SpringMVC源码解析之RequestMappingHandlerMapping:初始化
SpringMVC源码解析之Servlet
SpringMVC源码解析之GenericServlet和HttpServlet
SpringMVC源码解析之DispatcherServlet:生命周期init()和destroy()
SpringMVC源码解析之DispatcherServlet:请求处理
一、HandlerMapping
1. 简介
前面的博客已经提到,HandlerMapping是SpringMVC的策略组件之一,称作处理器映射器,其作用是根据请求获取到对应的处理器。
HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception;
HandlerMapping接口只定义了一个方法,即根据请求获取到对应的处理器。
2. HandlerMapping的类继承关系
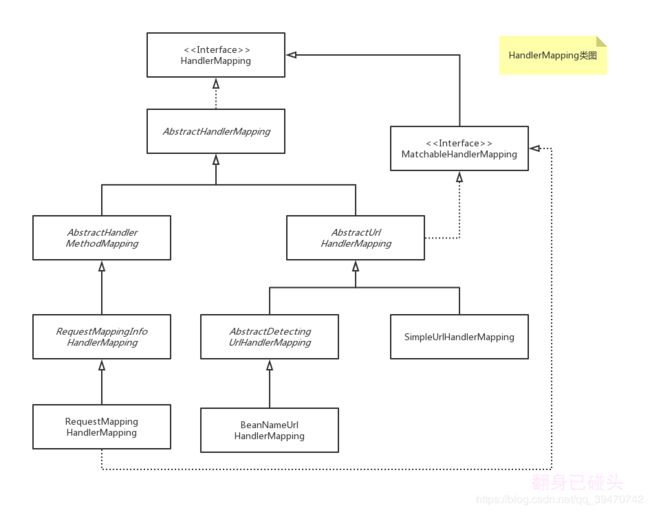
SpringMVC提供了不少的多层次的HandlerMapping的实现类,RequestMappingHandlerMapping根据注解RequestMapping进行处理器和请求的匹配,是我们日常开发中最常使用的方式,本文也只关注HandlerMapping到RequestMappingHandlerMapping的链路上的接口和类的实现。
3. RequestMappingHandlerMapping类图
二、initApplicationContext方法的解析
AbstractHandlerMapping继承了WebApplicationObjectSupport接口,通过initApplicationContext方法进行上下文的初始化。
1. 介绍
protected void initApplicationContext() throws BeansException {
//空的模板方法,可以对interceptors进行管理和操作
extendInterceptors(this.interceptors);
//侦测容器中的MappedInterceptor
detectMappedInterceptors(this.adaptedInterceptors);
initInterceptors();
}
initApplicationContext方法子这里的主要作用是初始化拦截器,在AbstractHandlerMapping中有两个与拦截器相关的属性,分别是:
interceptors:
SpringMVC中配置的拦截器集合,可以在注册HandlerMapping时通过属性进行设置,也可以在子类中通过重写模板方法extendInterceptors对interceptors进行
adaptedInterceptors:
(1)在detectMappedInterceptors方法中将Spring容器中的MappedInterceptor类型的bean对象加入搭配adaptedInterceptors
(2)在initInterceptors方法中将interceptors中的对象加入到adaptedInterceptors。(对于HandlerInterceptor类型的Interceptor直接加入,WebRequestInterceptor类型的封装成WebaRequestHandlerInterceptorAdapter加入,其它类型抛出异常)
adaptedInterceptors中的Interceptor是HandlerInterceptor类型,其子类MappedInterceptor类型的拦截器只对匹配的url的请求有效,其它类型的对所有请求有效。在SpringMVC4中,将MappedInterceptor保存在mappedInterceptors中,其它类型的保存在adaptedInterceptors中,SpringMVC5中还依旧保留着getMappedInterceptors等一些相关的方法。
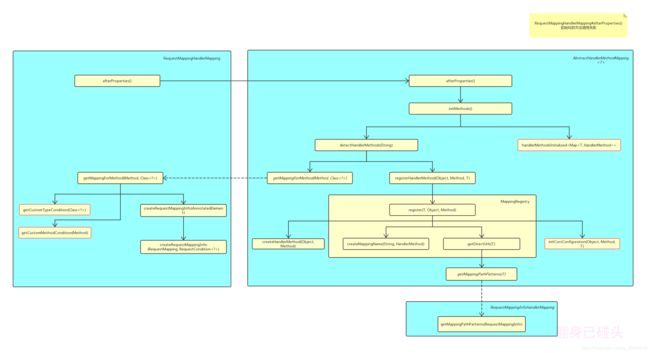
initApplicationContext方法的调用链如下图所示
2.AbstractHandlerMapping#extendInterceptors(List
protected void extendInterceptors(List该方法是一个空的模板方法,子类可以重写该方法以实现对interceptors属性的修改(包括添加和删除)。
在SpringMVC中,没有子类对该方法进行了重写。
3.AbstractHandlerMapping#detectMappedInterceptors(List)
protected void detectMappedInterceptors(List mappedInterceptors) {
mappedInterceptors.addAll(
BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(
obtainApplicationContext(), MappedInterceptor.class, true, false).values());
}
该方法用于检测Spring容器中的MappedInterceptor类型的bean并加入到集合中。
4. AbstractHandlerMapping#initInterceptors()
protected void initInterceptors() {
if (!this.interceptors.isEmpty()) {
for (int i = 0; i < this.interceptors.size(); i++) {
Object interceptor = this.interceptors.get(i);
if (interceptor == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Entry number " + i + " in interceptors array is null");
}
this.adaptedInterceptors.add(adaptInterceptor(interceptor));
}
}
}
将interceptors中的对象加入中adaptedInterceptors中。
5. AbstractHandlerMapping#adaptInterceptor(Object)
protected HandlerInterceptor adaptInterceptor(Object interceptor) {
//HandlerInterceptor类型不处理
if (interceptor instanceof HandlerInterceptor) {
return (HandlerInterceptor) interceptor;
}
//WebRequestInterceptor类型封装成适配器WebRequestHandlerInterceptorAdapater
else if (interceptor instanceof WebRequestInterceptor) {
return new WebRequestHandlerInterceptorAdapter((WebRequestInterceptor) interceptor);
}
//其它类型抛出异常
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Interceptor type not supported: " + interceptor.getClass().getName());
}
}
该方法将对象封装成HandlerInterceptor类型。
三、afterProperties的解析
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping实现了InitializaingBean接口,通过afterProperties方法进行初始化。
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping是一个泛型抽象类,从类名上可以看出其是对方法类型的处理器的抽象基本,泛型T可以简单理解成匹配条件的封装类,用来表示处理器使用的请求类型。
1. AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
/**
* Detects handler methods at initialization.
*/
//初始化,检测可以作为处理器的方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
initHandlerMethods();
}
1.1 initHandlerMethod
//扫描容器里的beans,检测并注册处理器方法
protected void initHandlerMethods() {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext());
}
//获取容器内的bean集合,detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts是否需要检查祖先容器,默认false
String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ?
BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(obtainApplicationContext(), Object.class) :
obtainApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class));
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (!beanName.startsWith(SCOPED_TARGET_NAME_PREFIX)) {
Class beanType = null;
try {
beanType = obtainApplicationContext().getType(beanName);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// An unresolvable bean type, probably from a lazy bean - let's ignore it.
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve target class for bean with name '" + beanName + "'", ex);
}
}
//抽象方法isHandler方法判断是否匹配
if (beanType != null && isHandler(beanType)) {
//从bean中检测处理器方法
detectHandlerMethods(beanName);
}
}
}
//空的模板方法,进行HandlerMethod的初始化
handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods());
}
该方法用于检测获取容器中的处理器并进行初始化。
(1)获取容器中的bean集合
(2)遍历bean集合,判断bean的类型是否匹配。如果匹配,从bean中检测匹配的方法作为处理器
(3)对处理器进行初始化
1.2 detectHandlerMethods
//找到handler中的方法作为处理器
protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) {
//确定类型
Class handlerType = (handler instanceof String ?
obtainApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass());
if (handlerType != null) {
//返回user-defined的类型,主要是从代理类型到实际类型
final Class userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType);
//找到类中方法和匹配条件的映射关系
Map methods = MethodIntrospector.selectMethods(userType,
(MethodIntrospector.MetadataLookup) method -> {
try {
//抽象方法getMappingForMethod
return getMappingForMethod(method, userType);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid mapping on handler class [" +
userType.getName() + "]: " + method, ex);
}
});
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug(methods.size() + " request handler methods found on " + userType + ": " + methods);
}
for (Map.Entry entry : methods.entrySet()) {
//获取在AOP中对应的方法,方法本身或对应的在接口上的或代理类上的方法
Method invocableMethod = AopUtils.selectInvocableMethod(entry.getKey(), userType);
T mapping = entry.getValue();
//注册HandlerMethod
registerHandlerMethod(handler, invocableMethod, mapping);
}
}
}
detectHandlerMethods的作用是找到handler对象中的方法作为处理器。
(1)找到类中可以作为处理器的方法并获取匹配条件T组成映射集Map
(2)遍历映射集,将方法和匹配条件T进行注册。
1.3 registerHandlerMethod
//对于HanlderMethod的管理由MappingRegistry负责
protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) {
this.mappingRegistry.register(mapping, handler, method);
}
1.4 MappingRegistry
MappingRegistry是AbstractHandlerMapping的内部类,负责对匹配条件集T进行注册及管理,内部维护着一系列的映射集map和一个读写锁。
//匹配条件T和MappingRegistration的映射关系
private final Map> registry = new HashMap<>();
//匹配条件T与执行器HanlderMethod的映射关系
private final Map mappingLookup = new LinkedHashMap<>();
//url与匹配条件集合的映射关系,一个url可以对应多个匹配条件
private final MultiValueMap urlLookup = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
//name与执行器集合的映射关系,一个name可以对应多个执行器,name由HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy确定,一般由类名和方法名组成
private final Map> nameLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//执行器HandlerMethod与跨域配置CorsConfiguration的映射关系
private final Map corsLookup = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
//读写锁
private final ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
对于Registration,同样也是AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的一个内部类,由匹配条件T及名称,处理器和匹配的url而成:
//匹配条件
private final T mapping;
//处理器
private final HandlerMethod handlerMethod;
//url集合
private final List directUrls;
//名称
@Nullable
private final String mappingName;
MappingRegistry的核心方法就是注册方法regsiter。
//MappingRegistry#registry
public void register(T mapping, Object handler, Method method) {
//读写锁加写锁
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().lock();
try {
//新建HandlerMethod对象
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method);
//校验唯一性,一个mapping最多只能对应一个HandlerMethod
assertUniqueMethodMapping(handlerMethod, mapping);
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Mapped \"" + mapping + "\" onto " + handlerMethod);
}
//加入mappingLookup
this.mappingLookup.put(mapping, handlerMethod);
//加入urlLookup
List directUrls = getDirectUrls(mapping);
for (String url : directUrls) {
this.urlLookup.add(url, mapping);
}
//加入nameLookup
String name = null;
if (getNamingStrategy() != null) {
name = getNamingStrategy().getName(handlerMethod, mapping);
addMappingName(name, handlerMethod);
}
//加入corsLookup
CorsConfiguration corsConfig = initCorsConfiguration(handler, method, mapping);
if (corsConfig != null) {
this.corsLookup.put(handlerMethod, corsConfig);
}
//加入registry
this.registry.put(mapping, new MappingRegistration<>(mapping, handlerMethod, directUrls, name));
}
finally {
this.readWriteLock.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
对于匹配名称,根据命名策略HandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy
对于url集,在getDirectUrls方法通过调用抽象方法getMappingPathPatterns获得。
private List getDirectUrls(T mapping) {
List urls = new ArrayList<>(1);
for (String path : getMappingPathPatterns(mapping)) {
if (!getPathMatcher().isPattern(path)) {
urls.add(path);
}
}
return urls;
}
2. RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping是AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
2.1 namingStrategy
protected RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping() {
setHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy(new RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy());
}
可以看到,默认的命名策略是RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy,其命名逻辑如下。
//RequestMappingInfoHandlerMethodMappingNamingStrategy#getName
@Override
public String getName(HandlerMethod handlerMethod, RequestMappingInfo mapping) {
//如果已经有name,直接使用
if (mapping.getName() != null) {
return mapping.getName();
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String simpleTypeName = handlerMethod.getBeanType().getSimpleName();
for (int i = 0 ; i < simpleTypeName.length(); i++) {
if (Character.isUpperCase(simpleTypeName.charAt(i))) {
sb.append(simpleTypeName.charAt(i));
}
}
sb.append(SEPARATOR).append(handlerMethod.getMethod().getName());
return sb.toString();
}
首选使用匹配条件的名称,否则命名方式为类名中的大写字母 + # + 方法名。
2.2 getMatchingMapping
protected RequestMappingInfo getMatchingMapping(RequestMappingInfo info, HttpServletRequest request) {
return info.getMatchingCondition(request);
}
匹配的url通过匹配通过RequestMappingInfo获得。
3. RequestMappingInfo
RequestMappingInfo是RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping及其子类RequestMappingHandlerMapping的泛型类,用来匹配http请求。
//省略方法
public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition\ {
@Nullable
//名称
private final String name;
//请求pattern,用来匹配url
private final PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition;
//请求方法,如GET|POST等等
private final RequestMethodsRequestCondition methodsCondition;
//请求参数,必须包含特定参数才能匹配
private final ParamsRequestCondition paramsCondition;
//请求头,必须包含特定值才能匹配
private final HeadersRequestCondition headersCondition;
//consumes,请求的content-type
private final ConsumesRequestCondition consumesCondition;
//produces,响应的content-type
private final ProducesRequestCondition producesCondition;
//自定义的条件
private final RequestConditionHolder customConditionHolder;
}
一般在日常开发中,RequestMappingInfo与注解RequestMapping中的属性一一对应,具体如RequestMappingHandlerMapping#createRequestMappingInfo(RequestMapping, RequestCondition)所示
protected RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(
RequestMapping requestMapping, @Nullable RequestCondition customCondition) {
RequestMappingInfo.Builder builder = RequestMappingInfo
.paths(resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(requestMapping.path()))
.methods(requestMapping.method())
.params(requestMapping.params())
.headers(requestMapping.headers())
.consumes(requestMapping.consumes())
.produces(requestMapping.produces())
.mappingName(requestMapping.name());
if (customCondition != null) {
builder.customCondition(customCondition);
}
return builder.options(this.config).build();
}
4. RequestMappingHandlerMapping
RequestMappingHandlerMapping是RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping的子类,同样的将RequestMappingInfo作为泛型类,并且RequestMappingInfo对象基于注解RequestMapping生成。
1. afterProperties
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
this.config = new RequestMappingInfo.BuilderConfiguration();
this.config.setUrlPathHelper(getUrlPathHelper());
this.config.setPathMatcher(getPathMatcher());
this.config.setSuffixPatternMatch(this.useSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setTrailingSlashMatch(this.useTrailingSlashMatch);
this.config.setRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch(this.useRegisteredSuffixPatternMatch);
this.config.setContentNegotiationManager(getContentNegotiationManager());
super.afterPropertiesSet();
}
RequestMappingHandlerMapping重写了afterProperties方法
(1)config属性的初始化
config属性用于基于RequestMapping注解生成RequestMappingInfo
(2)调用父类的afterProperties方法
即AbstractHandlerMethodMapping类的afterProperties方法
2. getMappingForMethod
protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class handlerType) {
//基于方法生成匹配条件RequestMappingInfo
RequestMappingInfo info = createRequestMappingInfo(method);
if (info != null) {
//基于类生成匹配条件RequestMappingInfo
RequestMappingInfo typeInfo = createRequestMappingInfo(handlerType);
if (typeInfo != null) {
//方法和类上的条件组合
info = typeInfo.combine(info);
}
}
return info;
}
根据方法和类调用createRequestMappingInfo方法生成RequestMappingInfo对象并组合返回。
对于两个RequestMappingInfo对象的组合,不同的属性的组合方式不同,可能是覆盖(如consumes, produces)、并集(如params, headers, methods)、字符串相加(如pattern),当然也可以自定义实现组合逻辑。
3. createRequestMappingInfo
private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(AnnotatedElement element) {
//获取注解
RequestMapping requestMapping = AnnotatedElementUtils.findMergedAnnotation(element, RequestMapping.class);
//获取condition,默认返回null
RequestCondition condition = (element instanceof Class ?
getCustomTypeCondition((Class) element) : getCustomMethodCondition((Method) element));、
//根据注解生成RequestMappingInfo对象
return (requestMapping != null ? createRequestMappingInfo(requestMapping, condition) : null);
}