HTTP2.0协议初探(一)
最近需要接触到HTTP2.0的测试工作,所以需要对HTTP2.0协议由浅至深进行了解,因此准备写一个系列的内容,目的是记录学习过程以及以后的工作。
协议简介
HTTP 全称为 HyperText Transfer Protocol,中文叫做超文本传输协议。用于 Web 应用层传输,是 Web 架构的核心,它至今公布有 3 个版本:
HTTP 0.9,只有基本的文本 GET 功能。
HTTP 1.0,完善的请求/响应模型,并将协议补充完整。
HTTP 1.1,在 1.0 基础上进行更新,增加了如 长久连接 keep-alive 与 chunked 等功能。
距最近 1999 年 6 月 HTTP 1.1 RFC 2616 发布以来至今已有 15 年。
而 HTTP 2.0 首个 draft 已于 2012 年 11 月发布,预计到明年初正式发布。它保证了与 HTTP 1.1 的完全语义兼容,最初考虑的是 Google SPDY 协议、微软的 SM 协议和 Network-Friendly HTTP 更新。最终各方推荐了 SPDY 协议,并在此基础上进行了相应更新。
HTTP 2.0 相比 1.1 的更新大部分集中于:
多路复用
HEAD 压缩
服务器推送
优先级请求
在目前的开发过程中,已经有很多公司的产品开始支持HTTP2.0,详细内容可以参见
详细支持列表
在这次的实际探究过程中,采用nghttp2工具进行Client以及Server的模拟交互,以后可能也会考虑其他工具的兼容性。
HTTP2.0内容
官方协议
HTTP2.0是由互联网工程任务组(IETF)的Hypertext Transfer Protocol Bis (httpbis)工作小组进行开发,目前稳定的协议版本内容选用draft-13,具体协议内容可以参考
Hypertext Transfer Protocol version 2
draft-ietf-httpbis-http2-13报文交互
nghttp2.0工具使用:
在linux下编译安装nghttp2.0,完成后就可以模拟HTTP2.0的客户端以及服务器,开启服务器端口进程:
nghttpd –no-tls 8080 -v -d /home/chenyan/Documents/html/
开启成功后,使用客户端访问服务器端口:
nghttp http://172.16.75.84:8080/1b.html -H':method:HEAD' -v如果成功后,设备打印信息如下:
客户端:
[ 0.000] send SETTINGS frame <length=12, flags=0x00, stream_id=0>
(niv=2)
[SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS(0x03):100]
[SETTINGS_INITIAL_WINDOW_SIZE(0x04):65535]
[ 0.001] send HEADERS frame <length=49, flags=0x05, stream_id=1>
; END_STREAM | END_HEADERS
(padlen=0)
; Open new stream
:authority: 172.16.75.84:8080
:method: HEAD
:path: /1b.html
:scheme: http
accept: */*
accept-encoding: gzip, deflate
user-agent: nghttp2/0.5.0
[ 0.004] recv SETTINGS frame <length=6, flags=0x00, stream_id=0>
(niv=1)
[SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS(0x03):100]
[ 0.005] send SETTINGS frame <length=0, flags=0x01, stream_id=0>
; ACK
(niv=0)
[ 0.005] recv SETTINGS frame <length=0, flags=0x01, stream_id=0>
; ACK
(niv=0)
[ 0.005] (stream_id=1, noind=0) :status: 200
[ 0.005] (stream_id=1, noind=0) server: nghttpd nghttp2/0.5.0
[ 0.005] (stream_id=1, noind=0) content-length: 2
[ 0.005] (stream_id=1, noind=0) cache-control: max-age=3600
[ 0.005] (stream_id=1, noind=0) date: Mon, 09 Mar 2015 07:58:59 GMT
[ 0.005] (stream_id=1, noind=0) last-modified: Mon, 17 Nov 2014 11:54:39 GMT
[ 0.005] recv HEADERS frame <length=81, flags=0x04, stream_id=1>
; END_HEADERS
(padlen=0)
; First response header
1
[ 0.005] recv DATA frame <length=2, flags=0x00, stream_id=1>
[ 0.005] recv DATA frame <length=0, flags=0x01, stream_id=1>
; END_STREAM
[ 0.005] send GOAWAY frame <length=8, flags=0x00, stream_id=0>
(last_stream_id=0, error_code=NO_ERROR(0x00), opaque_data(0)=[])服务器:
[id=1] [787.796] send SETTINGS frame <length=6, flags=0x00, stream_id=0>
(niv=1)
[SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS(0x03):100]
[id=1] [787.797] closed
[id=1] [792.803] send SETTINGS frame <length=6, flags=0x00, stream_id=0>
(niv=1)
[SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS(0x03):100]
[id=1] [792.803] closed
[id=1] [797.809] send SETTINGS frame <length=6, flags=0x00, stream_id=0>
(niv=1)
[SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS(0x03):100]
[id=1] [797.809] closed
[id=1] [17702.195] send SETTINGS frame <length=6, flags=0x00, stream_id=0>
(niv=1)
[SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS(0x03):100]
[id=1] [17702.199] recv SETTINGS frame <length=12, flags=0x00, stream_id=0>
(niv=2)
[SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS(0x03):100]
[SETTINGS_INITIAL_WINDOW_SIZE(0x04):65535]
[id=1] [17702.199] (stream_id=1, noind=0) :authority: 172.16.75.84:8080
[id=1] [17702.199] (stream_id=1, noind=0) :method: HEAD
[id=1] [17702.199] (stream_id=1, noind=0) :path: /1b.html
[id=1] [17702.199] (stream_id=1, noind=0) :scheme: http
[id=1] [17702.199] (stream_id=1, noind=0) accept: */*
[id=1] [17702.199] (stream_id=1, noind=0) accept-encoding: gzip, deflate
[id=1] [17702.199] (stream_id=1, noind=0) user-agent: nghttp2/0.5.0
[id=1] [17702.199] recv HEADERS frame <length=49, flags=0x05, stream_id=1>
; END_STREAM | END_HEADERS
(padlen=0)
; Open new stream
[id=1] [17702.199] send SETTINGS frame <length=0, flags=0x01, stream_id=0>
; ACK
(niv=0)
[id=1] [17702.199] send HEADERS frame <length=81, flags=0x04, stream_id=1>
; END_HEADERS
(padlen=0)
; First response header
:status: 200
cache-control: max-age=3600
content-length: 2
date: Mon, 09 Mar 2015 07:58:59 GMT
last-modified: Mon, 17 Nov 2014 11:54:39 GMT
server: nghttpd nghttp2/0.5.0
[id=1] [17702.199] send DATA frame <length=2, flags=0x00, stream_id=1>
[id=1] [17702.199] send DATA frame <length=0, flags=0x01, stream_id=1>
; END_STREAM
[id=1] [17702.199] stream_id=1 closed
[id=1] [17702.200] recv SETTINGS frame <length=0, flags=0x01, stream_id=0>
; ACK
(niv=0)
[id=1] [17702.200] recv GOAWAY frame <length=8, flags=0x00, stream_id=0>
(last_stream_id=0, error_code=NO_ERROR(0x00), opaque_data(0)=[])
[id=1] [17702.200] closed如果仔细阅读上述的log信息,也就能大概理解整个报文交互过程,但是为了更加深入研究,采用wireshark抓包进行分析效果更好。
先将抓到的.cap文件导入wireshark,找到具体的TCP交互内容,右键选择Follow TCP stream,再次右键选择Decode As…由于wireshark早已支持了HTTP2.0,所以在transport中选择HTTP2.0,Apply后就可以查看整个报文信息了。

首先分析第一个报文:
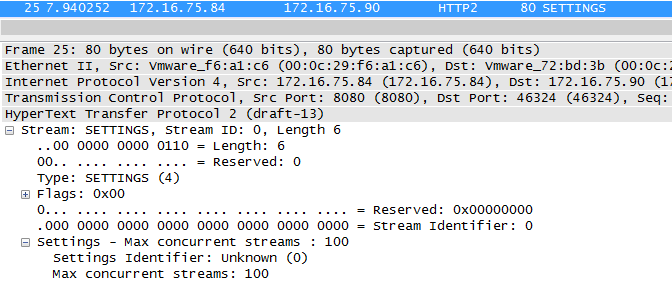
在TCP三次握手结束之后,Server回发送一个Setting报文,其中包括了server上的一些配置信息,比如最大同时连接数等
6.5.2. Defined SETTINGS Parameters
The following parameters are defined:
SETTINGS_HEADER_TABLE_SIZE (0x1):
Allows the sender to inform the remote endpoint of the maximum size of the header compression table used to decode header blocks. The> encoder can select any size equal to or less than this value by using signaling specific to the header compression format inside a header block. The initial value is 4,096 bytes.SETTINGS_ENABLE_PUSH (0x2):
This setting can be use to disable server push [PushResources]. An endpoint MUST NOT send a PUSH_PROMISE [PUSH_PROMISE] frame if it receives this parameter set to a value of 0. An endpoint that has both set this parameter to 0 and had it acknowledged MUST treat the receipt of a PUSH_PROMISE [PUSH_PROMISE] frame as a connection error [ConnectionErrorHandler] of type PROTOCOL_ERROR [PROTOCOL_ERROR]. The initial value is 1, which indicates that server push is permitted. Any value other than 0 or 1 MUST be treated as a connection error [ConnectionErrorHandler] of type PROTOCOL_ERRORSETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS (0x3):
Indicates the maximum number of concurrent streams that the sender will allow. This limit is directional: it applies to the number of streams that the sender permits the receiver to create. Initially there is no limit to this value. It is recommended that this value be no smaller than 100, so as to not unnecessarily limit parallelism. A value of 0 for SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS SHOULD NOT be treated as special by endpoints. A zero value does prevent the creation of new streams, however this can also happen for any limit that is exhausted with active streams. Servers SHOULD only set a zero value for short durations; if a server does not wish to accept requests, closing the connection could be preferable.SETTINGS_INITIAL_WINDOW_SIZE (0x4):
Indicates the sender's initial window size (in bytes) for stream level flow control. The initial value is 65,535. This setting affects the window size of all streams, including existing streams, see Section 6.9.2. Values above the maximum flow control window size of 2^31 - 1 MUST be treated as a connection error [ConnectionErrorHandler] of type FLOW_CONTROL_ERROR [FLOW_CONTROL_ERROR].An endpoint that receives a SETTINGS frame with any unknown or unsupported identifier MUST ignore that setting.
在nghttp2中,如果Client没有收到来自server的setting参数时,会断开HTTP连接,并且会有如下提示
[ 0.001] send SETTINGS frame <length=12, flags=0x00, stream_id=0>
(niv=2)
[SETTINGS_MAX_CONCURRENT_STREAMS(0x03):100]
[SETTINGS_INITIAL_WINDOW_SIZE(0x04):65535]
[ 0.001] send HEADERS frame <length=42, flags=0x05, stream_id=1>
; END_STREAM | END_HEADERS
(padlen=0)
; Open new stream
:authority: 10.1.1.11
:method: HEAD
:path: /1b.html
:scheme: http
accept: */*
accept-encoding: gzip, deflate
user-agent: nghttp2/0.5.0
[ 10.011] send GOAWAY frame <length=8, flags=0x00, stream_id=0>
(last_stream_id=0, error_code=SETTINGS_TIMEOUT(0x04), opaque_data(0)=[])
Some requests were not processed. total=1, processed=0当Client收到setting报文后,就需要根据服务器的setting信息,发送自己的请求了:
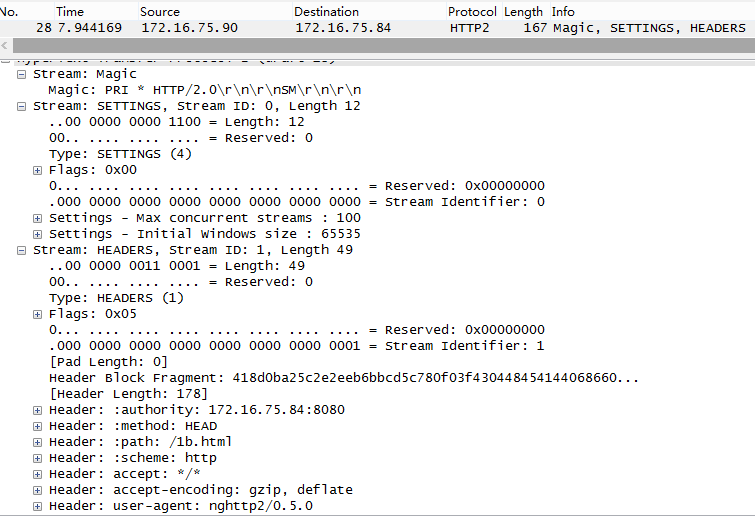
首先是Magic头,其中包含了HTTP2.0自定义的信息如RFC所描述:
Upon establishment of a TCP connection and determination that HTTP/2
will be used by both peers, each endpoint MUST send a connection
preface as a final confirmation and to establish the initial SETTINGS
parameters for the HTTP/2 connection.The client connection preface starts with a sequence of 24 octets,
which in hex notation are:
0x505249202a20485454502f322e300d0a0d0a534d0d0a0d0a(the string PRI * HTTP/2.0\r\n\r\nSM\r\n\r\n). This sequence is
followed by a SETTINGS [SETTINGS] frame (Section 6.5).
作用按照现在的理解为,表明Client的连接类型为HTTP2.0,涉及到与HTTP1.1的兼容问题;然后为setting头,表明Client接受服务器的配置,并且定义此次连接的其他参数;最后为header头,类似于HTTP1.1内容一样,同样也包含method、path、accept、user-agent等信息,其中关注到authority头,内容和HTTP1.1的host字段类似,但是比host内容附加了端口号信息。
确认服务器的返回信息:
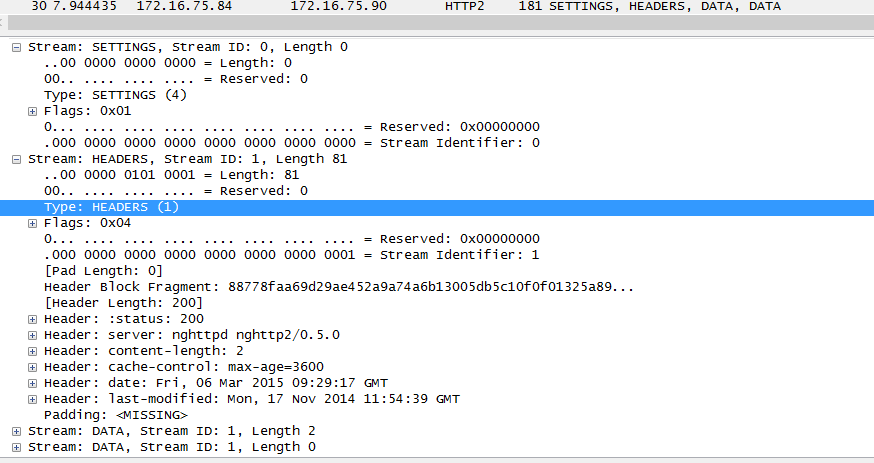
在返回报文中,也包含了setting报文头,但是整个报文头内没有任何的setting信息,同样的,返回的报文头header里面,client请求方法为head,服务器只应该返回头内容,所以返回的status、server、content-length等字段完全正确,可是出现了DATA头,并且包含了body内容,理论上应该只有get操作会出现这种结果。
最后为HTTP2.0断开连接的过程:
client在发送一个空的setting报文后,发送了端口连接的goaway头,在goaway头中,包括了一个error字段,表明此次连接没有出现问题,正常断开连接,而在上述说到的没有得到setting值的交互中,client断开连接的goway报文,明显带有断开原因,如图所示:

- 总结
第一章到此结束,再以后的探究过程中,会重点解决上述问题,并且会关注到其他请求方式的处理过程,同时会考虑与HTTP1.1的兼容性问题。
