本节讲点:
NIO引入:分析普通Socket通信中存在的IO问题--阻塞通信,并分析传统的线程池的优缺点,进而引入NIO解决方案
NIO核心框架:讲解NIO的4个核心概念所对应的框架包,包括缓存Buffer、字符集Charset、通道Channel及选择器Selector
缓存Buffer:是包含数据且用于读写的线性表结构。
字符集Charset:提供Unicode字符串映射到字节序列及逆映射操作
通道Channel:包含Socket、File和Pipe3种管道,双向的
选择器Selector:将多元异步I/O操作集中到一个或多个线程中
NIO通道编程
文件通道FileChannel:用于实现对文件的读写、锁定和映射
Socket通道SocketChannel:实现基于Socket的通道
ServerSocket通道ServerSocketChannel:基于SeverSocket通道
数据报通道DatagramChannel:实现基于DatagramSocket的通道
NIO引入
基于Socket通信存在的问题 -- I/O阻塞通信
阻塞监听客户端输入。BufferedReader类的readLine()方法阻塞。
阻塞监听客户端连接。accept()方法的调用造成阻塞
读取阻塞。产生大量的String垃圾BufferedReader创建了缓存区从客户端套接字读入数据,但是同样创建了一些字符串存储这些数据。
传统解决方法 --- 使用线程池
面对大量用户请求时,需要使用大量的线程,这一般是实现一个线程池来处理请求
线程池是服务器可以处理多个连接,但是它们同样引发了许多问题。每个线程都拥有自己的栈空间并且占用一些CPU时间,耗费很大。
最新的解决方案 --- NIO非阻塞通信
NIO的非阻塞I/O机制是围绕选择器和通道构建的。Channel类表示服务器和客户端之间的一种通信机制。与反应器模式一致,Selector是Channel的多路复用器。
在NIO解决方案中的缓存区、Selector、Channel等概念,
缓存区:表示数据存放的容器,提供可读写的数据缓存区
字符集:用来对缓存区数据进行解码和编码,在字节和Unicode字符之间
通道:用来接收或发送数据,提供文件、套接字等的连接
选择器:它们与可选择通道一起定义了多路、无阻塞的I/O设施
NIO框架位于Java.nio包中,它为每个概念都提供了核心的支撑类
缓存区Buffer的4个基本属性
capacity:容量,一般在Buffer被创建时指定。int capacity();//返回此缓存区容量
limit:限制。在Buffer上进行的操作不能越过这个下标。当写数据到Buffer中时,limit一般和capacity相等,当读数据时,limit代表Buffer中有效数据的长度,取得和修改限制的方法如下:
int limit();//返回此缓存区的限制
Buffer limit(int newLimit);//设置此缓存区的限制
position:读写操作当前下标。当使用Buffer的相对位置进行读写操作时,读写会从这个下标进行,并完成操作后,Buffer会更显下标值,
int position();//返回此缓存区的位置
Buffer position(int newPosition);//设置此缓存区的位置
mark:一个临时存放的位置下标
字符集Charset -- 编码与解码
通过构造java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder和java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder将字符序列CharBuffer转换成ByteBuffer和逆转换
从CharBuffer到ByteBuffer的编码转换
Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
CharsetEncoder encoder = charset.newEncoder();
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = encoder.encode(charBuffer);
从ByteBuffer到CharBuffer的解码转换
Charset charset = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
CharsetDecoder decoder = charset.newDecoder();
CharBuffer charBuffer = decoder.decode(byteBuffer);
通道Channel
NIO中提供了Channel通道类来读写Buffer。Channel是一个连接,可用于接收和发送数据。因为Channel连接的是底层的物理设备,它可以直接支持设备的读写,或者文件锁。
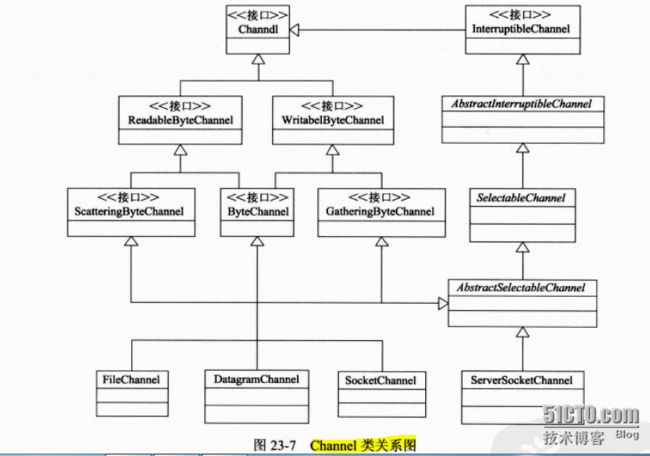
最下面的4个类为具体实现类。共包括7个接口类、3个抽象类和4个实现类
Channel是最顶层的接口。
ReadableByteChannel和WritableByteChannel分别提供对通道读取和写入Byte数据的功能
ByteChannel用来将读取和写入的功能合并
ScatteringByteChannel和GatheringByteChannel分别提供了批量读取和写入ByteBuffer数组的能力
InterruptibleChannel提供了多线程异步关闭的能力
7个接口类的详细方法如下:
Channel代表一个可以进行IO操作的通道。定义了一下方法
boolean isOpen();//判断此通道是否处于打开状态 void close();//关闭这个Channel,相关资源被释放
ReadableByteChannel和WritableByteChannel分别定义了一个读取和写入byte数据的Channel接口。分别定义了read()和write()方法。
int read(ByteBuffer dst);//将字节序列从此通道中读入到给定的缓存区 int write(ByteBuffer src);//将字节序列从给定的缓存区写入此通道
ByteChannel没有定义新的方法,它的作用只是把ReadableByteChannel和WritableByteChannel合并在一起
ScatteringByteChannel可以一次将数据从通道读入多个ByteBuffer中。而GatheringByteBufferChannel可以一次将多个ByteBuffer中的数据写入通道。提供的方法如下
long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts);//将字节序列从此通道中读入给定的缓存区 long read(ByteBuffer[],int offset,int length);//讲字节序列从此通道中读入给定的缓存区,位置从offset开始到length long write(ByteBuffer[] src);//将字节序列从给定的缓存区写入此通道 long write(ByteBuffer[] src,int offset,int length);//将字节序列从给定的缓存区写入此通道,位置从offset开始到length
InterruptibleChannel用来提供一个可以被异步关闭的Channel,它覆盖了Channel接口的关闭方法close()。
选择器Selector
Selector是非阻塞I/O的核心,可以同时监控多个SelectableChannel的I/O状况,对每一个监听到的事件都产生一个SelectionKey对象。使用Selector为SelectableChannel所用,需要经历如下3个步骤
(1)创建选择器Selector。
Selector类提供了静态方法,用于创建新的一个Selector实例。
static Selector open();
/**实例如下*/
try{
//创建一个Selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
}catch(IOException e){}
(2)注册到SelectableChannel
SelectableChannel在打开后,可以使用register()将它注册到特定的选择器,实现通道与选择器的事件绑定。
/**注册到SelectableChannel示例
* 必须使用configureBlocking(false)将通道设置为非阻塞
* 才可以向Selector注册SelectableChannel对象
*/
try{
//创建一个Selector
Selector selector = Selector.open();
//注册到Selector
SelectableChannel socket = SocketChannle.open();
socket.configureBlocking(false);//设置为非阻塞模式
socket.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}catch(IOException e){
}
(3)处理监听事件对象SelectionKey
static int OP_ACCEPT;//用于套接字接受操作的操作集位 static int OP_CONNECT;//用于套接字连接操作的操作集位 static int OP_READ;//用于读取操作的操作集位 static int OP_WRITE;//用于写入操作的操作集位
注册了事件类型以后,就可以使用Selector的select()监听该事件
int select();//监控所有注册的channel int select(long timeout);//可以设置超时的select()操作 int selectNow();//进行一个立即返回的select()操作 Selector wakeup();//使一个还未返回的selecor()操作立即返回
一旦有该事件触发,就可以使用Selecor的selectedKeys()方法返回所有该事件的列表。可以循环处理该事件列表,在处理前删除当前事件,防止重复处理。
/**监听事件处理过程*/
while(true){
//监听事件
selector.select();
//事件来源列表
Iterator it = selecotr.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
SelectorKey key = it.next();
//删除当前事件
it.remove();
//判断事件类型
if(key.isConnectable()){
//连接事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
//注册新的事件
channel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else if(key.isReadable){
//读取数据事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channle();
//注册新的事件
channel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
}else if(key.isWritable){
//写入数据事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channle();
//注册新的事件
channel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
}
}
NIO通道编程详解
文件通道FileChannel:用于对文件的读取、写入、锁定和映射
Socket通道SocketChannel:实现基于Socket的通道
ServerSocket通道ServerSocketChannel:实现基于ServerSocket的通道
数据报通道DatagramChannel:实现基于DatagramSocket的通道
1、文件通道FileChannel
在Channel使用中,文件通道FileChannel是最具有代表性的。FileChannel实现了类似输入输出流的功能,用于读取、写入、锁定和映射文件。
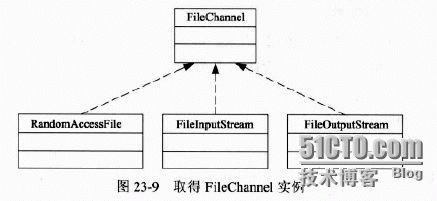
(1)创建FileChannel对象
FileChannel并没有向我们提供打开文件的方法,我们可以通过调用RandomAccessFile、fileInputStream和FileOutputStream类实例的getChannel(0方法获取其实例,如图示
给出示例演示3中获取FileChannel对象的方法,注意在打开文件后要关闭FileChannel和来源文件对象
package org.test.nio;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.RandomAccessFile;
import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class TestFileChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO 获取FileChannel实例
//1、根据RandomAccessFile获得
try {
//RandomAccessFile打开文件rw适用于读写FileChannel
RandomAccessFile randomFile = new RandomAccessFile("D:\\DownloadFile\\test.txt", "rw");
FileChannel channel = randomFile.getChannel();
channel.close();
randomFile.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
//2、根据FileInputStream获取
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\DownloadFile\\test.txt");
FileChannel channel = fis.getChannel();
channel.close();
fis.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
//3、根据FileOutputStream获取
try {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(":\\DownloadFile\\test.txt");
FileChannel channel = fos.getChannel();
channel.close();
fos.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
(2)从FileChannel中读取数据
FileChannel提供了4个方法读取数据
a、读入缓存区对象 abstract int read(ByteBuffer dst);
b、读入缓存区数组 long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts);
c、读入缓存区数据 long read(ByteBuffer[] dsts,int offset,int length);
d、从给定位置缓存区数组 abstract int read(ByteBuffer dst,long postion);//返回当前文件的位置,额可以通过size()返回文件的大小。
//读取数据 ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(10); channel.read(byteBuffer); System.out.println(new String(byteBuffer.array()));
(3)向FileChannel写入数据
FileChannel提供了4个方法写入数据
a、写入缓存区对象 abstract int write(ByteBuffer dst);
b、写入缓存区数组 long write(ByteBuffer[] dsts);
c、写入缓存区数据 long write(ByteBuffer[] dsts,int offset,int length);
d、将缓存区数据写入通道中的指定位置 abstract int write(ByteBuffer dst,long postion);//返回当前文件的位置,额可以通过size()返回文件的大小。执行写入操作后,使用force(true)函数强制将所有对此通道的文件更新写入包含该文件中,防止缓存。
//写入数据
ByteBuffer byteBuffer = ByteBuffer.wrap("我是写入的内容".getBytes());
channel.write(byteBuffer);
(4)使用文件锁
FileChannel提供了两种加锁机制,分别对应lock()和tryLock(),两者区别在于,lock是同步的,直至成功才返回,tryLock是异步的,无论成不成功都立即返回。
(5)使用内存映射
MappedByteBuffer是通过FileChannel创建的文件到内存的映射。MappedByteBuffer是一个直接缓存区。
try {
File file = new File("D:\\DownloadFile\\test1.txt");
if(!file.exists()){
if(file.createNewFile()){
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
}
}
//使用内存映射复制文件
FileChannel channel = new FileInputStream("D:\\DownloadFile\\test.txt").getChannel();
FileChannel channel2 = new FileOutputStream(file).getChannel();
//映射第一个文件到内存
MappedByteBuffer buffer = channel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, channel.size());
//写入到第二个文件
channel2.write(buffer);
channel.close();
channel2.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
2、Socket通道SocketChannel
为了实现基础的非阻塞套接字读写操作,我们需要处理两个类,InetSocketAddress类,它指定连接到哪里,以及SocketChannel类,它执行实际的读写操作。
InetSocketAddress类与InetAddress类相似,用于创建指向某一个主机和端口的地址对象。
InetSocketAddress(InetAddress addr,int port);//根据IP地址和端口号创建 InetSocketAddress(int port);//IP地址为通配符地址,端口号指定 InetSocketAddress(String hostname,int port);//根据主机名和端口号指定
创建的InetSocketAddress对象可以通过以下方法取得其中的属性,并可转化为InetAddress
String getHostName();// int getPort();// InetAddress getAddress();//
套接字类SocketChannel类似于Socket,可以用于创建一个套接字对象,不同的是,它具有非阻塞的功能。与Socket的使用过程很相似。Socket具体使用方法,请见http://aku28907.blog.51cto.com/5668513/1775429
Socket使用工作过程:
(1)创建一个SocketChannel对象:SocketChannel socket = SocketChannel.open();
(2)设置为非阻塞模式:socket.configureBlocking(false);
(3)注册到Selector:socket.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
(4)开始连接到远程地址:InetSocketAddress ip = new InetSocketAddress("localhost",12345);socket.connect(ip);
(5)开始处理读写事件
在使用selector的select()开始监听后,第一个监听到的事件是连接事件。
连接事件:在新客户端连接后,必须使用finishConnect()显示地完成连接,然后将该客户端注册为读或写事件,以继续监听该客户端的监听
if(key.isConnectable()){
//连接事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
if(channel.isConnectionPeading()){
channel.finishConnect();//显示地完成连接
}
channel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
读取数据事件:在读取数据时,可以使用SocketChannel的read()方法读取到ByteBuffer对象中,并使用×××CharsetDecoder进行解码输出。
if(key.isReadable()){
//读取数据事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channle();
//注册新的事件
channel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
//读取数据
CharsetDecoder decoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newDecoder();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int count = channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println(count + ":" + decoder.decode(buffer));
}
写入数据事件:在写入数据时,可以使用SocketChannel的write()方法写入编码后的ByteBuffer数据
if(key.isWritable()){
//写入数据事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channle();
channel.register(selecotr,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//写入数据
CharsetEncoder encoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newEncoder();
channel.write(encoder.encode(CharBuffer.wrap("Hello")));
}
关闭连接:selector.close();socket.close();
完成代码示例如下:
(后续客户端将基于此示例进行完善)
package org.test.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ClosedChannelException;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.CharacterCodingException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class TestSocketChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Selector selector = null;
SocketChannel socket = null;
try {
// TODO 创建一个Selector
selector = Selector.open();
// TODO 创建并注册Socket
socket = SocketChannel.open();
socket.configureBlocking(false);
socket.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
// TODO 连接到远程地址
InetSocketAddress ip = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 12345);
socket.connect(ip);
//TODO 监听事件
while(true){
selector.select();
//事件来源列表
Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = it.next();
//删除当前事件
it.remove();
//判断当前事件类型
if(key.isConnectable()){
//连接事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else if(key.isReadable()){
//读取数据事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
//读取数据
CharsetDecoder decoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newDecoder();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int count = channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println(count + ":" + decoder.decode(buffer));
}else if(key.isWritable()){
//写入数据事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//写入数据
CharsetEncoder encoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newEncoder();
channel.write(encoder.encode(CharBuffer.wrap("Hello")));
}
}
}
} catch (ClosedChannelException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (CharacterCodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
try {
selector.close();
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
3、ServerSocket通道ServerSocketChannel
ServerSocketChannel类似于ServerSocket,可以用于创建一个服务端套接字对象,它具有非阻塞的功能。与ServerSocket的使用过程相似,ServerSocketChannel的工作过程如下:
(1)创建一个ServerSocketChannel对象:ServerSocketChannel server = ServerSocketChannel.open();
(2)设置为非阻塞模式:server.configureBlocking(false);
(3)注册到Selector:server.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
(4)开始启动端口监听
创建一个InetSocketAddress地址对象,使用SocketChannel的socket()函数取得ServerSocket对象,然后再使用ServerSocket的bind()函数绑定到指定的地址端口
InetSocketAddress ip = new InetSocketAddress("localhost",12345); server.socket().bind(ip);
(5)开始处理客户端连接事件和处理时间
客户端连接事件、读取数据事件和关闭连接
完整实例如下:
(后续实例中,我们将完善此服务端代码)
package org.test.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ClosedChannelException;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.CharacterCodingException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class TestServerSocketChannel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Selector selector = null;
ServerSocketChannel server = null;
try {
// TODO 创建一个Selector
selector = Selector.open();
// TODO 创建Socket并注册
server = ServerSocketChannel.open();
server.configureBlocking(false);
server.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// TODO 启动端口监听
InetSocketAddress ip = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 12345);
server.socket().bind(ip);
// TODO 监听事件
while(true){
//监听事件
selector.select();
//事件来源列表
Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = it.next();
//删除该事件
it.remove();
//判断事件类型
if(key.isConnectable()){
//连接事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
if(channel.isConnectionPending()){
channel.finishConnect();
}
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else if(key.isReadable()){
//读取数据事件
//读取数据事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
//读取数据
CharsetDecoder decoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newDecoder();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int count = channel.read(buffer);
System.out.println(count + ":" + decoder.decode(buffer));
} else if(key.isWritable()){
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//写入数据
CharsetEncoder encoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newEncoder();
channel.write(encoder.encode(CharBuffer.wrap("Hello")));
}
}
}
} catch (ClosedChannelException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (CharacterCodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
//关闭
try {
selector.close();
server.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
实例一:支持多客户端的Client/Server任务响应程序
演示一个可以接受多个客户端请求的服务器程序,服务端使用非阻塞模式监听多个客户端的连接和发送来的消息,在收到消息后根据消息命令来处理不同的业务逻辑,然后回复给客户端,客户端通过控制台输入的字符串发送给服务器端。
服务器端代码
package org.test.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ClosedChannelException;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.CharacterCodingException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class NIOServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Selector selector = null;
ServerSocketChannel server = null;
try {
// TODO 创建一个Selector
selector = Selector.open();
// TODO 创建Socket并注册
server = ServerSocketChannel.open();
server.configureBlocking(false);
server.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
// TODO 启动端口监听
InetSocketAddress ip = new InetSocketAddress(12345);
server.socket().bind(ip);
// TODO 监听事件
while(true){
//监听事件
selector.select();
//事件来源列表
Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
SelectionKey key = it.next();
//删除该事件
it.remove();
//判断事件类型
if(key.isAcceptable()){
//连接事件
ServerSocketChannel server2 = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
SocketChannel channel = server2.accept();
channel.configureBlocking(false);
if(channel.isConnectionPending()){
channel.finishConnect();
}
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("accept客户端连接:"
+ channel.socket().getInetAddress().getHostName()
+ channel.socket().getPort());
}else if(key.isReadable()){
//读取数据事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
//读取数据
CharsetDecoder decoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newDecoder();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
int count = channel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
String msg = decoder.decode(buffer).toString();
System.out.println(count + "收到:" + msg);
//写入数据
CharsetEncoder encoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newEncoder();
channel.write(encoder.encode(CharBuffer.wrap("server"+msg)));
} else if(key.isWritable()){
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel)key.channel();
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
//写入数据
CharsetEncoder encoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newEncoder();
channel.write(encoder.encode(CharBuffer.wrap("Hello")));
}
}
}
} catch (ClosedChannelException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (CharacterCodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
//关闭
try {
selector.close();
server.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
客户端代码
package org.test.nio;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
public class NIOClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
NIOClientThread clientThread = new NIOClientThread();
clientThread.start();
//输入输出流
BufferedReader sin = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
try {
//循环读取键盘输入
String readLine;
while((readLine = sin.readLine()) != null){
if(readLine.equals("bye")){
clientThread.close();
System.exit(0);
}
clientThread.send(readLine);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
客户端处理线程
package org.test.nio;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.ClosedChannelException;
import java.nio.channels.SelectionKey;
import java.nio.channels.Selector;
import java.nio.channels.SocketChannel;
import java.nio.charset.CharacterCodingException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class NIOClientThread extends Thread {
private CharsetDecoder decoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newDecoder();
private CharsetEncoder encoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newEncoder();
private Selector selector = null;
private SocketChannel socket = null;
private SelectionKey clientKey = null;
// TODO 启动客户端
public NIOClientThread() {
try {
// 创建一个Selector
selector = Selector.open();
// 创建并注册Socket
socket = SocketChannel.open();
socket.configureBlocking(false);
clientKey = socket.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
// 连接到远程地址
InetSocketAddress ip = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 12345);
socket.connect(ip);
} catch (ClosedChannelException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// TODO 读取事件
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 监听事件
while (true) {
selector.select(1);
// 事件来源列表
Iterator it = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
SelectionKey key = it.next();
// 删除当前事件
it.remove();
// 判断当前事件类型
if (key.isConnectable()) {
// 连接事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
if(channel.isConnectionPending()){
channel.finishConnect();
}
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
System.out.println("连接服务器端成功!");
} else if (key.isReadable()) {
// 读取数据事件
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
channel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE);
// 读取数据
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
int count = channel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
String msg = decoder.decode(buffer).toString();
System.out.println(count + "收到:" + msg);
}
}
}
} catch (ClosedChannelException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (CharacterCodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// TODO 发送消息
public void send(String msg) {
// 写入数据事件
try {
SocketChannel channel = (SocketChannel) clientKey.channel();
channel.write(encoder.encode(CharBuffer.wrap(msg)));
} catch (CharacterCodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// TODO 关闭客户端
public void close(){
try {
selector.close();
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
运行结果
服务器端: accept客户端连接:1.0.0.127.in-addr.arpa52591 15收到:你好服务器 accept客户端连接:1.0.0.127.in-addr.arpa52596 9收到:啊啊啊 客户端: 连接服务器端成功! 你好服务器 21收到:server你好服务器 连接服务器端成功! 啊啊啊 15收到:server啊啊啊
4、数据报通道DatagramChannel
DatagramChannel与DatagramSocket类似,用于实现非阻塞的数据报通信。与DatagramSocket的使用过程相似,Datagram的使用过程见:http://aku28907.blog.51cto.com/5668513/1782137。DatagramChannel的工作过程如下:
(1)创建一个DatagramChannel对象:socket = DatagramChannel.open();
(2)开始连接到远程地址
创建一个InetSocketAddress地址对象,使用SocketChannel的connect()函数连接该地址
InetSocketAddress ip = new InetSocketAddress("localhost",12345);
socket.connect(ip);
(3)发送或者接收数据
可以使用socket的write()来发送Buffer对象的数据,用receive()来接收Buffer数据。
socket.write(buffer);
socket.receive(buffer);
实例二:利用数据报通信的Client/Server程序
(示例比较简单,有兴趣的博友可以参照SocketChannel进行改造下)
服务器端
package org.test.nio.udp;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.SocketException;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel;
import java.nio.charset.CharacterCodingException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetDecoder;
public class UDPServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DatagramChannel socket = null;
try {
//创建socket
socket = DatagramChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress ip = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 12345);
socket.socket().bind(ip);
//循环监听
while(true){
CharsetDecoder decoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newDecoder();
ByteBuffer buffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(64);
socket.receive(buffer);
buffer.flip();
System.out.println(decoder.decode(buffer).toString());
}
} catch (SocketException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (CharacterCodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
客户端
package org.test.nio.udp;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.nio.CharBuffer;
import java.nio.channels.DatagramChannel;
import java.nio.charset.CharacterCodingException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.CharsetEncoder;
public class UDPClient {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
DatagramChannel socket = null;
try {
//创建一个Socket
socket = DatagramChannel.open();
InetSocketAddress ip = new InetSocketAddress("localhost", 12345);
socket.connect(ip);
//发送数据
CharsetEncoder encoder = Charset.forName("UTF-8").newEncoder();
socket.write(encoder.encode(CharBuffer.wrap("Hello")));
} catch (CharacterCodingException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} finally{
try {
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
运行结果: