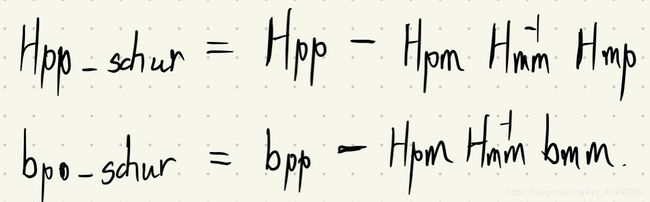VIO学习笔记(五)—— 单目 Bundle Adjustment 求解代码
单目 Bundle Adjustment 求解代码分析,相关资料请参考我的这篇博客。完整的工程在这里。
单目 Bundle Adjustment 求解代码
- 相机数据
- 定义顶点加法
- 残差计算
- Jacobians计算
- check jacobians
- Hessian计算
- Hessian矩阵模型
- Jacobian乘法模型
- Hessian矩阵变化过程
- Hessian矩阵最终形式
- slam的舒尔补操作
- Hessian矩阵的舒尔模型
- 舒尔补计算公式
- 舒尔补变换
- 变量计算
- toy example 1 marg变量测试代码
相机数据
相关的产生仿真数据的代码可以参考我的这篇博客。
/*
* 产生世界坐标系下的虚拟数据: 相机姿态, 特征点, 以及每帧观测
*/
void GetSimDataInWordFrame(vector<Frame> &cameraPoses, vector<Eigen::Vector3d> &points) {
int featureNums = 20; // 特征数目,假设每帧都能观测到所有的特征
int poseNums = 3; // 相机数目
double radius = 8;
for (int n = 0; n < poseNums; ++n) {
double theta = n * 2 * M_PI / (poseNums * 4); // 1/4 圆弧
// 绕 z轴 旋转
Eigen::Matrix3d R;
R = Eigen::AngleAxisd(theta, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ());
Eigen::Vector3d t = Eigen::Vector3d(radius * cos(theta) - radius, radius * sin(theta), 1 * sin(2 * theta));
cameraPoses.push_back(Frame(R, t));
}
// 随机数生成三维特征点
std::default_random_engine generator;
std::normal_distribution<double> noise_pdf(0., 1. / 1000.); // 2pixel / focal
for (int j = 0; j < featureNums; ++j) {
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> xy_rand(-4, 4.0);
std::uniform_real_distribution<double> z_rand(4., 8.);
Eigen::Vector3d Pw(xy_rand(generator), xy_rand(generator), z_rand(generator));
points.push_back(Pw);
// 在每一帧上的观测量
for (int i = 0; i < poseNums; ++i) {
Eigen::Vector3d Pc = cameraPoses[i].Rwc.transpose() * (Pw - cameraPoses[i].twc);
Pc = Pc / Pc.z(); // 归一化图像平面
Pc[0] += noise_pdf(generator);
Pc[1] += noise_pdf(generator);
cameraPoses[i].featurePerId.insert(make_pair(j, Pc));
}
}
}
定义顶点加法
定义pose的加法运算,将pose拆分成平移和旋转,平移直接进行加法,旋转采用李代数进行更新。
void VertexPose::Plus(const VecX &delta) {
VecX ¶meters = Parameters();
parameters.head<3>() += delta.head<3>(); //pose的前三维平移向量
Qd q(parameters[6], parameters[3], parameters[4], parameters[5]); //pose的旋转部分,四元数表示的
q = q * Sophus::SO3d::exp(Vec3(delta[3], delta[4], delta[5])).unit_quaternion(); // right multiplication with so3
q.normalized();
parameters[3] = q.x();
parameters[4] = q.y();
parameters[5] = q.z();
parameters[6] = q.w();
// Qd test = Sophus::SO3d::exp(Vec3(0.2, 0.1, 0.1)).unit_quaternion() * Sophus::SO3d::exp(-Vec3(0.2, 0.1, 0.1)).unit_quaternion();
// std::cout << test.x()<<" "<< test.y()<<" "<
}
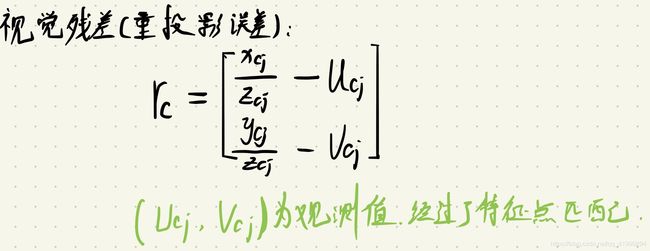
残差计算
计算边的残差。相关内容请参照我的这篇博客的VIO 中基于逆深度的重投影误差和残差 Jacobian 的推导部分。
void EdgeReprojection::ComputeResidual() {
//verticies_顶点顺序必须为InveseDepth、T_World_From_Body1、T_World_From_Body2。
double inv_dep_i = verticies_[0]->Parameters()[0]; //逆深度信息
VecX param_i = verticies_[1]->Parameters();
Qd Qi(param_i[6], param_i[3], param_i[4], param_i[5]); //旋转
Vec3 Pi = param_i.head<3>(); //平移
VecX param_j = verticies_[2]->Parameters();
Qd Qj(param_j[6], param_j[3], param_j[4], param_j[5]); //旋转
Vec3 Pj = param_j.head<3>(); //平移
//vio中基于逆深度的冲投影误差
Vec3 pts_camera_i = pts_i_ / inv_dep_i;
Vec3 pts_imu_i = qic * pts_camera_i + tic; //相机坐标转换为imu坐标
Vec3 pts_w = Qi * pts_imu_i + Pi; //imu坐标系变换到世界坐标系
Vec3 pts_imu_j = Qj.inverse() * (pts_w - Pj); //世界坐标系变换到imu坐标系
Vec3 pts_camera_j = qic.inverse() * (pts_imu_j - tic); //imu坐标系变换的相机坐标系
double dep_j = pts_camera_j.z();
residual_ = (pts_camera_j / dep_j).head<2>() - pts_j_.head<2>(); /// J^t * J * delta_x = - J^t * r
// residual_ = information_ * residual_; // remove information here, we multi information matrix in problem solver
}
Jacobians计算
相关内容请参照我的这篇博客的残差 Jacobian 的推导部分。
void EdgeReprojection::ComputeJacobians() {
//verticies_顶点顺序必须为InveseDepth、T_World_From_Body1、T_World_From_Body2。
double inv_dep_i = verticies_[0]->Parameters()[0]; //逆深度
VecX param_i = verticies_[1]->Parameters(); //i时刻位姿
Qd Qi(param_i[6], param_i[3], param_i[4], param_i[5]);
Vec3 Pi = param_i.head<3>();
VecX param_j = verticies_[2]->Parameters(); //j时刻位姿
Qd Qj(param_j[6], param_j[3], param_j[4], param_j[5]);
Vec3 Pj = param_j.head<3>();
Vec3 pts_camera_i = pts_i_ / inv_dep_i;
Vec3 pts_imu_i = qic * pts_camera_i + tic;
Vec3 pts_w = Qi * pts_imu_i + Pi;
Vec3 pts_imu_j = Qj.inverse() * (pts_w - Pj);
Vec3 pts_camera_j = qic.inverse() * (pts_imu_j - tic);
double dep_j = pts_camera_j.z();
Mat33 Ri = Qi.toRotationMatrix();
Mat33 Rj = Qj.toRotationMatrix();
Mat33 ric = qic.toRotationMatrix();
Mat23 reduce(2, 3);
//残差对j时刻路标点的jacobian
reduce << 1. / dep_j, 0, -pts_camera_j(0) / (dep_j * dep_j),
0, 1. / dep_j, -pts_camera_j(1) / (dep_j * dep_j);
// reduce = information_ * reduce;
//j时刻路标点对i时刻pose的jacobian
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 6> jacobian_pose_i;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 6> jaco_i;
jaco_i.leftCols<3>() = ric.transpose() * Rj.transpose();
jaco_i.rightCols<3>() = ric.transpose() * Rj.transpose() * Ri * -Sophus::SO3d::hat(pts_imu_i);
jacobian_pose_i.leftCols<6>() = reduce * jaco_i;
//j时刻路标点对j时刻pose的jacobian
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 6> jacobian_pose_j;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 6> jaco_j;
jaco_j.leftCols<3>() = ric.transpose() * -Rj.transpose();
jaco_j.rightCols<3>() = ric.transpose() * Sophus::SO3d::hat(pts_imu_j);
jacobian_pose_j.leftCols<6>() = reduce * jaco_j;
//j时刻路标点对逆深度jacobian
Eigen::Vector2d jacobian_feature;
jacobian_feature = reduce * ric.transpose() * Rj.transpose() * Ri * ric * pts_i_ * -1.0 / (inv_dep_i * inv_dep_i);
jacobians_[0] = jacobian_feature;
jacobians_[1] = jacobian_pose_i;
jacobians_[2] = jacobian_pose_j;
}
check jacobians
if(true)
{
std::cout << "//---------------- check jacobians -----------------//" << std::endl;
std::cout << jacobians_[0] <<std::endl;
const double eps = 1e-6;
inv_dep_i += eps;
Eigen::Vector3d pts_camera_i = pts_i_ / inv_dep_i;
Eigen::Vector3d pts_imu_i = qic * pts_camera_i + tic;
Eigen::Vector3d pts_w = Qi * pts_imu_i + Pi;
Eigen::Vector3d pts_imu_j = Qj.inverse() * (pts_w - Pj);
Eigen::Vector3d pts_camera_j = qic.inverse() * (pts_imu_j - tic);
Eigen::Vector2d tmp_residual;
double dep_j = pts_camera_j.z();
tmp_residual = (pts_camera_j / dep_j).head<2>() - pts_j_.head<2>();
tmp_residual = information_ * tmp_residual;
std::cout <<"num jacobian: "<< (tmp_residual - residual_) / eps <<std::endl;
}
比较计算结果与数值结果,一下为输出结果
//---------------- check jacobians -----------------//
-6.26683
-11.4615
num jacobian: -6.26683
-11.4615
//---------------- check jacobians -----------------//
-1.40693
-6.67589
num jacobian: -1.40693
-6.6759
//---------------- check jacobians -----------------//
-6.21937
-9.82836
num jacobian: -6.21937
-9.82837
//---------------- check jacobians -----------------//
-1.98315
-5.9814
num jacobian: -1.98316
-5.98141
Hessian计算
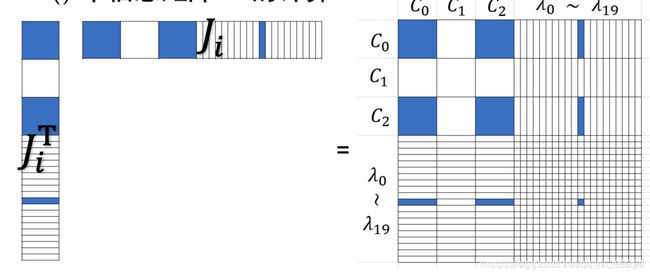
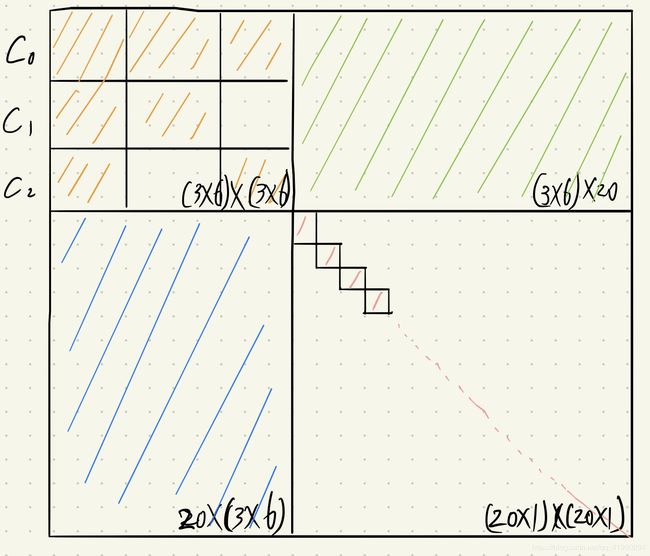
void Problem::MakeHessian() {
TicToc t_h;
// 直接构造大的 H 矩阵
ulong size = ordering_generic_; //38维,3×6+20
// cout << "//-------------size--------------//" << endl;
// cout << size << endl;
MatXX H(MatXX::Zero(size, size));
VecX b(VecX::Zero(size));
int iiii = 1;
for (auto &edge: edges_) {
int iii = 1;
edge.second->ComputeResidual();
edge.second->ComputeJacobians();
auto jacobians = edge.second->Jacobians();
auto verticies = edge.second->Verticies();
assert(jacobians.size() == verticies.size());
for (size_t i = 0; i < verticies.size(); ++i) {
auto v_i = verticies[i];
if (v_i->IsFixed()) continue; // Hessian 里不需要添加它的信息,也就是它的雅克比为 0
auto jacobian_i = jacobians[i];
ulong index_i = v_i->OrderingId();
ulong dim_i = v_i->LocalDimension();
// cout << "//-------------------index_i------------------//" << endl;
// cout << index_i << endl;
MatXX JtW = jacobian_i.transpose() * edge.second->Information();
// cout << "//---------------JtW---------------------//" << endl;
// cout << JtW << endl;
for (size_t j = i; j < verticies.size(); ++j) {
auto v_j = verticies[j];
if (v_j->IsFixed()) continue;
auto jacobian_j = jacobians[j];
ulong index_j = v_j->OrderingId();
ulong dim_j = v_j->LocalDimension();
assert(v_j->OrderingId() != -1);
MatXX hessian = JtW * jacobian_j;
// 所有的信息矩阵叠加起来
// TODO:: home work. 完成 H index 的填写.
H.block(index_i, index_j, dim_i, dim_j).noalias() += hessian;
cout << iiii<< ": " << iii << "//--------------H---------------//" << endl;
cout << H << endl;
if (j != i) {
// 对称的下三角
// TODO:: home work. 完成 H index 的填写.
H.block(index_j, index_i, dim_j, dim_i).noalias() += hessian.transpose();
cout << iiii<< ": " << iii << "//--------------H---------------//" << endl;
cout << H << endl;
}
iii++;
}
b.segment(index_i, dim_i).noalias() -= JtW * edge.second->Residual();
}
// cout << "//--------------H---------------//" << endl;
// cout << H << endl;
// cout << "//--------------b---------------//" << endl;
// cout << b << endl;
iiii++;
}
Hessian_ = H;
b_ = b;
t_hessian_cost_ += t_h.toc();
// cout << "//--------------H---------------//" << endl;
// cout << H << endl;
// cout << "//--------------b---------------//" << endl;
// cout << b << endl;
// Eigen::JacobiSVD svd(H, Eigen::ComputeThinU | Eigen::ComputeThinV);
// std::cout << svd.singularValues() <
if (err_prior_.rows() > 0) {
b_prior_ -= H_prior_ * delta_x_.head(ordering_poses_); // update the error_prior
}
Hessian_.topLeftCorner(ordering_poses_, ordering_poses_) += H_prior_;
b_.head(ordering_poses_) += b_prior_;
delta_x_ = VecX::Zero(size); // initial delta_x = 0_n;
}
Hessian矩阵模型
Jacobian乘法模型
Hessian矩阵变化过程
Hessian矩阵最终形式
slam的舒尔补操作
/*
* Solve Hx = b, we can use PCG iterative method or use sparse Cholesky
*/
void Problem::SolveLinearSystem() {
if (problemType_ == ProblemType::GENERIC_PROBLEM) {
// 非 SLAM 问题直接求解
// PCG solver
MatXX H = Hessian_;
for (ulong i = 0; i < Hessian_.cols(); ++i) {
H(i, i) += currentLambda_;
}
// delta_x_ = PCGSolver(H, b_, H.rows() * 2);
delta_x_ = Hessian_.inverse() * b_;
} else {
// SLAM 问题采用舒尔补的计算方式
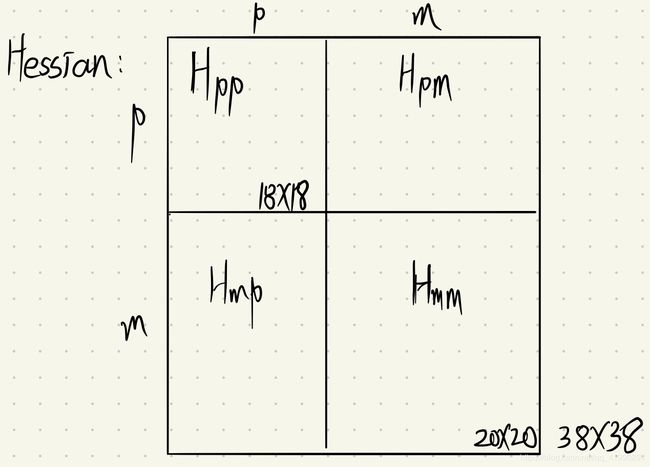
// step1: schur marginalization --> Hpp, bpp
int reserve_size = ordering_poses_;
int marg_size = ordering_landmarks_;
// TODO:: home work. 完成矩阵块取值,Hmm,Hpm,Hmp,bpp,bmm
MatXX Hmm = Hessian_.block(reserve_size, reserve_size, marg_size, marg_size);
MatXX Hpm = Hessian_.block(0, reserve_size, reserve_size, marg_size);
MatXX Hmp = Hessian_.block(reserve_size, 0, marg_size, reserve_size);
VecX bpp = b_.segment(0, reserve_size);
VecX bmm = b_.segment(reserve_size, marg_size);
// Hmm 是对角线矩阵,它的求逆可以直接为对角线块分别求逆,如果是逆深度,对角线块为1维的,则直接为对角线的倒数,这里可以加速
MatXX Hmm_inv(MatXX::Zero(marg_size, marg_size));
for (auto landmarkVertex : idx_landmark_vertices_) {
int idx = landmarkVertex.second->OrderingId() - reserve_size;
int size = landmarkVertex.second->LocalDimension();
Hmm_inv.block(idx, idx, size, size) = Hmm.block(idx, idx, size, size).inverse();
}
// TODO:: home work. 完成舒尔补 Hpp, bpp 代码
MatXX tempH = Hpm * Hmm_inv;
H_pp_schur_ = Hessian_.block(0, 0, ordering_poses_, ordering_poses_) - tempH * Hmp;
b_pp_schur_ = bpp - tempH * bmm;
// step2: solve Hpp * delta_x = bpp
VecX delta_x_pp(VecX::Zero(reserve_size));
// PCG Solver
for (ulong i = 0; i < ordering_poses_; ++i) {
H_pp_schur_(i, i) += currentLambda_;
}
int n = H_pp_schur_.rows() * 2; // 迭代次数
// 哈哈,小规模问题,搞 pcg 花里胡哨
delta_x_pp = PCGSolver(H_pp_schur_, b_pp_schur_, n);
delta_x_.head(reserve_size) = delta_x_pp;
// std::cout << delta_x_pp.transpose() << std::endl;
// TODO:: home work. step3: solve landmark
VecX delta_x_ll(marg_size);
delta_x_ll = Hmm_inv * (bmm - Hmp * delta_x_pp);
delta_x_.tail(marg_size) = delta_x_ll;
}
}
Hessian矩阵的舒尔模型
舒尔补计算公式
舒尔补变换
变量计算
toy example 1 marg变量测试代码
关于toy example 1的相关内容请参照我的这篇博客的toy example 1和回顾 toy example 1 中去除变量 x3 的操作部分。
相关的信息矩阵为:
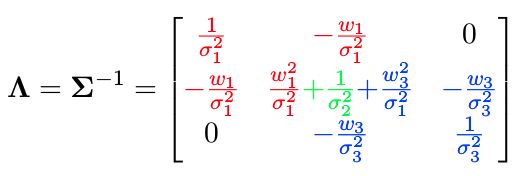

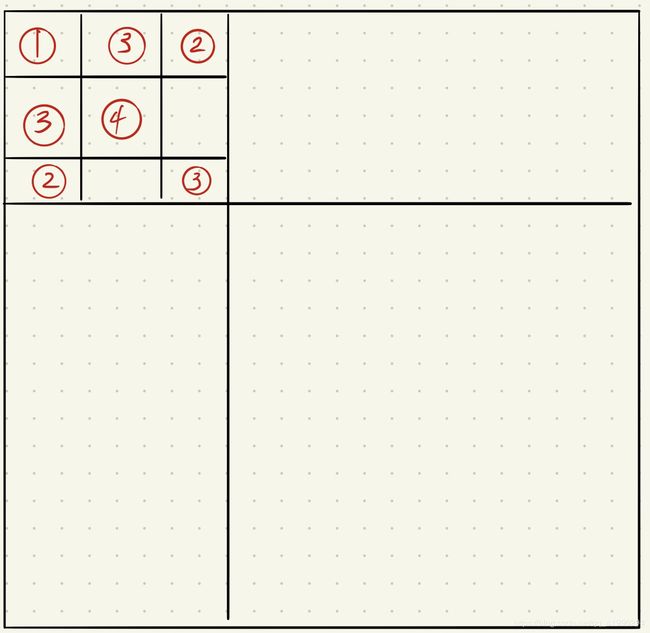
void Problem::TestMarginalize() {
// Add marg test
int idx = 1; // marg 中间那个变量
int dim = 1; // marg 变量的维度
int reserve_size = 3; // 总共变量的维度
double delta1 = 0.1 * 0.1;
double delta2 = 0.2 * 0.2;
double delta3 = 0.3 * 0.3;
int cols = 3;
MatXX H_marg(MatXX::Zero(cols, cols));
H_marg << 1./delta1, -1./delta1, 0,
-1./delta1, 1./delta1 + 1./delta2 + 1./delta3, -1./delta3,
0., -1./delta3, 1/delta3;
std::cout << "---------- TEST Marg: before marg------------"<< std::endl;
std::cout << H_marg << std::endl;
// TODO:: home work. 将变量移动到右下角
/// 准备工作: move the marg pose to the Hmm bottown right
// 将 row i 移动矩阵最下面
Eigen::MatrixXd temp_rows = H_marg.block(idx, 0, dim, reserve_size);
Eigen::MatrixXd temp_botRows = H_marg.block(idx + dim, 0, reserve_size - idx - dim, reserve_size);
H_marg.block(idx, 0, dim, reserve_size) = temp_botRows;
H_marg.block(idx + dim, 0, reserve_size - idx - dim, reserve_size) = temp_rows;
// 将 col i 移动矩阵最右边
Eigen::MatrixXd temp_cols = H_marg.block(0, idx, reserve_size, dim);
Eigen::MatrixXd temp_rightCols = H_marg.block(0, idx + dim, reserve_size, reserve_size - idx - dim);
H_marg.block(0, idx, reserve_size, reserve_size - idx - dim) = temp_rightCols;
H_marg.block(0, reserve_size - dim, reserve_size, dim) = temp_cols;
std::cout << "---------- TEST Marg: 将变量移动到右下角------------"<< std::endl;
std::cout<< H_marg <<std::endl;
/// 开始 marg : schur
double eps = 1e-8;
int m2 = dim;
int n2 = reserve_size - dim; // 剩余变量的维度
Eigen::MatrixXd Amm = 0.5 * (H_marg.block(n2, n2, m2, m2) + H_marg.block(n2, n2, m2, m2).transpose());
Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Eigen::MatrixXd> saes(Amm);
Eigen::MatrixXd Amm_inv = saes.eigenvectors() * Eigen::VectorXd(
(saes.eigenvalues().array() > eps).select(saes.eigenvalues().array().inverse(), 0)).asDiagonal() *
saes.eigenvectors().transpose();
// TODO:: home work. 完成舒尔补操作
Eigen::MatrixXd Arm = H_marg.block(0,n2,n2,m2);
Eigen::MatrixXd Amr = H_marg.block(n2,0,m2,n2);
Eigen::MatrixXd Arr = H_marg.block(0,0,n2,n2);
Eigen::MatrixXd tempB = Arm * Amm_inv;
Eigen::MatrixXd H_prior = Arr - tempB * Amr;
std::cout << "---------- TEST Marg: after marg------------"<< std::endl;
std::cout << H_prior << std::endl;
}
结果如下:
---------- TEST Marg: before marg------------
100 -100 0
-100 136.111 -11.1111
0 -11.1111 11.1111
---------- TEST Marg: 将变量移动到右下角------------
100 0 -100
0 11.1111 -11.1111
-100 -11.1111 136.111
---------- TEST Marg: after marg------------
26.5306 -8.16327
-8.16327 10.2041