Ubuntu 14.04 64bit上解析wireshark抓包pcap文件格式和源码实现
pcap文件格式是常用的数据报存储格式,包括wireshark在内的主流抓包软件都可以生成这种格式的数据包
下面对这种格式的文件简单分析一下:
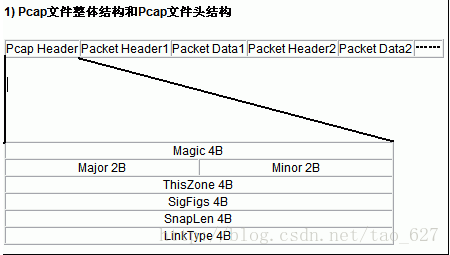
pcap文件的格式为:
文件头 24字节
数据报头 + 数据报 数据包头为16字节,后面紧跟数据报
数据报头 + 数据报 ......
文件头 24字节
数据报头 + 数据报 数据包头为16字节,后面紧跟数据报
数据报头 + 数据报 ......
pcap.h里定义了文件头的格式
struct pcap_file_header {
bpf_u_int32 magic;
u_short version_major;
u_short version_minor;
bpf_int32 thiszone;
bpf_u_int32 sigfigs;
bpf_u_int32 snaplen;
bpf_u_int32 linktype;
};
struct pcap_file_header {
bpf_u_int32 magic;
u_short version_major;
u_short version_minor;
bpf_int32 thiszone;
bpf_u_int32 sigfigs;
bpf_u_int32 snaplen;
bpf_u_int32 linktype;
};
Pcap文件头24B各字段说明:
Magic:4B:0x1A 2B 3C 4D:用来标示文件的开始
Major:2B,0×02 00:当前文件主要的版本号
Minor:2B,0×04 00当前文件次要的版本号
ThisZone:4B当地的标准时间;全零
SigFigs:4B时间戳的精度;全零
SnapLen:4B最大的存储长度
LinkType:4B链路类型
常用类型:
0 BSD loopback devices, except for later OpenBSD
1 Ethernet, and Linux loopback devices
6 802.5 Token Ring
7 ARCnet
8 SLIP
9 PPP
10 FDDI
100 LLC/SNAP-encapsulated ATM
101 “raw IP”, with no link
102 BSD/OS SLIP
103 BSD/OS PPP
104 Cisco HDLC
105 802.11
108 later OpenBSD loopback devices (with the AF_value in network byte order)
113 special Linux “cooked” capture
114 LocalTalk
1 Ethernet, and Linux loopback devices
6 802.5 Token Ring
7 ARCnet
8 SLIP
9 PPP
10 FDDI
100 LLC/SNAP-encapsulated ATM
101 “raw IP”, with no link
102 BSD/OS SLIP
103 BSD/OS PPP
104 Cisco HDLC
105 802.11
108 later OpenBSD loopback devices (with the AF_value in network byte order)
113 special Linux “cooked” capture
114 LocalTalk
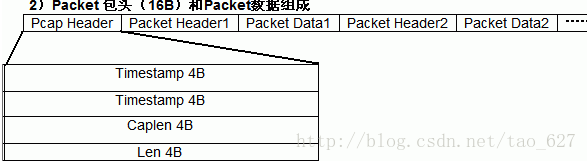
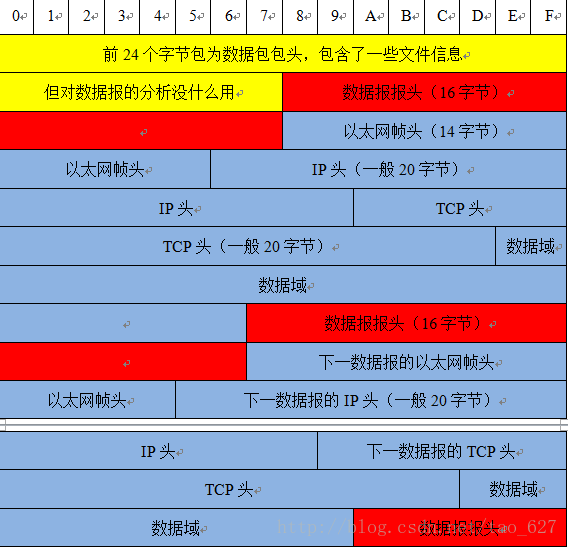
字段说明:
Timestamp:时间戳高位,精确到seconds(值是自从January 1, 1970 00:00:00 GMT以来的秒数来记)
Timestamp:时间戳低位,精确到microseconds (数据包被捕获时候的微秒(microseconds)数,是自ts-sec的偏移量)
Caplen:当前数据区的长度,即抓取到的数据帧长度,由此可以得到下一个数据帧的位置。
Len:离线数据长度:网络中实际数据帧的长度,一般不大于caplen,多数情况下和Caplen数值相等。
(例如,实际上有一个包长度是1500 bytes(Len=1500),但是因为在Global Header的snaplen=1300有限制,所以只能抓取这个包的前1300个字节,这个时候,Caplen = 1300 )
Packet 数据:即 Packet(通常就是链路层的数据帧)具体内容,长度就是Caplen,这个长度的后面,就是当前PCAP文件中存放的下一个Packet数据包,也就 是说:PCAP文件里面并没有规定捕获的Packet数据包之间有什么间隔字符串,下一组数据在文件中的起始位置。我们需要靠第一个Packet包确定。 最后,Packet数据部分的格式其实就是标准的网路协议格式了可以任何网络教材上找得到。
下面是我针对网上相关代码的修改和精炼,主要就是改进了读包方法,每次先读包头,再一次性读取该包数据,并在该包数据内依次解析Ethernet帧,IP帧,TCP帧或是UDP帧。另外改进了异常处理机制,保证退出时文件要关闭,内存要释放。注意运行在64位Linux系统上面;
文件pcap_file_parse.c
//description: parse wireshark pcap file and write it into local file
//platform: Ubuntu 14.04 64bit Desktop version
//compile: gcc -g pcap_file_parse.c -o pcap_file_parse
//run: ./pcap_file_parse test.pcap
//author: [email protected], QQ:48019671
//date: 2014-05-24
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "pcap_utils.h" //公共函数存放在这里
#define STRSIZE 1024
#define SNAP_LEN 1518 // 以太网帧最大长度
#define SIZE_ETHERNET 14 // 以太网包头长度 mac 6*2, type: 2
#define SIZE_UDP 8 // UDP包头8字节
int main(int argc, char **argv){
if(argc<=1 || argc>2){
printf("Usage: %s \n", argv[0]);
return 0;
}
struct pcap_file_header *file_header;
struct pcap_pkthdr *ptk_header;
struct ether_header *eth_header;
struct iphdr *ip_header;
struct tcphdr *tcp_header;
struct udphdr *udp_header;
const char *payload;
int size_packet, size_payload, size_ip, size_tcp;
FILE *fp, *output;
int pkt_offset, i=0;
char buf[STRSIZE], capture_time[STRSIZE];
u_char *packet = NULL;
if((fp=fopen(argv[1], "r")) == NULL){
printf("Error: can not open input pcap file\n");
exit(0);
}
if((output=fopen("./output.txt", "w+")) == NULL){
printf("Error: can not open the output file\n");
exit(0);
}
file_header = (struct pcap_file_header*)malloc(sizeof(struct pcap_file_header));
ptk_header = (struct pcap_pkthdr*)malloc(sizeof(struct pcap_pkthdr));
//validate the pcap file format
int read_size = fread(file_header, sizeof(char), 24, fp);
if(read_size != 24){
printf("cannot read pcacp file header, invalid format\n");
goto cleanup;
}
printf("Pcap file header: %X, %hu, %hu, %u, %u\n",file_header->magic,file_header->version_major,file_header->version_minor,file_header->snaplen,file_header->linktype);
//allocate a common packet buffer to use
packet = (u_char*)malloc(file_header->snaplen * sizeof(char));
pkt_offset = 24;
while(fseek(fp, pkt_offset, SEEK_SET) == 0){
i++;
memset(buf,0,sizeof(buf));
memset(packet,0,sizeof(packet));
//read pcap packet header
if(fread(buf, 16, 1, fp) != 1){
printf("\nPacket No#%d: cannot read pcap_pkt_header of pcap file\n", i);
break;
}
ptk_header->ts.tv_sec = *(bpf_u_int32*)buf;
ptk_header->caplen = *(bpf_u_int32*)(buf+8);
ptk_header->len = *(bpf_u_int32*)(buf+12);
size_packet = ptk_header->caplen;
pkt_offset += 16 + size_packet;
strftime(capture_time, sizeof(capture_time), "%Y-%m-%d %T", localtime(&(ptk_header->ts.tv_sec)));
printf("capture time: %s, packet len: %u\n", capture_time, size_packet);
//read a complete packet
if(fread(packet, 1, size_packet, fp) != size_packet){
printf("Packet NO.%d: cannot read a whole packet\n", i);
break;
}
eth_header = (struct ether_header*)packet;
//read ip frame header
ip_header = (struct iphdr *)(packet + SIZE_ETHERNET);
size_ip = (ip_header->ihl)*4;
/* if (size_ip < 20) {
printf("无效的IP头长度: %u bytes\n", size_ip);
break;
}*/
if ( (ip_header->protocol != IPPROTO_TCP)&&(ip_header->protocol!=IPPROTO_UDP) ){ // TCP,UDP,ICMP,IP
continue;
}
if(ip_header->protocol==IPPROTO_TCP){
/* TCP头 */
tcp_header = (struct tcphdr *)(packet + SIZE_ETHERNET + size_ip);
size_tcp = (tcp_header->th_off)*4;
if (size_tcp < 20) {
printf("无效的TCP头长度: %u bytes\n", size_tcp);
break;
}
int sport = ntohs(tcp_header->th_sport);
int dport = ntohs(tcp_header->th_dport);
printf("%s:%d -> ", inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr*)(&ip_header->saddr)), sport);
printf("%s:%d ", inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr*)(&ip_header->daddr)), dport);
//内容
payload = (u_char *)(packet + SIZE_ETHERNET + size_ip + size_tcp);
//内容长度
size_payload = ntohs(ip_header->tot_len) - (size_ip + size_tcp);
if (size_payload > 0) {
printf("seq:%d ack:%d flag:%d payload:%d bytes\n", ntohs(tcp_header->th_seq), ntohs(tcp_header->th_ack), ntohs(tcp_header->th_flags), size_payload );
printf("=====================================TCP=====================================\n");
print_payload(payload, size_payload);
}
}else if(ip_header->protocol==IPPROTO_UDP){
udp_header = (struct udphdr *)(packet + SIZE_ETHERNET + size_ip);
int sport = ntohs(udp_header->source);
int dport = ntohs(udp_header->dest);
printf("%s:%d -> ", inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr*)(&ip_header->saddr)), sport);
printf("%s:%d ", inet_ntoa(*(struct in_addr*)(&ip_header->daddr)), dport);
//内容
payload = (u_char *)(packet + SIZE_ETHERNET + size_ip + SIZE_UDP);
//内容长度
size_payload = ntohs(ip_header->tot_len) - (size_ip + SIZE_UDP);
if (size_payload > 0) {
printf("payload:%d bytes\n", size_payload );
printf("=====================================UDP=====================================\n");
print_payload(payload, size_payload);
}
}
}
cleanup:
if(file_header)
free(file_header);
if(ptk_header)
free(ptk_header);
if(packet)
free(packet);
fclose(fp);
fclose(output);
return 0;
}
文件pcap_utils.h
#include
#include
#include
/*
* print data in rows of 16 bytes: offset hex ascii
*
* 00000 47 45 54 20 2f 20 48 54 54 50 2f 31 2e 31 0d 0a GET / HTTP/1.1..
*/
void
print_hex_ascii_line(const u_char *payload, int len, int offset)
{
int i;
int gap;
const u_char *ch;
/* offset */
printf("%05d ", offset);
/* hex */
ch = payload;
for(i = 0; i < len; i++) {
printf("%02X ", *ch);
ch++;
/* print extra space after 8th byte for visual aid */
if (i == 7)
printf(" ");
}
/* print space to handle line less than 8 bytes */
if (len < 8)
printf(" ");
/* fill hex gap with spaces if not full line */
if (len < 16) {
gap = 16 - len;
for (i = 0; i < gap; i++) {
printf(" ");
}
}
printf(" ");
/* ascii (if printable) */
ch = payload;
for(i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (isprint(*ch))
printf("%c", *ch);
else
printf(".");
ch++;
}
printf("\n");
}
/*
* print packet payload data (avoid printing binary data)
*/
void
print_payload(const u_char *payload, int len)
{
int len_rem = len;
int line_width = 16; /* number of bytes per line */
int line_len;
int offset = 0; /* zero-based offset counter */
const u_char *ch = payload;
if (len <= 0)
return;
/* data fits on one line */
if (len <= line_width) {
print_hex_ascii_line(ch, len, offset);
return;
}
/* data spans multiple lines */
for ( ;; ) {
/* compute current line length */
line_len = line_width % len_rem;
/* print line */
print_hex_ascii_line(ch, line_len, offset);
/* compute total remaining */
len_rem = len_rem - line_len;
/* shift pointer to remaining bytes to print */
ch = ch + line_len;
/* add offset */
offset = offset + line_width;
/* check if we have line width chars or less */
if (len_rem <= line_width) {
/* print last line and get out */
print_hex_ascii_line(ch, len_rem, offset);
break;
}
}
}
使用方法:
gcc -g pcap_file_parse.c -o pcap_file_parse.c
假设要解析的pcap文件为test.pcap,有两种方法,一种是解析结果直接输出到屏幕上,另一种是写到指定的文件中,分别对应
./pcap_file_parse test.pcap
./pcap_file_parse test.pcap > output.txt
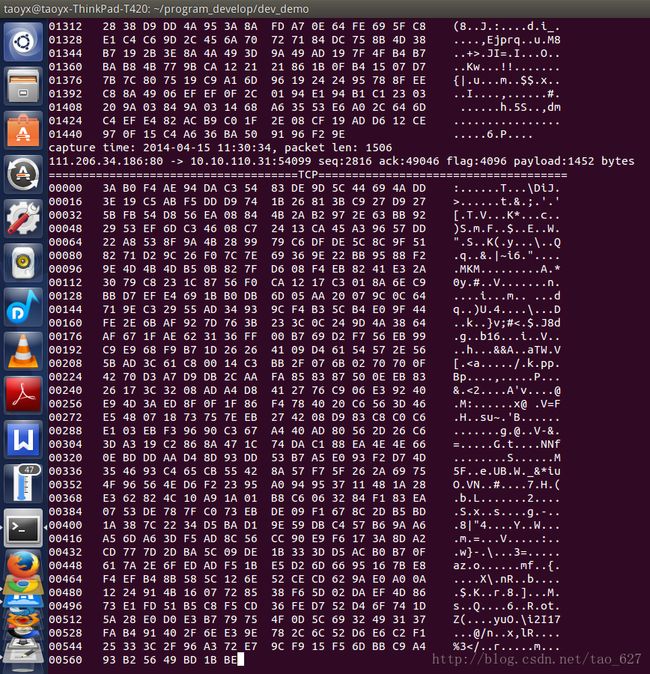
下面是代码运行效果图
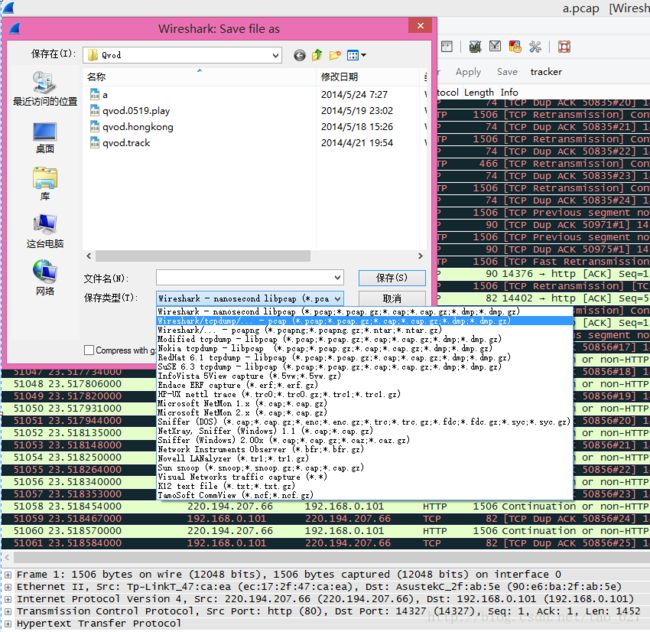
应该注意的问题
1.使用wireshark等抓包时,必须存为pcap文件格式,否则上面的代码解析将会出错.参见下面的截图