Spring声明式事务管理(XML与注解方式)
事务控制概述
编程式事务控制
自己手动控制事务,就叫做编程式事务控制。
Jdbc代码:
Conn.setAutoCommite(false); // 设置手动控制事务
Hibernate代码:
Session.beginTransaction(); // 开启一个事务
细粒度的事务控制:
可以对指定的方法、指定的方法的某几行添加事务控制。(比较灵活,但开发起来比较繁琐: 每次都要开启、提交、回滚.)
声明式事务控制
Spring提供了对事务的管理, 这个就叫声明式事务管理。
Spring提供了对事务控制的实现。用户如果想用Spring的声明式事务管理,只需要在配置文件中配置即可; 不想使用时直接移除配置。这个实现了对事务控制的最大程度的解耦。
Spring声明式事务管理,核心实现就是基于Aop。
粗粒度的事务控制:
只能给整个方法应用事务,不可以对方法的某几行应用事务。(因为aop拦截的是方法。)
Spring声明式事务管理器类:
Jdbc技术:DataSourceTransactionManager
Hibernate技术:HibernateTransactionManager
XML方式
目录结构
操作流程
1) 引入spring-aop相关的4个jar文件
2) 引入aop名称空间 【XML配置方式需要引入】
3) 引入tx名称空间 【事务方式必须引入】
1、tx包下面的类
2、Spring-tx.xml配置文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
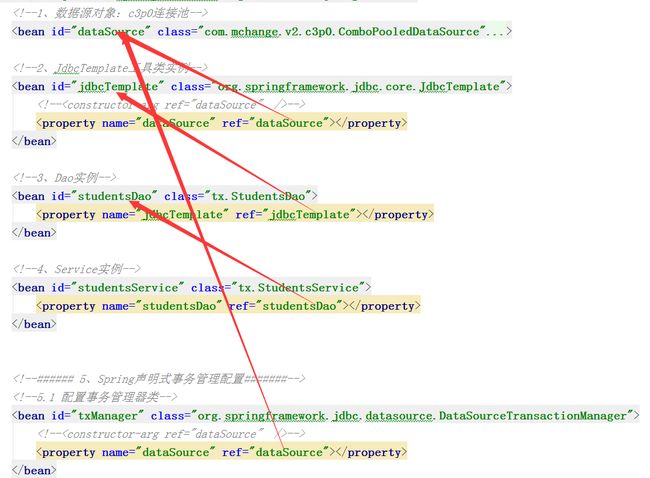
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver">property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://192.168.100.17/lgdtest">property>
<property name="user" value="root">property>
<property name="password" value="123456">property>
<property name="initialPoolSize" value="3">property>
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="10">property>
<property name="maxStatements" value="100">property>
<property name="acquireIncrement" value="10">property>
bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<bean id="studentsDao" class="tx.StudentsDao">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate">property>
bean>
<bean id="studentsService" class="tx.StudentsService">
<property name="studentsDao" ref="studentsDao">property>
bean>
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="txManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="get" read-only="true">tx:method>
<tx:method name="find" read-only="true">tx:method>
<tx:method name="*" read-only="false">tx:method>
tx:attributes>
tx:advice>
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* tx.StudentsService.*(..))" />
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pt"/>
aop:config>
beans>注解方式
使用注解实现Spring的声明式事务管理,更加简单!
目录结构
操作流程
1) 必须引入Aop相关的jar文件
2) bean.xml中指定注解方式实现声明式事务管理以及应用的事务管理器类
3)在需要添加事务控制的地方,写上: @Transactional
@Transactional注解:
1)应用事务的注解
2)定义到方法上: 当前方法应用spring的声明式事务
3)定义到类上: 当前类的所有的方法都应用Spring声明式事务管理;
4)定义到父类上: 当执行父类的方法时候应用事务。
1、tx_anno包下面的类
package tx_anno;
/**
* Created by liguodong on 2015/11/12.
*/
public class Students {
int id;
String name;
double sal;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getSal() {
return sal;
}
public void setSal(double sal) {
this.sal = sal;
}
}
package tx_anno;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* Created by liguodong on 2015/11/13.
*/
@Repository
public class StudentsDao {
@Resource
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void save(Students students){
String sql = "insert into students(id,name) values(?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,students.getId(),students.getName());
}
}
package tx_anno;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
/**
* Created by liguodong on 2015/11/13.
*/
@Service
public class StudentsService {
@Resource
public StudentsDao studentsDao;
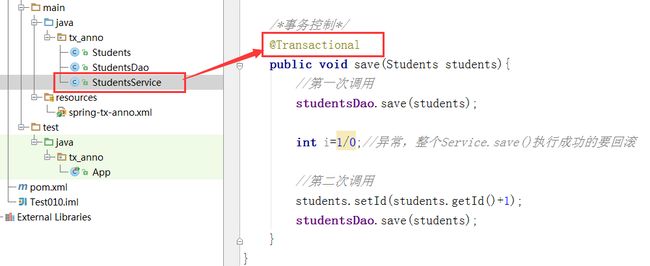
/*事务控制*/
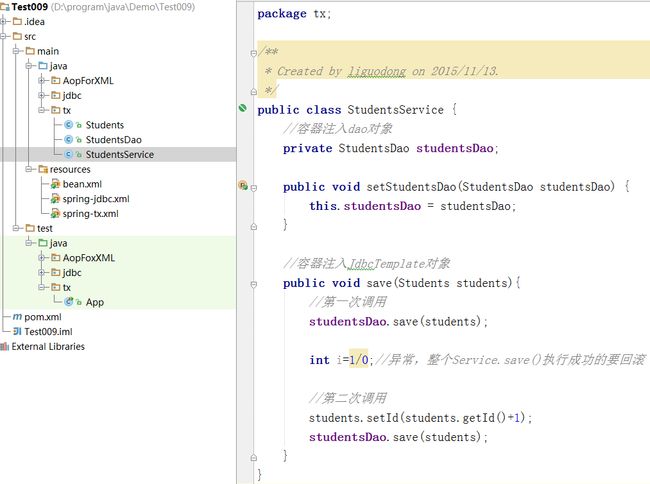
@Transactional
public void save(Students students){
//第一次调用
studentsDao.save(students);
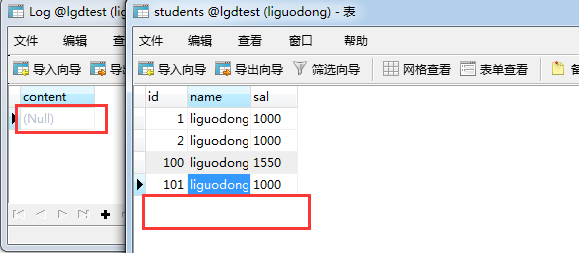
int i=1/0;//异常,整个Service.save()执行成功的要回滚
//第二次调用
students.setId(students.getId()+1);
studentsDao.save(students);
}
}2、spring-tx-anno.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver">property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://192.168.100.17/lgdtest">property>
<property name="user" value="root">property>
<property name="password" value="123456">property>
<property name="initialPoolSize" value="3">property>
<property name="maxPoolSize" value="10">property>
<property name="maxStatements" value="100">property>
<property name="acquireIncrement" value="10">property>
bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource">property>
bean>
<context:component-scan base-package="tx_anno"/>
<bean id="txManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
bean>
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="txManager" />
beans>其他
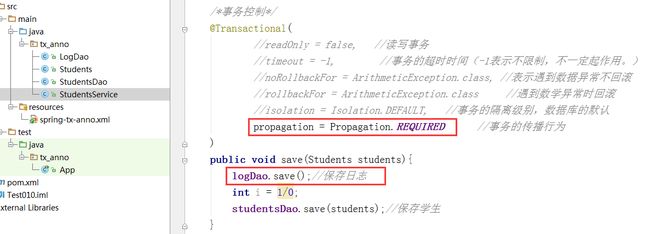
事务属性
事务传播行为:
Propagation.REQUIRED
指定当前的方法必须在事务的环境下执行;
如果当前运行的方法,已经存在事务, 就会加入当前的事务;
Propagation.REQUIRED_NEW
指定当前的方法必须在事务的环境下执行;
如果当前运行的方法,已经存在事务: 事务会挂起; 会始终开启一个新的事务,执行完后; 刚才挂起的事务才继续运行。