PCL经典代码赏析四:点云滤波
文章目录
- 更新:2019年8月
- 说明
- PCL 滤波介绍
- 直通滤波器对点云进行滤波处理
- VoxelGrid滤波器对点云进行下采样
- statisticalOutlierRemoval滤波器移除离群点
- 使用参数化模型投影点云
- 从一个点云中提取索引
- ConditionalRemoval 或 RadiusOutlinerRemoval 移除离群点
更新:2019年8月
为了促进同行业人员(特指 LiDAR 点云处理人员或相近行业)的技术交流,解决平时开发过程中遇到的技术性问题,博主建立一个QQ群,欢迎大家积极加入,共同引领点云行业的快速发展 ~
群名:LiDAR点云部落
群号:190162198
说明
- 以下均为 Being_young 前辈所写,现转载过来,再加上自己的理解,重新写了一遍,方便自己日后使用
- 博客地址:http://blog.csdn.net/u013019296/article/
PCL 滤波介绍
在获取点云数据时 ,由于设备精度,操作者经验环境因素带来的影响,以及电磁波的衍射特性,被测物体表面性质变化和数据拼接配准操作过程的影响,点云数据中讲不可避免的出现一些噪声。在点云处理流程中滤波处理作为预处理的第一步,对后续的影响比较大,只有在滤波预处理中将噪声点 ,离群点,孔洞,数据压缩等按照后续处理定制,才能够更好的进行配准,特征提取,曲面重建,可视化等后续应用处理,PCL中点云滤波模块提供了很多灵活实用的滤波处理算法,例如:双边滤波,高斯滤波,条件滤波,直通滤波,基于随机采样一致性滤波等。
- PCL中点云滤波的方案
- 点云数据密度不规则需要平滑
- 因为遮挡等问题造成离群点需要去除
- 大量数据需要下采样
- 噪声数据需要去除
- 对应的方案如下
- 按照给定的规则限制过滤去除点
- 通过常用滤波算法修改点的部分属性
- 对数据进行下采样
- 去除噪音
直通滤波器对点云进行滤波处理
最简单的例子:比如说高程筛选
#include VoxelGrid滤波器对点云进行下采样
使用体素化网格方法实现下采样,即减少点的数量 减少点云数据,并同时保存点云的形状特征,在提高配准,曲面重建,形状识别等算法速度中非常实用,PCL是实现的VoxelGrid类通过输入的点云数据创建一个三维体素栅格,容纳后每个体素内用体素中所有点的重心来近似显示体素中其他点,这样该体素内所有点都用一个重心点最终表示,对于所有体素处理后得到的过滤后的点云,这种方法比用体素中心(注意中心和重心)逼近的方法更慢,但是对于采样点对应曲面的表示更为准确。
#include statisticalOutlierRemoval滤波器移除离群点
**问题描述:**激光扫描通常会产生密度不均匀的点云数据集,另外测量中的误差也会产生稀疏的离群点,此时,估计局部点云特征(例如采样点处法向量或曲率变化率)时运算复杂,这会导致错误的数值,反过来就会导致点云配准等后期的处理失败。
**解决办法:**对每个点的邻域进行一个统计分析,并修剪掉一些不符合标准的点。具体方法为在输入数据中对点到临近点的距离分布的计算,对每一个点,计算它到所有临近点的平均距离(假设得到的结果是一个高斯分布,其形状是由均值和标准差决定),那么平均距离在标准范围之外的点,可以被定义为离群点并从数据中去除。
#include 使用参数化模型投影点云
如何将点投影到一个参数化模型上(平面或者球体等),参数化模型通过一组参数来设定,对于平面来说使用其等式形式。在PCL中有特定存储常见模型系数的数据结构
#include 实验结果可以看出投影前的Z轴都不为0 ,都是随机产生的值,投影之后,打印的结果表明,xy的值都没有改变,z都变为0
所以该投影滤波类就是输入点云和投影模型,输出为投影到模型上之后的点云。
从一个点云中提取索引
基于某一分割算法提取点云中的一个子集
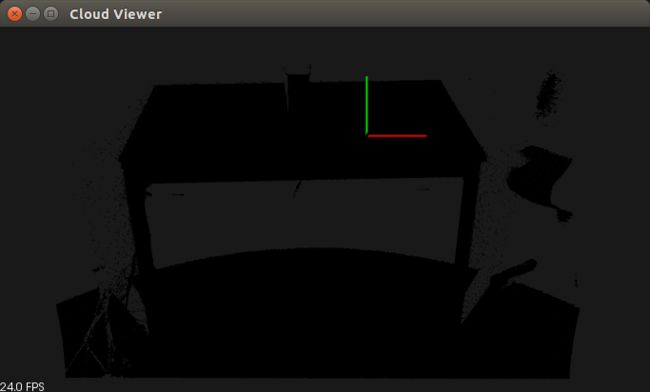
#include 图一 原始点云图像
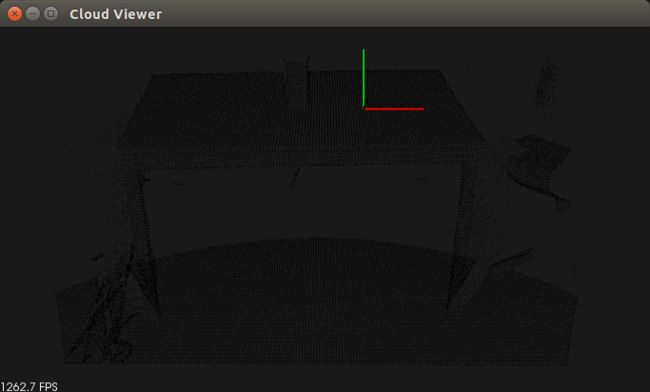
图二 点云下采样
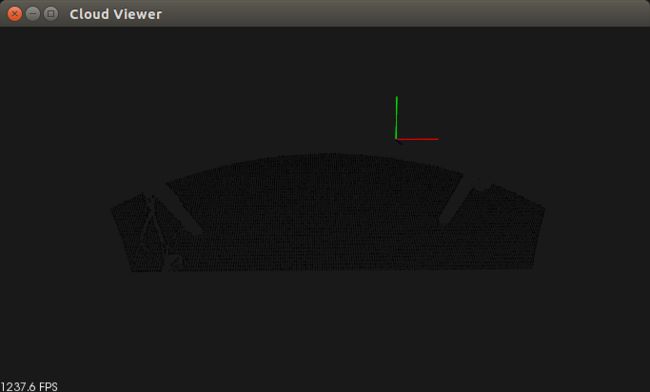
图三 分割得到平面模型1
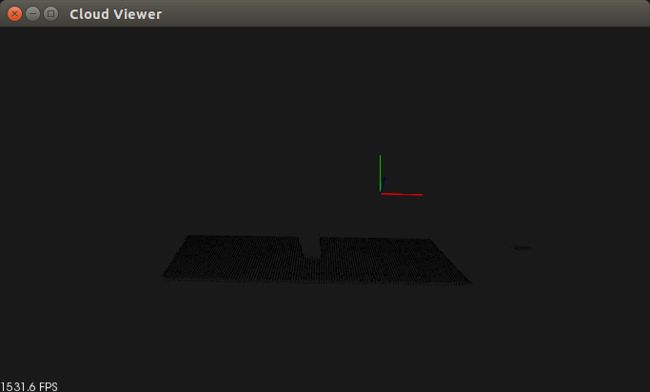
图四 分割得到平面模型2
ConditionalRemoval 或 RadiusOutlinerRemoval 移除离群点
- ConditionalRemoval 滤波器的理解
- 可以一次删除满足对输入的点云设定的一个或多个条件指标的所有的数据点
- 删除点云中不符合用户指定的一个或者多个条件的数据点
- ConditionalRemoval 滤波器的理解
- 可以一次删除满足对输入的点云设定的一个或多个条件指标的所有的数据点
- 删除点云中不符合用户指定的一个或者多个条件的数据点
#include