原创:springMVC源码深度剖析-(初始化)
1. 什么是MVC
mvc是一种设计模式,帮助使用者更好搭建和编写项目,在b/s,c/s架构中经常使用,mvc表示全称为Model-View-controller,即模型-视图-控制三层结构,三层每层负责不同的功能,其中,model层用于封装简单的javaBean和复杂的javaBean,包括业务层,甚至dao层,只要是个javabean都属于model(注意不要狭义的以为,java仅仅只是pojo对象,他也可以是一个包含复杂逻辑的service),pojo对象的代码都是包含的,视图层主要是页面,用于返回给用户的,直观的一种可视化的界面,比如jsp,html
2.什么是springMVC
SpringMVC是整个spring中的一个很小的组成,准确的说他是spring WEB这个模块的下一个子模块,springMVC本质上是一个servlet,因为他间接的继承了httpServlet至于什么是servlet,本文就不做过多的解释了,可以参照我之前的博客链接如下:servlet教程
- 友情链接:servlet教程
3.DispatcherServlet的继承关系图
DispatcherServlet的继承关系图,能清晰的了解整个层次。
4.DispatcherServlet初始化(此图很重要,下面有用到)
当Web项目启动时,做初始化工作,所以我们大部分是配置在Web.xml里面,这样项目一启动,就会执行相关的初始化工作,下面是Web.xml代码
<servlet>
<servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServletservlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocationparam-name>
<param-value>classpath:Springmvc.xmlparam-value>
init-param -->
<load-on-startup>1load-on-startup>
servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>springMVCservlet-name>
<url-pattern>/url-pattern>
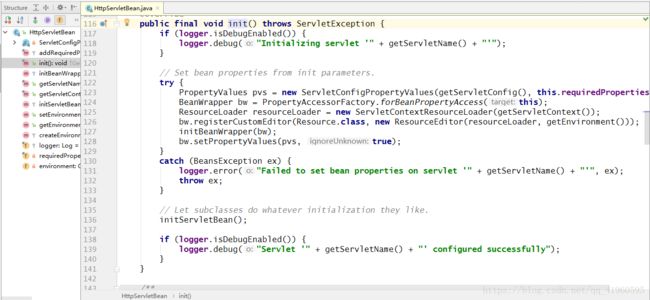
servlet-mapping>既然DispatcherServlet是一个servlet,那么就一定会有执行init,service等方法, DispatcherServlet继承了FrameworkServlet,FrameworkServlet继承了HttpServletBean,HttpServletBean继承了HttpServlet 类,而HttpServletBean类有一个入口点就是重写了init方法,如图所示:
init方法里有涉及到了BeanWrapper,PropertyValues,ResourceLoader。我这里大概介绍一下
1.PropertyValues:获取Web.xml里面的servlet的init-param(web.xml)
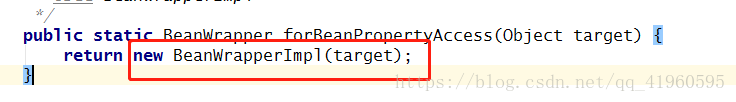
2.BeanWrapper:封装了bean的行为,提供了设置和获取属性值,它有对应的BeanWrapperImpl
3.ResourceLoader:可以根据一个资源地址加载文件资源。classpath:这种方式指定SpringMVC框架bean配置文件的来源
4.1 PropertyValues
**
下面是PropertyValues源码讲解
public ServletConfigPropertyValues(ServletConfig config, Set<String> requiredProperties)
throws ServletException {
Set<String> missingProps = (requiredProperties != null && !requiredProperties.isEmpty()) ?
new HashSet<String>(requiredProperties) : null;
//获取当前Servlet在web.xml中配置的名字,返回一个枚举对象
Enumeration<String> en = config.getInitParameterNames();
//遍历
while (en.hasMoreElements()) {
//获取name,也就是我上图web.xml中的param-name里的值:contextConfigLocation
String property = en.nextElement();
//根据name获取值,也就是我上图web.xml中的param-value里的值:classpath:Springmvc.xml
Object value = config.getInitParameter(property);
addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(property, value));
if (missingProps != null) {
missingProps.remove(property);
}
}
// Fail if we are still missing properties.
if (missingProps != null && missingProps.size() > 0) {
throw new ServletException(
"Initialization from ServletConfig for servlet '" + config.getServletName() +
"' failed; the following required properties were missing: " +
StringUtils.collectionToDelimitedString(missingProps, ", "));
}
}
}4.2 BeanWrapper
为给定类型的所有属性注册给定的自定义属性编辑器,提供了设置和获取属性值,它有对应的BeanWrapperImpl,如图所示
4.3 initServletBean()
这里会调用其子类FrameworkServlet的initServletBean()方法,我们来看看这个方法具体做了些什么
@Override
protected final void initServletBean() throws ServletException {
getServletContext().log("Initializing Spring FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "'");
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization started");
}
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
//初始化SpringMVC 上下文容器
this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
//已经加载了WebApplicationContext。默认的实现是空的
initFrameworkServlet();
}
catch (ServletException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
this.logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex);
throw ex;
}
if (this.logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
this.logger.info("FrameworkServlet '" + getServletName() + "': initialization completed in " +
elapsedTime + " ms");
}
}this.webApplicationContext = initWebApplicationContext();
初始化SpringMVC上下文容器,对initWebApplicationContext();进行跟踪,查看这个方法做了什么事情?
protected WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext() {
//获取根节点上下文,通过ContextLoaderListener加载,服务器启动便加载
WebApplicationContext rootContext =
WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(getServletContext());
WebApplicationContext wac = null;
if (this.webApplicationContext != null) {
wac = this.webApplicationContext;
if (wac instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) wac;
if (!cwac.isActive()) {
if (cwac.getParent() == null) {
//设置根节点上下文为父上下文
cwac.setParent(rootContext);
}
//设置id等等
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac);
}
}
}
if (wac == null) {
//查找servletContext中已有的WebApplicationContext作为上下文
wac = findWebApplicationContext();
}
if (wac == null) {
//创建本地的上下文,同时设置根节点上下文为父上下文,设置id等等(具体看下面)
wac = createWebApplicationContext(rootContext);
}
if (!this.refreshEventReceived) {
onRefresh(wac);
}
if (this.publishContext) {
// 将DispatcherServlet的上下文放入servlet上下文中
String attrName = getServletContextAttributeName();
getServletContext().setAttribute(attrName, wac);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Published WebApplicationContext of servlet '" + getServletName() +
"' as ServletContext attribute with name [" + attrName + "]");
}
}
return wac;
}接下来,我们在看一下createWebApplicationContext(rootContext)的具体实现
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
Class contextClass = getContextClass();
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"' will try to create custom WebApplicationContext context of class '" +
contextClass.getName() + "'" + ", using parent context [" + parent + "]");
}
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Fatal initialization error in servlet with name '" + getServletName() +
"': custom WebApplicationContext class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type ConfigurableWebApplicationContext");
}
//通过反射创建mvc容器
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
//设置环境
wac.setEnvironment(getEnvironment());
//设置根上下文为父上下文
wac.setParent(parent);
//设置springmvc.xml的路径
wac.setConfigLocation(getContextConfigLocation());
//初始化springmvc容器
configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(wac);
return wac;
}