宋宝华: Linux实时补丁的原理和实践
第一章: 硬实时Linux(RT-Preempt Patch)在PC上的编译、使用和测试 第二章: 硬实时Linux(RT-Preempt Patch)的中断线程化
硬实时Linux(RT-Preempt Patch)在PC上的编译、使用和测试
Vanilla kernel的问题
Linux kernel在spinlock、irq上下文方面无法抢占,因此高优先级任务被唤醒到得以执行的时间并不能完全确定。同时,Linux kernel本身也不处理优先级反转。RT-Preempt Patch是在Linux社区kernel的基础上,加上相关的补丁,以使得Linux满足硬实时的需求。本文描述了该patch在PC上的实践。我们的 测试环境为Ubuntu 10.10,默认情况下使用Ubuntu 10.10自带的kernel:
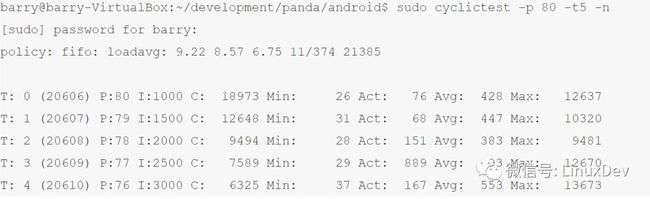
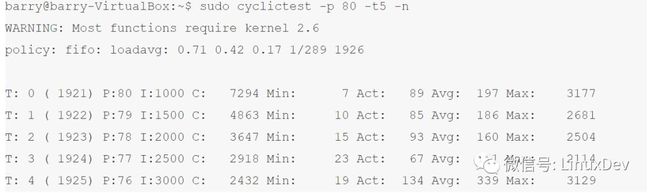
在Ubuntu 10.10,apt-get install rt-tests安装rt测试工具集,运行其中的cyclictest测试工具,默认创建5个SCHED_FIFO策略的realtime线程,优先级 76-80,运行周期是1000,1500,2000,2500,3000微秒:
由此可见在标准Linux内,rt线程投入运行的jitter非常不稳定,最小值在26-37微秒,平均值为68-889微秒,而最大值则分布在9481-13673微秒之间。
我们还是运行这个测试,但是在运行这个测试的过程中引入更多干扰,如mount /dev/sdb1 ~/development,则结果变为:
mount过程中引入的irq、softirq和spinlock导致最大jitter明显地加大甚至达到了331482us,充分显示出了标准Linux内核中RT线程投入运行时间的不可预期性(硬实时要求意味着可预期)。
如果我们编译一份kernel,选择的是“Voluntary Kernel Preemption (Desktop)“,这类似于2.4不支持kernel抢占的情况,我们运行同样的case,时间的不确定性大地几乎让我们无法接受:
RT-Preempt Patch使能
RT-Preempt Patch对Linux kernel的主要改造包括:
Making in-kernel locking-primitives (using spinlocks) preemptible though reimplementation with rtmutexes:
Critical sections protected by i.e. spinlock_t and rwlock_t are now preemptible. The creation of non-preemptible sections (in kernel) is still possible with raw_spinlock_t (same APIs like spinlock_t)
Implementing priority inheritance for in-kernel spinlocks and semaphores. For more information on priority inversion and priority inheritance please consult Introduction to Priority Inversion (http://www.embedded.com/electronics-blogs/beginner-s-corner/4023947/Introduction-to-Priority-Inversion)
Converting interrupt handlers into preemptible kernel threads: The RT-Preempt patch treats soft interrupt handlers in kernel thread context, which is represented by a task_struct like a common userspace process. However it is also possible to register an IRQ in kernel context.
Converting the old Linux timer API into separate infrastructures for high resolution kernel timers plus one for timeouts, leading to userspace POSIX timers with high resolution.
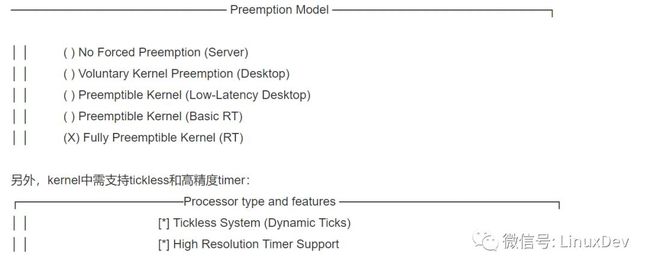
在本试验中,我们取的带RT- Preempt Patch的kernel tree是git://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/rt/linux-stable- rt.git,使用其v3.4-rt-rebase branch,编译kernel时选中了"Fully Preemptible Kernel"抢占模型:
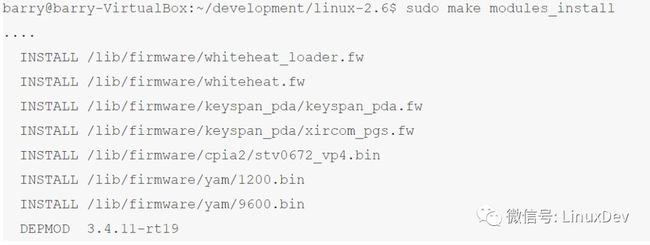
make modules_install、make install、mkintramfs后,我们得到一个可以在Ubuntu中启动的RT kernel。具体编译方法可详见http://www.linuxidc.com/Linux/2012-01/50749.htm,根据该文修改版本 号等信息即可,我们运行的命令包括:
安装模块
安装kernel
barry@barry-VirtualBox:~/development/linux-2.6$ sudo make install
sh /home/barry/development/linux-2.6/arch/x86/boot/install.sh 3.4.11-rt19 arch/x86/boot/bzImage \
System.map "/boot"
制作initrd
barry@barry-VirtualBox:~/development/linux-2.6$ sudo mkinitramfs 3.4.11-rt19 -o /boot/initrd.img-3.4.11-rt19
修改grub配置
在grub.conf中增加新的启动entry,仿照现有的menuentry,增加一个新的,把其中的相关版本号都变更为3.4.11-rt19,我们的修改如下:
menuentry 'Ubuntu, with Linux 3.4.11-rt19' --class ubuntu --class gnu-linux --class gnu --class os {
recordfail
insmod part_msdos
insmod ext2
set root='(hd0,msdos1)'
search --no-floppy --fs-uuid --set a0db5cf0-6ce3-404f-9808-88ce18f0177a
linux /boot/vmlinuz-3.4.11-rt19 root=UUID=a0db5cf0-6ce3-404f-9808-88ce18f0177a ro quiet splash
initrd /boot/initrd.img-3.4.11-rt19
}
开机时选择3.4.11-rt19启动:
RT-Preempt Patch试用
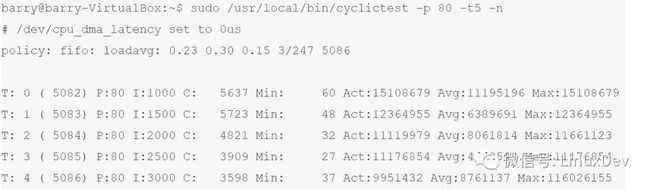
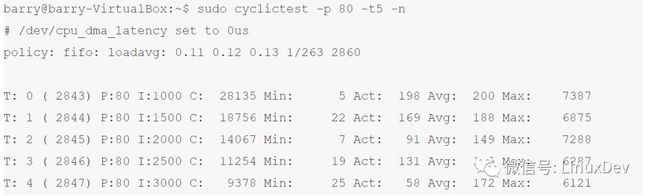
运行同样的测试cyclictest benchmark工具,结果迥异:
我们还是运行这个测试,但是在运行这个测试的过程中引入更多干扰,如mount /dev/sdb1 ~/development,则结果变为:
时间在可预期的范围内,没有出现标准kernel里面jitter达到331482的情况。需要说明的是,这个jitter大到超过了我们的预期,达到了10ms量级,相信是受到了我们的测试都是在Virtualbox虚拟机进行的影响。按照其他文档显示,这个jitter应该在数十us左右。
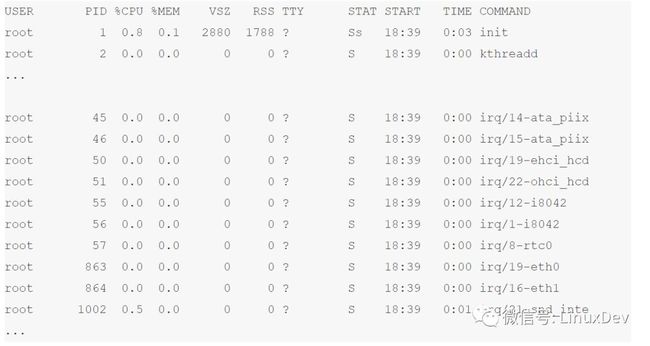
我们在这个kernel里面运行ps aux命令,可以看出线程化了的irq:
在其中编写一个RT 线程的应用程序,通常需要如下步骤:
Setting a real time scheduling policy and priority.
Locking memory so that page faults caused by virtual memory will not undermine deterministic behavior
Pre-faulting the stack, so that a future stack fault will not undermine deterministic behavior
例 子test_rt.c,其中的mlockall是为了防止进程的虚拟地址空间对应的物理页面被swap出去,而stack_prefault()则故意提 前导致stack往下增长8KB,因此其后的函数调用和局部变量的使用将不再导致栈增长(依赖于page fault和内存申请):
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define MY_PRIORITY (49) /* we use 49 as the PRREMPT_RT use 50
as the priority of kernel tasklets
and interrupt handler by default */
#define MAX_SAFE_STACK (8*1024) /* The maximum stack size which is
guaranteed safe to access without
faulting */
#define NSEC_PER_SEC (1000000000) /* The number of nsecs per sec. */
void stack_prefault(void) {
unsigned char dummy[MAX_SAFE_STACK];
memset(dummy, 0, MAX_SAFE_STACK);
return;
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
struct timespec t;
struct sched_param param;
int interval = 50000; /* 50us*/
/* Declare ourself as a real time task */
param.sched_priority = MY_PRIORITY;
if(sched_setscheduler(0, SCHED_FIFO, ¶m) == -1) {
perror("sched_setscheduler failed");
exit(-1);
}
/* Lock memory */
if(mlockall(MCL_CURRENT|MCL_FUTURE) == -1) {
perror("mlockall failed");
exit(-2);
}
/* Pre-fault our stack */
stack_prefault();
clock_gettime(CLOCK_MONOTONIC ,&t);
/* start after one second */
t.tv_sec++;
while(1) {
/* wait until next shot */
clock_nanosleep(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, TIMER_ABSTIME, &t, NULL);
/* do the stuff */
/* calculate next shot */
t.tv_nsec += interval;
while (t.tv_nsec >= NSEC_PER_SEC) {
t.tv_nsec -= NSEC_PER_SEC;
t.tv_sec++;
}
}
}
编译之:gcc -o test_rt test_rt.c -lrt。本节就到这里,后续我们会有一系列博文来描述RT-Preempt Patch对kernel的主要改动,以及其工作原理。
硬实时Linux(RT-Preempt Patch)的中断线程化
底半部:线程化IRQ
线程化中断的支持在2009年已经进入Linux官方内核,详见Thomas Gleixner的patch:
http://git.kernel.org/?p=linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux-2.6.git;a=commit;h=3aa551c9b4c40018f0e261a178e3d25478dc04a9
该patch提供一个能力,驱动可以通过
申请一个线程化的IRQ,kernel会为中断的底半部创建一个名字为irq/%d-%s的线程,%d对应着中断号。其中顶半部(硬中断)handler在做完必要的处理工作之后,会返回IRQ_WAKE_THREAD,之后kernel会唤醒irq/%d-%s线程,而该kernel线程会调用thread_fn函数,因此,该线程成为底半部。在后续维护的过程中,笔者曾参与进一步完善该功能的讨论,后续patch包括nested、oneshot等的支持,详见patch:
http://git.kernel.org/?p=linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux-2.6.git;a=commit;h=399b5da29b9f851eb7b96e2882097127f003e87c
http://git.kernel.org/?p=linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux-2.6.git;a=commit;h=70aedd24d20e75198f5a0b11750faabbb56924e2
http://git.kernel.org/?p=linux/kernel/git/torvalds/linux-2.6.git;a=commit;h=b25c340c195447afb1860da580fe2a85a6b652c5
该机制目前在kernel中使用已经十分广泛,可以认为是继softirq(含tasklet)和workqueue之后的又一大中断底半部方式。
顶半部:强制线程化
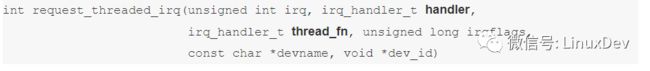
在使能Linux RT-Preempt后,默认情况下会强制透过request_irq()申请的IRQ的顶半部函数在线程中执行,我们都知道request_irq的原型为:
这意味着通过request_irq()申请的IRQ,在没有Rt-Preepmt的情况下,kernel并不会为其创建irq线程,因为它在最终调用request_threaded_irq()的时候传递的thread_fn为NULL。
如果使能了RT-Preempt Patch的情况下,其中的genirq-force-threading.patch会强制ARM使用threaded irq:
在RT-Preempt Patch中,会针对使能了IRQ_FORCED_THREADING的情况,对这一原先没有线程化IRQ的case进行强制线程化,代码见__setup_irq():
887 static int
888 __setup_irq(unsigned int irq, struct irq_desc *desc, struct irqaction *new)
889 {
890 ...
903
904 /*
905 * Check whether the interrupt nests into another interrupt
906 * thread.
907 */
908 nested = irq_settings_is_nested_thread(desc);
909 if (nested) {
910 ...
920 } else {
921 if (irq_settings_can_thread(desc))
922 irq_setup_forced_threading(new);
923 }
925 /*
926 * Create a handler thread when a thread function is supplied
927 * and the interrupt does not nest into another interrupt
928 * thread.
929 */
930 if (new->thread_fn && !nested) {
931 struct task_struct *t;
932
933 t = kthread_create(irq_thread, new, "irq/%d-%s", irq,
934 new->name);
935 ...
939 /*
940 * We keep the reference to the task struct even if
941 * the thread dies to avoid that the interrupt code
942 * references an already freed task_struct.
943 */
944 get_task_struct(t);
945 new->thread = t;
946 }
我们重点看一下其中的922行:
第878行和879行,强制将原先的handler复制给thread_fn,而又强制把原来的handler变更为irq_default_primary_handler(),而这个函数,其实神马都不做,只是直接返回IRQ_WAKE_THREAD:
第874的IRQF_ONESHOT就用到了我们前面说的oneshot功能。
所以,RT-Preempt实际上是把原先的顶半部底半部化了,而现在伪造了一个假的顶半部,它只是直接返回一个IRQ_WAKE_THREAD标记而已。
我们来看一下一个中断发生后,Linux RT-Preempt处理的全过程,首先是会跳到
arch/arm/kernel/entry-armv.S
arch/arm/include/asm/entry-macro-multi.S
中的汇编入口,再进入arm/kernel/irq.c下的asm_do_IRQ 、handle_IRQ,之后generic的handle_irq_event_percpu()被调用:
133 handle_irq_event_percpu(struct irq_desc *desc, struct irqaction *action)
134 {
135 irqreturn_t retval = IRQ_NONE;
136 unsigned int flags = 0, irq = desc->irq_data.irq;
137
138 do {
139 irqreturn_t res;
140
141 trace_irq_handler_entry(irq, action);
142 res = action->handler(irq, action->dev_id);
143 trace_irq_handler_exit(irq, action, res);
144
145 if (WARN_ONCE(!irqs_disabled(),"irq %u handler %pF enabled interrupts\n",
146 irq, action->handler))
147 local_irq_disable();
148
149 switch (res) {
150 case IRQ_WAKE_THREAD:
151 /*
152 * Catch drivers which return WAKE_THREAD but
153 * did not set up a thread function
154 */
155 if (unlikely(!action->thread_fn)) {
156 warn_no_thread(irq, action);
157 break;
158 }
159
160 irq_wake_thread(desc, action);
161
162 /* Fall through to add to randomness */
163 case IRQ_HANDLED:
164 flags |= action->flags;
165 break;
166
167 default:
我们关注其中的第142行,本质上是调用irq_default_primary_handler(),接到150行,由于 irq_default_primary_handler()返回了IRQ_WAKE_THREAD,因此,generic的中断处理流程会执行 irq_wake_thread(desc, action);去唤醒前面的irq/%d-%s线程,该线程的代码是
789 static int irq_thread(void *data)
790 {
791 static const struct sched_param param = {
792 .sched_priority = MAX_USER_RT_PRIO/2,
793 };
794 struct irqaction *action = data;
795 struct irq_desc *desc = irq_to_desc(action->irq);
796 irqreturn_t (*handler_fn)(struct irq_desc *desc,
797 struct irqaction *action);
798
799 if (force_irqthreads && test_bit(IRQTF_FORCED_THREAD,
800 &action->thread_flags))
801 handler_fn = irq_forced_thread_fn;
802 else
803 handler_fn = irq_thread_fn;
804
805 sched_setscheduler(current, SCHED_FIFO, ¶m);
806 current->irq_thread = 1;
807
808 while (!irq_wait_for_interrupt(action)) {
809 irqreturn_t action_ret;
810
811 irq_thread_check_affinity(desc, action);
812
813 action_ret = handler_fn(desc, action);
814 if (!noirqdebug)
815 note_interrupt(action->irq, desc, action_ret);
816
817 wake_threads_waitq(desc);
818 }
819
820 /*
821 * This is the regular exit path. __fr
其中的813行会调用最终的被赋值给thread_fn的原来的handler,这样原来的中断顶半部就整个在irq_thread里面执行了,实现了所谓的顶半部的线程化。
绕开顶半部线程化
当然,在使能了RT-Preempt的情况之下,我们仍然可以绕开顶半部线程化的过程,避免前面的强势变更,只需要申请中断的时候设置IRQ_NOTHREAD标志,如其中的patch:
Subject: arm: Mark pmu interupt IRQF_NO_THREAD
From: Thomas Gleixner
Date: Wed, 16 Mar 2011 14:45:31 +0100
PMU interrupt must not be threaded. Remove IRQF_DISABLED while at it
as we run all handlers with interrupts disabled anyway.
Signed-off-by: Thomas Gleixner
---
arch/arm/kernel/perf_event.c | 2 +-
1 file changed, 1 insertion(+), 1 deletion(-)
Index: linux-stable/arch/arm/kernel/perf_event.c
===================================================================
--- linux-stable.orig/arch/arm/kernel/perf_event.c
+++ linux-stable/arch/arm/kernel/perf_event.c
@@ -430,7 +430,7 @@ armpmu_reserve_hardware(struct arm_pmu *
}
err = request_irq(irq, handle_irq,
- IRQF_DISABLED | IRQF_NOBALANCING,
+ IRQF_NOBALANCING | IRQF_NO_THREAD,
"arm-pmu", armpmu);
if (err) {
r_err("unable to request IRQ%d for ARM PMU counters\n",
1
Linux进程调度微课
报名:《Linux任督二脉》之《进程调度》4节系列微课(5.22-25)