Android项目中遇到的坑之(Android圆角圆形图 二)
接着上一篇的问题来研究研究:
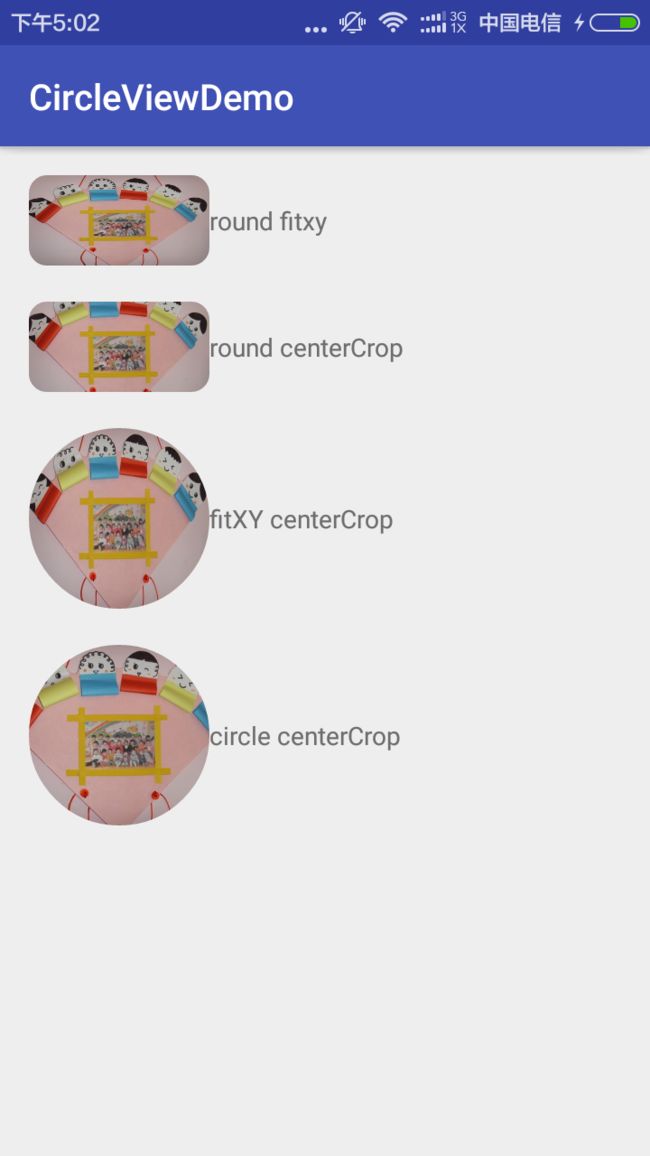
**问题来了:效果是有了,但有发现么?我设置的scaleType只有fitxy
是有效果的,其他的都没有效果了。设置为其他的scaleType都变成matrix那种效果了,也就是图片默认从控件的左上角开始摆放。**
我们先看看ImageView的scaleType
以下内容来自http://www.2cto.com/kf/201411/348601.html
让我们看看scaleType的各类效果图:
ImageView的scaleType的属性有好几种,分别是matrix(默认)、center、centerCrop、centerInside、fitCenter、fitEnd、fitStart、fitXY
android:scaleType=”center”
保持原图的大小,显示在ImageView的中心。当原图的size大于ImageView的size,超过部分裁剪处理。
android:scaleType=”centerCrop”
以填满整个ImageView为目的,将原图的中心对准ImageView的中心,等比例放大原图,直到填满ImageView为止(指的是ImageView的宽和高都要填满),原图超过ImageView的部分作裁剪处理。
android:scaleType=”centerInside”
以原图完全显示为目的,将图片的内容完整居中显示,通过按比例缩小原图的size宽(高)等于或小于ImageView的宽(高)。如果原图的size本身就小于ImageView的size,则原图的size不作任何处理,居中显示在ImageView。
android:scaleType=”matrix”
不改变原图的大小,从ImageView的左上角开始绘制原图,原图超过ImageView的部分作裁剪处理。
android:scaleType=”fitCenter”
把原图按比例扩大或缩小到ImageView的ImageView的高度,居中显示
android:scaleType=”fitEnd”
把原图按比例扩大(缩小)到ImageView的高度,显示在ImageView的下部分位置
android:scaleType=”fitStart”
把原图按比例扩大(缩小)到ImageView的高度,显示在ImageView的上部分位置
android:scaleType=”fitXY”
把原图按照指定的大小在View中显示,拉伸显示图片,不保持原比例,填满ImageView.
下面附上效果图:
原图为Pocoyo的头像,上图为原图的size大于ImageView的size,下图为原图的size小于ImageView的size

已经展示的很清楚了,也就是说我们的RoundImageView只支持fitxy跟martrix两种方式,我们看看ImageView的源码找找原因
问题1:为什么只支持fitxy跟matrix方式呢?
我们看看ImageView源码
private void configureBounds() {
if (mDrawable == null || !mHaveFrame) {
return;
}
final int dwidth = mDrawableWidth;
final int dheight = mDrawableHeight;
final int vwidth = getWidth() - mPaddingLeft - mPaddingRight;
final int vheight = getHeight() - mPaddingTop - mPaddingBottom;
final boolean fits = (dwidth < 0 || vwidth == dwidth)
&& (dheight < 0 || vheight == dheight);
if (dwidth <= 0 || dheight <= 0 || ScaleType.FIT_XY == mScaleType) {
/* If the drawable has no intrinsic size, or we're told to
scaletofit, then we just fill our entire view.
*/
mDrawable.setBounds(0, 0, vwidth, vheight);
mDrawMatrix = null;
} else {
......
}
}我们看到这么一行代码:
mDrawable.setBounds(0, 0, vwidth, vheight);当为fitxy的时候给mDrawable(也就是我们设置的那张图片)设置了bounds为vwidth,vheight,也就是控件的宽高。所以fitxy时才会铺满整个屏幕的。
搞懂了fitxy,那么matrix又是怎么样的呢?
我们看看onDraw方法:
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
if (mDrawable == null) {
return; // couldn't resolve the URI
}
if (mDrawableWidth == 0 || mDrawableHeight == 0) {
return; // nothing to draw (empty bounds)
}
if (mDrawMatrix == null && mPaddingTop == 0 && mPaddingLeft == 0) {
mDrawable.draw(canvas);
} else {
final int saveCount = canvas.getSaveCount();
canvas.save();
if (mCropToPadding) {
final int scrollX = mScrollX;
final int scrollY = mScrollY;
canvas.clipRect(scrollX + mPaddingLeft, scrollY + mPaddingTop,
scrollX + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight,
scrollY + mBottom - mTop - mPaddingBottom);
}
canvas.translate(mPaddingLeft, mPaddingTop);
if (mDrawMatrix != null) {
canvas.concat(mDrawMatrix);
}
mDrawable.draw(canvas);
canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount);
}
}有点长,我们看到有一行代码:
if (mDrawMatrix != null) {
canvas.concat(mDrawMatrix);
}canvas.concat(mDrawMatrix);是指给canvas做一些改变,比如缩放、平移…… 也就是说源码中通过我们设置的scaleType来通过算法计算mDrawMatrix ,然后再onDraw方法中赋给了canvas,但是我们重写了onDraw方法,也就是说mDrawMatrix 压根就不起作用了,所以当我们在RoundImageView中执行
//最后把我们准备好的Bitmap画在canvas上
canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap,0,0,null);的时候,图片就是默认不缩放,原图从控件的左上角开始摆放的。
到此,我们终于弄懂了我们遇到的问题,既然遇到了,那我们就解决下问题。
我们看看ImageView到底是怎么缩放图片的:
private void configureBounds() {
if (mDrawable == null || !mHaveFrame) {
return;
}
final int dwidth = mDrawableWidth;
final int dheight = mDrawableHeight;
final int vwidth = getWidth() - mPaddingLeft - mPaddingRight;
final int vheight = getHeight() - mPaddingTop - mPaddingBottom;
final boolean fits = (dwidth < 0 || vwidth == dwidth)
&& (dheight < 0 || vheight == dheight);
if (dwidth <= 0 || dheight <= 0 || ScaleType.FIT_XY == mScaleType) {
/* If the drawable has no intrinsic size, or we're told to
scaletofit, then we just fill our entire view.
*/
mDrawable.setBounds(0, 0, vwidth, vheight);
mDrawMatrix = null;
} else {
// We need to do the scaling ourself, so have the drawable
// use its native size.
mDrawable.setBounds(0, 0, dwidth, dheight);
if (ScaleType.MATRIX == mScaleType) {
// Use the specified matrix as-is.
if (mMatrix.isIdentity()) {
mDrawMatrix = null;
} else {
mDrawMatrix = mMatrix;
}
} else if (fits) {
// The bitmap fits exactly, no transform needed.
mDrawMatrix = null;
} else if (ScaleType.CENTER == mScaleType) {
// Center bitmap in view, no scaling.
mDrawMatrix = mMatrix;
mDrawMatrix.setTranslate(Math.round((vwidth - dwidth) * 0.5f),
Math.round((vheight - dheight) * 0.5f));
} else if (ScaleType.CENTER_CROP == mScaleType) {
mDrawMatrix = mMatrix;
float scale;
float dx = 0, dy = 0;
if (dwidth * vheight > vwidth * dheight) {
scale = (float) vheight / (float) dheight;
dx = (vwidth - dwidth * scale) * 0.5f;
} else {
scale = (float) vwidth / (float) dwidth;
dy = (vheight - dheight * scale) * 0.5f;
}
mDrawMatrix.setScale(scale, scale);
mDrawMatrix.postTranslate(Math.round(dx), Math.round(dy));
} else if (ScaleType.CENTER_INSIDE == mScaleType) {
mDrawMatrix = mMatrix;
float scale;
float dx;
float dy;
if (dwidth <= vwidth && dheight <= vheight) {
scale = 1.0f;
} else {
scale = Math.min((float) vwidth / (float) dwidth,
(float) vheight / (float) dheight);
}
dx = Math.round((vwidth - dwidth * scale) * 0.5f);
dy = Math.round((vheight - dheight * scale) * 0.5f);
mDrawMatrix.setScale(scale, scale);
mDrawMatrix.postTranslate(dx, dy);
} else {
// Generate the required transform.
mTempSrc.set(0, 0, dwidth, dheight);
mTempDst.set(0, 0, vwidth, vheight);
mDrawMatrix = mMatrix;
mDrawMatrix.setRectToRect(mTempSrc, mTempDst, scaleTypeToScaleToFit(mScaleType));
}
}
}就是我们上面所说的,先通过我们设置的scaleType计算mDrawMatrix,
然后再onDraw方法中赋给canvans,再贴一遍ImageView的onDraw方法。
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
if (mDrawable == null) {
return; // couldn't resolve the URI
}
if (mDrawableWidth == 0 || mDrawableHeight == 0) {
return; // nothing to draw (empty bounds)
}
if (mDrawMatrix == null && mPaddingTop == 0 && mPaddingLeft == 0) {
mDrawable.draw(canvas);
} else {
final int saveCount = canvas.getSaveCount();
canvas.save();
if (mCropToPadding) {
final int scrollX = mScrollX;
final int scrollY = mScrollY;
canvas.clipRect(scrollX + mPaddingLeft, scrollY + mPaddingTop,
scrollX + mRight - mLeft - mPaddingRight,
scrollY + mBottom - mTop - mPaddingBottom);
}
canvas.translate(mPaddingLeft, mPaddingTop);
if (mDrawMatrix != null) {
canvas.concat(mDrawMatrix);
}
mDrawable.draw(canvas);
canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount);
}
}我们自己重写了onDraw方法,也就是我们只需要像ImageView一样,把configureBounds方法搬到我们的控件中就可以了,好了,我们试试:
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
Bitmap bitmap = mWeakReference==null?null:mWeakReference.get();
if(bitmap==null || bitmap.isRecycled()){
//获取一下设置的图片资源
Drawable drawable=getDrawable();
if(drawable!=null){
//创建一个空白画布,用来画模板跟原图
bitmap=Bitmap.createBitmap(getWidth(),getHeight(),Bitmap.Config.ARGB_8888);
////修改过的代码
Matrix matrix=null;
Canvas dstCanvas=new Canvas(bitmap);
dstCanvas.save();
if (getScaleType()==ScaleType.FIT_XY){
drawable.setBounds(0,0,getWidth(),getHeight());
matrix=null;
}else{
matrix=new Matrix();
configureBounds(drawable,matrix);
}
if(matrix!=null){
dstCanvas.concat(matrix);
}
drawable.draw(dstCanvas);
dstCanvas.restore();
////修改过的代码
//画模板
if(mMaskBitmap==null||mMaskBitmap.isRecycled()){
mMaskBitmap=getShapeBitmap();
}
dstCanvas.drawBitmap(mMaskBitmap,0,0,mPaint);
mPaint.setXfermode(null);
}
}
//最后把我们准备好的Bitmap画在canvas上
canvas.drawBitmap(bitmap,0,0,null);
}private void configureBounds(Drawable drawable, Matrix matrix) {
ScaleType mScaleType = getScaleType();
//获取图片的宽高
int dwidth = drawable.getIntrinsicWidth();
int dheight = drawable.getIntrinsicHeight();
int vwidth =getWidth();
int vheight = getHeight();
if (ScaleType.MATRIX == mScaleType) {
/////
} else if (ScaleType.CENTER_CROP == mScaleType) {
float scale;
float dx = 0, dy = 0;
if (dwidth * vheight > vwidth * dheight) {
scale = (float) vheight / (float) dheight;
dx = (vwidth - dwidth * scale) * 0.5f;
} else {
scale = (float) vwidth / (float) dwidth;
dy = (vheight - dheight * scale) * 0.5f;
}
matrix.setScale(scale, scale);
matrix.postTranslate(Math.round(dx), Math.round(dy));
} else if (ScaleType.CENTER_INSIDE == mScaleType) {
float scale;
float dx;
float dy;
if (dwidth <= vwidth && dheight <= vheight) {
scale = 1.0f;
} else {
scale = Math.min((float) vwidth / (float) dwidth,
(float) vheight / (float) dheight);
}
dx = Math.round((vwidth - dwidth * scale) * 0.5f);
dy = Math.round((vheight - dheight * scale) * 0.5f);
matrix.setScale(scale, scale);
matrix.postTranslate(dx, dy);
} else {
matrix.setRectToRect(new RectF(drawable.getBounds()), new RectF(0, 0, getWidth(), getHeight()), scaleTypeToScaleToFit(mScaleType));
}
}直接拖的ImageView的源码,不要问我算法为什么是这样,我也研究了蛮久,数学不好(^__^) 嘻嘻……
到这又郁闷了,scaleTypeToScaleToFit方法没法copy了,怎么办? 反射呗!说干咱就干。
private Matrix.ScaleToFit scaleTypeToScaleToFit(ScaleType mScaleType) {
Class mClass=ImageView.class;
try {
Method method = mClass.getDeclaredMethod("scaleTypeToScaleToFit", new Class[]{ScaleType.class});
method.setAccessible(true);
if(method!=null){
Matrix.ScaleToFit fit = (Matrix.ScaleToFit) (method.invoke(null, new Object[]{mScaleType}));
return fit;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return Matrix.ScaleToFit.FILL;
}不懂的童鞋自己去脑补下javase的东西哈!!
终于是完美的呈现了,从来没写过这么长的博客,小伙伴默默点个赞哈,大牛勿喷!!(^__^) 嘻嘻……
最后附上github地址:https://github.com/913453448/CircleViewDemo