。
从功能上来讲,爬虫一般分为数据采集,处理,储存三个部分。爬虫从一个或若干初始网页的URL开始,获得初始网页上的URL,在抓取网页的过程中,不断从当前页面上抽取新的URL放入队列,直到满足系统的一定停止条件。
3.2.为什么学网络爬虫
我们初步认识了网络爬虫,但是为什么要学习网络爬虫呢?只有清晰地知道我们的学习目的,才能够更好地学习这一项知识。在此,总结了4种常见的学习爬虫的原因:
1.可以实现搜索引擎
我们学会了爬虫编写之后,就可以利用爬虫自动地采集互联网中的信息,采集回来后进行相应的存储或处理,在需要检索某些信息的时候,只需在采集回来的信息中进行检索,即实现了私人的搜索引擎。
2.大数据时代,可以让我们获取更多的数据源。
在进行大数据分析或者进行数据挖掘的时候,需要有数据源进行分析。我们可以从某些提供数据统计的网站获得,也可以从某些文献或内部资料中获得,但是这些获得数据的方式,有时很难满足我们对数据的需求,而手动从互联网中去寻找这些数据,则耗费的精力过大。此时就可以利用爬虫技术,自动地从互联网中获取我们感兴趣的数据内容,并将这些数据内容爬取回来,作为我们的数据源,再进行更深层次的数据分析,并获得更多有价值的信息。
3.可以更好地进行搜索引擎优化(SEO)。
对于很多SEO从业者来说,为了更好的完成工作,那么就必须要对搜索引擎的工作原理非常清楚,同时也需要掌握搜索引擎爬虫的工作原理。
而学习爬虫,可以更深层次地理解搜索引擎爬虫的工作原理,这样在进行搜索引擎优化时,才能知己知彼,百战不殆。
4.有利于就业。
从就业来说,爬虫工程师方向是不错的选择之一,因为目前爬虫工程师的需求越来越大,而能够胜任这方面岗位的人员较少,所以属于一个比较紧缺的职业方向,并且随着大数据时代和人工智能的来临,爬虫技术的应用将越来越广泛,在未来会拥有很好的发展空间。
4.HttpClient
网络爬虫就是用程序帮助我们访问网络上的资源,我们一直以来都是使用HTTP协议访问互联网的网页,网络爬虫需要编写程序,在这里使用同样的HTTP协议访问网页。
这里我们使用Java的HTTP协议客户端 HttpClient这个技术,来实现抓取网页数据。
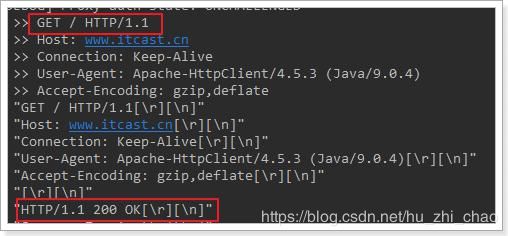
4.1.GET请求
访问传智官网,请求url地址:
http://www.itcast.cn/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建HttpClient对象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
//创建HttpGet请求
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://www.itcast.cn/");
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
//使用HttpClient发起请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
//判断响应状态码是否为200
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
//如果为200表示请求成功,获取返回数据
String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8");
//打印数据长度
System.out.println(content);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放连接
if (response == null) {
try {
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
httpClient.close();
}
}
}
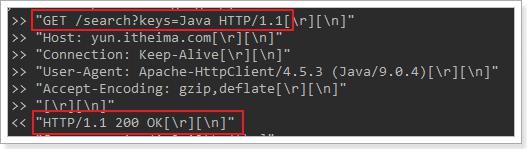
4.2.带参数的GET请求
在传智中搜索学习视频,地址为:
http://yun.itheima.com/search?keys=Java
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建HttpClient对象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
//创建HttpGet请求,带参数的地址https://www.baidu.com/s?wd=HttpClient
String uri = "http://yun.itheima.com/search?keys=Java";
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(uri);
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
//使用HttpClient发起请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
//判断响应状态码是否为200
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
//如果为200表示请求成功,获取返回数据
String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8");
//打印数据长度
System.out.println(content);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放连接
if (response == null) {
try {
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
httpClient.close();
}
}
}
4.3.POST请求
使用POST访问传智官网,请求url地址:
http://www.itcast.cn/
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建HttpClient对象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
//创建HttpGet请求
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://www.itcast.cn/");
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
//使用HttpClient发起请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
//判断响应状态码是否为200
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
//如果为200表示请求成功,获取返回数据
String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8");
//打印数据长度
System.out.println(content);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放连接
if (response == null) {
try {
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
httpClient.close();
}
}
}
请求结果:
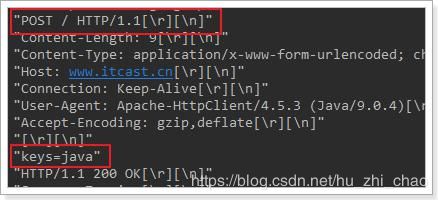
4.4.带参数的POST请求
在传智中搜索学习视频,使用POST请求,url地址为:
http://yun.itheima.com/search
url地址没有参数,参数keys=java放到表单中进行提交
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建HttpClient对象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
//创建HttpGet请求
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost("http://www.itcast.cn/");
//声明存放参数的List集合
List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair("keys", "java"));
//创建表单数据Entity
UrlEncodedFormEntity formEntity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(params, "UTF-8");
//设置表单Entity到httpPost请求对象中
httpPost.setEntity(formEntity);
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
//使用HttpClient发起请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
//判断响应状态码是否为200
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
//如果为200表示请求成功,获取返回数据
String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8");
//打印数据长度
System.out.println(content);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放连接
if (response == null) {
try {
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
httpClient.close();
}
}
}
请求结果
4.5.连接池
如果每次请求都要创建HttpClient,会有频繁创建和销毁的问题,可以使用连接池来解决这个问题。
测试以下代码,并断点查看每次获取的HttpClient都是不一样的。
public static void main(String[] args) {
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager cm = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager();
// 设置最大连接数
cm.setMaxTotal(200);
// 设置每个主机的并发数
cm.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(20);
doGet(cm);
doGet(cm);
}
private static void doGet(PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager cm) {
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom().setConnectionManager(cm).build();
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://www.itcast.cn/");
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// 判断状态码是否是200
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
// 解析数据
String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8");
System.out.println(content.length());
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放连接
if (response == null) {
try {
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//不能关闭HttpClient
//httpClient.close();
}
}
}
4.6.请求参数
有时候因为网络,或者目标服务器的原因,请求需要更长的时间才能完成,我们需要自定义相关时间
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建HttpClient对象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.createDefault();
//创建HttpGet请求
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://www.itcast.cn/");
//设置请求参数
RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
.setConnectTimeout(1000)//设置创建连接的最长时间
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(500)//设置获取连接的最长时间
.setSocketTimeout(10 * 1000)//设置数据传输的最长时间
.build();
httpGet.setConfig(requestConfig);
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
//使用HttpClient发起请求
response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
//判断响应状态码是否为200
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
//如果为200表示请求成功,获取返回数据
String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8");
//打印数据长度
System.out.println(content);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//释放连接
if (response == null) {
try {
response.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
httpClient.close();
}
}
}
5.Jsoup
我们抓取到页面之后,还需要对页面进行解析。可以使用字符串处理工具解析页面,也可以使用正则表达式,但是这些方法都会带来很大的开发成本,所以我们需要使用一款专门解析html页面的技术。
5.1.jsoup介绍
jsoup 是一款Java 的HTML解析器,可直接解析某个URL地址、HTML文本内容。它提供了一套非常省力的API,可通过DOM,CSS以及类似于jQuery的操作方法来取出和操作数据。
jsoup的主要功能如下:
1.从一个URL,文件或字符串中解析HTML;
2.使用DOM或CSS选择器来查找、取出数据;
3.可操作HTML元素、属性、文本;
先加入Jsoup依赖:
<!--Jsoup-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jsoup</groupId>
<artifactId>jsoup</artifactId>
<version>1.10.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
<!--工具-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.6</version>
</dependency>
5.2.jsoup解析
5.2.1.解析url
Jsoup可以直接输入url,它会发起请求并获取数据,封装为Document对象
@Test
public void testJsoupUrl() throws Exception {
// 解析url地址
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new URL("http://www.itcast.cn/"), 1000);
//获取title的内容
Element title = document.getElementsByTag("title").first();
System.out.println(title.text());
}
PS:虽然使用Jsoup可以替代HttpClient直接发起请求解析数据,但是往往不会这样用,因为实际的开发过程中,需要使用到多线程,连接池,代理等等方式,而jsoup对这些的支持并不是很好,所以我们一般把jsoup仅仅作为Html解析工具使用
5.2.2.解析字符串
先准备以下html文件
<html>
<head>
<title>传智播客官网-一样的教育,不一样的品质</title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="city">
<h3 id="city_bj">北京中心</h3>
<fb:img src="/2018czgw/images/slogan.jpg" class="slogan"/>
<div class="city_in">
<div class="city_con" style="display: none;">
<ul>
<li id="test" class="class_a class_b">
<a href="http://www.itcast.cn" target="_blank">
<span class="s_name">北京</span>
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="http://sh.itcast.cn" target="_blank">
<span class="s_name">上海</span>
</a>
</li>
<li>
<a href="http://gz.itcast.cn" target="_blank">
<span abc="123" class="s_name">广州</span>
</a>
</li>
<ul>
<li>天津</li>
</ul>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
Jsoup可以直接输入字符串,并封装为Document对象
@Test
public void testJsoupString() throws Exception {
//读取文件获取
String html = FileUtils.readFileToString(new File("D:\\jsoup.html"), "UTF-8");
// 解析字符串
Document document = Jsoup.parse(html);
//获取title的内容
Element title = document.getElementsByTag("title").first();
System.out.println(title.text());
}
5.2.3.解析文件
Jsoup可以直接解析文件,并封装为Document对象
@Test
public void testJsoupHtml() throws Exception {
// 解析文件
Document document = Jsoup.parse(new File("D:\\jsoup.html"),"UTF-8");
//获取title的内容
Element title = document.getElementsByTag("title").first();
System.out.println(title.text());
}
5.2.4.使用dom方式遍历文档
元素获取
1.根据id查询元素getElementById
2.根据标签获取元素getElementsByTag
3.根据class获取元素getElementsByClass
4.根据属性获取元素getElementsByAttribute
//1. 根据id查询元素getElementById
Element element = document.getElementById("city_bj");
//2. 根据标签获取元素getElementsByTag
element = document.getElementsByTag("title").first();
//3. 根据class获取元素getElementsByClass
element = document.getElementsByClass("s_name").last();
//4. 根据属性获取元素getElementsByAttribute
element = document.getElementsByAttribute("abc").first();
element = document.getElementsByAttributeValue("class", "city_con").first();
元素中获取数据
1.从元素中获取id
2.从元素中获取className
3.从元素中获取属性的值attr
4.从元素中获取所有属性attributes
5.从元素中获取文本内容text
//获取元素
Element element = document.getElementById("test");
//1. 从元素中获取id
String str = element.id();
//2. 从元素中获取className
str = element.className();
//3. 从元素中获取属性的值attr
str = element.attr("id");
//4. 从元素中获取所有属性attributes
str = element.attributes().toString();
//5. 从元素中获取文本内容text
str = element.text();
5.2.5.使用选择器语法查找元素
jsoup elements对象支持类似于CSS (或jquery)的选择器语法,来实现非常强大和灵活的查找功能。这个select 方法在Document, Element,或Elements对象中都可以使用。且是上下文相关的,因此可实现指定元素的过滤,或者链式选择访问。
Select方法将返回一个Elements集合,并提供一组方法来抽取和处理结果。
5.2.6.Selector选择器概述
tagname: 通过标签查找元素,比如:span
#id: 通过ID查找元素,比如:# city_bj
.class: 通过class名称查找元素,比如:.class_a
[attribute]: 利用属性查找元素,比如:[abc]
[attr=value]: 利用属性值来查找元素,比如:[class=s_name]
//tagname: 通过标签查找元素,比如:span
Elements span = document.select("span");
for (Element element : span) {
System.out.println(element.text());
}
//#id: 通过ID查找元素,比如:#city_bjj
String str = document.select("#city_bj").text();
//.class: 通过class名称查找元素,比如:.class_a
str = document.select(".class_a").text();
//[attribute]: 利用属性查找元素,比如:[abc]
str = document.select("[abc]").text();
//[attr=value]: 利用属性值来查找元素,比如:[class=s_name]
str = document.select("[class=s_name]").text();
5.2.7.Selector选择器组合使用
el#id: 元素+ID,比如: h3#city_bj
el.class: 元素+class,比如: li.class_a
el[attr]: 元素+属性名,比如: span[abc]
任意组合: 比如:span[abc].s_name
ancestor child: 查找某个元素下子元素,比如:.city_con li 查找"city_con"下的所有li
parent > child: 查找某个父元素下的直接子元素,比如:
.city_con > ul > li 查找city_con第一级(直接子元素)的ul,再找所有ul下的第一级li
parent > *: 查找某个父元素下所有直接子元素
//el#id: 元素+ID,比如: h3#city_bj
String str = document.select("h3#city_bj").text();
//el.class: 元素+class,比如: li.class_a
str = document.select("li.class_a").text();
//el[attr]: 元素+属性名,比如: span[abc]
str = document.select("span[abc]").text();
//任意组合,比如:span[abc].s_name
str = document.select("span[abc].s_name").text();
//ancestor child: 查找某个元素下子元素,比如:.city_con li 查找"city_con"下的所有li
str = document.select(".city_con li").text();
//parent > child: 查找某个父元素下的直接子元素,
//比如:.city_con > ul > li 查找city_con第一级(直接子元素)的ul,再找所有ul下的第一级li
str = document.select(".city_con > ul > li").text();
//parent > * 查找某个父元素下所有直接子元素.city_con > *
str = document.select(".city_con > *").text();
6.爬虫案例
学习了HttpClient和Jsoup,就掌握了如何抓取数据和如何解析数据,接下来,我们做一个小练习,把京东的手机数据抓取下来。
主要目的是HttpClient和Jsoup的学习。
6.1.需求分析
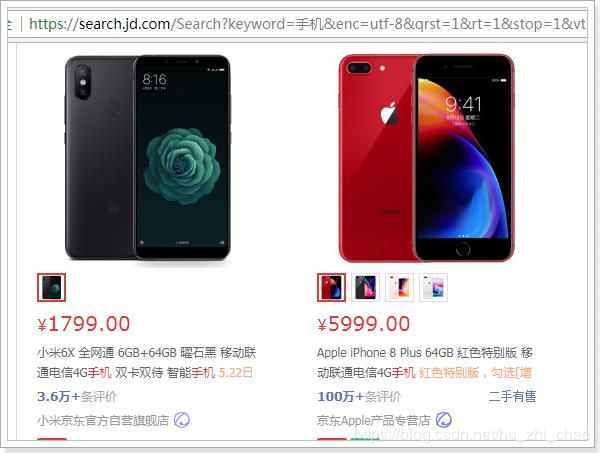
首先访问京东,搜索手机,分析页面,我们抓取以下商品数据:
商品图片、价格、标题、商品详情页
可能抓取不到,只是举个例子
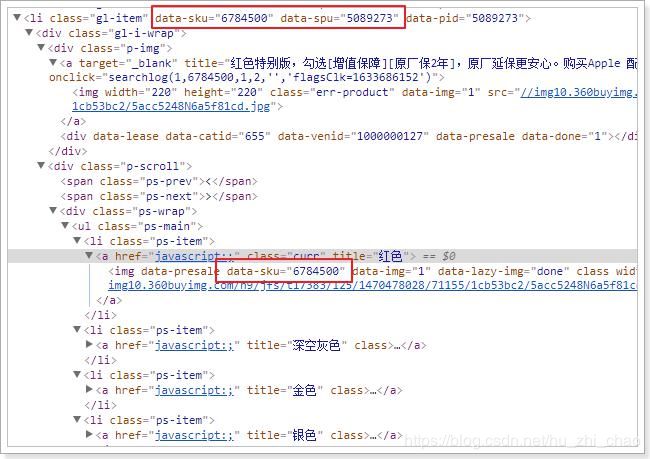
6.1.1.SPU和SKU
除了以上四个属性以外,我们发现上图中的苹果手机有四种产品,我们应该每一种都要抓取。那么这里就必须要了解spu和sku的概念
SPU = Standard Product Unit (标准产品单位)
SPU是商品信息聚合的最小单位,是一组可复用、易检索的标准化信息的集合,该集合描述了一个产品的特性。通俗点讲,属性值、特性相同的商品就可以称为一个SPU。
例如上图中的苹果手机就是SPU,包括红色、深灰色、金色、银色
SKU=stock keeping unit(库存量单位)
SKU即库存进出计量的单位, 可以是以件、盒、托盘等为单位。SKU是物理上不可分割的最小存货单元。在使用时要根据不同业态,不同管理模式来处理。在服装、鞋类商品中使用最多最普遍。
例如上图中的苹果手机有几个款式,红色苹果手机,就是一个sku
6.2.开发准备
6.2.1.数据库表分析
根据需求分析,我们创建的表如下:
CREATE TABLE `jd_item` (
`id` bigint(10) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '主键id',
`spu` bigint(15) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品集合id',
`sku` bigint(15) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品最小品类单元id',
`title` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品标题',
`price` bigint(10) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品价格',
`pic` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品图片',
`url` varchar(200) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '商品详情地址',
`created` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '创建时间',
`updated` datetime DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '更新时间',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `sku` (`sku`) USING BTREE
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=1 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='京东商品表';
6.2.2.添加依赖
使用Spring Boot+Spring Data JPA和定时任务进行开发,
需要创建Maven工程并添加以下依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.2.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>cn.itcast.crawler</groupId>
<artifactId>itcast-crawler-jd</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<!--SpringMVC-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--SpringData Jpa-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--MySQL连接包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- HttpClient -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--Jsoup-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jsoup</groupId>
<artifactId>jsoup</artifactId>
<version>1.10.3</version>
</dependency>
<!--工具包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
6.2.3.添加配置文件
加入application.properties配置文件
#DB Configuration:
spring.datasource.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/crawler
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
#JPA Configuration:
spring.jpa.database=MySQL
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
6.3.代码实现
6.3.1.编写pojo
根据数据库表,编写pojo
@Entity
@Table(name = "jd_item")
public class Item {
//主键
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
//标准产品单位(商品集合)
private Long spu;
//库存量单位(最小品类单元)
private Long sku;
//商品标题
private String title;
//商品价格
private Double price;
//商品图片
private String pic;
//商品详情地址
private String url;
//创建时间
private Date created;
//更新时间
private Date updated;
set/get
}
6.3.2.编写dao
public interface ItemDao extends JpaRepository<Item,Long> {
}
6.3.3.编写Service
ItemService接口
public interface ItemService {
//根据条件查询数据
public List<Item> findAll(Item item);
//保存数据
public void save(Item item);
}
ItemServiceImpl实现类
@Service
public class ItemServiceImpl implements ItemService {
@Autowired
private ItemDao itemDao;
@Override
public List<Item> findAll(Item item) {
Example example = Example.of(item);
List list = this.itemDao.findAll(example);
return list;
}
@Override
@Transactional
public void save(Item item) {
this.itemDao.save(item);
}
}
6.3.4.编写引导类
@SpringBootApplication
//设置开启定时任务
@EnableScheduling
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
6.3.5.封装HttpClient
我们需要经常使用HttpClient,所以需要进行封装,方便使用
@Component
public class HttpUtils {
private PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager cm;
public HttpUtils() {
this.cm = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager();
// 设置最大连接数
cm.setMaxTotal(200);
// 设置每个主机的并发数
cm.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(20);
}
//获取内容
public String getHtml(String url) {
// 获取HttpClient对象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom().setConnectionManager(cm).build();
// 声明httpGet请求对象
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(url);
// 设置请求参数RequestConfig
httpGet.setConfig(this.getConfig());
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 使用HttpClient发起请求,返回response
response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// 解析response返回数据
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
String html = "";
// 如果response。getEntity获取的结果是空,在执行EntityUtils.toString会报错
// 需要对Entity进行非空的判断
if (response.getEntity() != null) {
html = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8");
}
return html;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (response != null) {
// 关闭连接
response.close();
}
// 不能关闭,现在使用的是连接管理器
// httpClient.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
//获取图片
public String getImage(String url) {
// 获取HttpClient对象
CloseableHttpClient httpClient = HttpClients.custom().setConnectionManager(cm).build();
// 声明httpGet请求对象
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(url);
// 设置请求参数RequestConfig
httpGet.setConfig(this.getConfig());
CloseableHttpResponse response = null;
try {
// 使用HttpClient发起请求,返回response
response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
// 解析response下载图片
if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) {
// 获取文件类型
String extName = url.substring(url.lastIndexOf("."));
// 使用uuid生成图片名
String imageName = UUID.randomUUID().toString() + extName;
// 声明输出的文件
OutputStream outstream = new FileOutputStream(new File("D:/images/" + imageName));
// 使用响应体输出文件
response.getEntity().writeTo(outstream);
// 返回生成的图片名
return imageName;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (response != null) {
// 关闭连接
response.close();
}
// 不能关闭,现在使用的是连接管理器
// httpClient.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return null;
}
//获取请求参数对象
private RequestConfig getConfig() {
RequestConfig config = RequestConfig.custom().setConnectTimeout(1000)// 设置创建连接的超时时间
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(500) // 设置获取连接的超时时间
.setSocketTimeout(10000) // 设置连接的超时时间
.build();
return config;
}
}
6.3.6.实现数据抓取
使用定时任务,可以定时抓取最新的数据
@Component
public class ItemTask {
@Autowired
private HttpUtils httpUtils;
@Autowired
private ItemService itemService;
public static final ObjectMapper MAPPER = new ObjectMapper();
//设置定时任务执行完成后,再间隔100秒执行一次
@Scheduled(fixedDelay = 1000 * 100)
public void process() throws Exception {
//分析页面发现访问的地址,页码page从1开始,下一页oage加2
String url = "https://search.jd.com/Search?keyword=%E6%89%8B%E6%9C%BA&enc=utf-8&qrst=1&rt=1&stop=1&vt=2&cid2=653&cid3=655&s=5760&click=0&page=";
//遍历执行,获取所有的数据
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i = i + 2) {
//发起请求进行访问,获取页面数据,先访问第一页
String html = this.httpUtils.getHtml(url + i);
//解析页面数据,保存数据到数据库中
this.parseHtml(html);
}
System.out.println("执行完成");
}
//解析页面,并把数据保存到数据库中
private void parseHtml(String html) throws Exception {
//使用jsoup解析页面
Document document = Jsoup.parse(html);
//获取商品数据
Elements spus = document.select("div#J_goodsList > ul > li");
//遍历商品spu数据
for (Element spuEle : spus) {
//获取商品spu
Long spuId = Long.parseLong(spuEle.attr("data-spu"));
//获取商品sku数据
Elements skus = spuEle.select("li.ps-item img");
for (Element skuEle : skus) {
//获取商品sku
Long skuId = Long.parseLong(skuEle.attr("data-sku"));
//判断商品是否被抓取过,可以根据sku判断
Item param = new Item();
param.setSku(skuId);
List<Item> list = this.itemService.findAll(param);
//判断是否查询到结果
if (list.size() > 0) {
//如果有结果,表示商品已下载,进行下一次遍历
continue;
}
//保存商品数据,声明商品对象
Item item = new Item();
//商品spu
item.setSpu(spuId);
//商品sku
item.setSku(skuId);
//商品url地址
item.setUrl("https://item.jd.com/" + skuId + ".html");
//创建时间
item.setCreated(new Date());
//修改时间
item.setUpdated(item.getCreated());
//获取商品标题
String itemHtml = this.httpUtils.getHtml(item.getUrl());
String title = Jsoup.parse(itemHtml).select("div.sku-name").text();
item.setTitle(title);
//获取商品价格
String priceUrl = "https://p.3.cn/prices/mgets?skuIds=J_"+skuId;
String priceJson = this.httpUtils.getHtml(priceUrl);
//解析json数据获取商品价格
double price = MAPPER.readTree(priceJson).get(0).get("p").asDouble();
item.setPrice(price);
//获取图片地址
String pic = "https:" + skuEle.attr("data-lazy-img").replace("/n9/","/n1/");
System.out.println(pic);
//下载图片
String picName = this.httpUtils.getImage(pic);
item.setPic(picName);
//保存商品数据
this.itemService.save(item);
}
}
}
}