K8S使用dashboard管理集群
今年3月份在公司的内部k8s培训会上,开发同事表示使用dashboard的可以满足日常开发需求,例如查看pod的日志,执行exec指令,查看pod的运行状态等,但对basic认证的权限控制表示担忧。
之前介绍过在1.5.2版本上部署dashboard服务,在1.9.1版本离线部署中,也介绍过dashboard服务的RBAC配置和使用技巧。因此本文将在前文基础上完善Heapster的整合与利用token对用户权限进行控制。
dashboard的特点主要如下:
1、能够直观的看到rc、deployment、pod、services等k8s组件的运行情况和日志信息。
2、结合heapster和influxdb后,dashboard的监控图表上可以看到pod的cpu和内存消耗情况。
Heapster介绍
1、Heapster是容器集群监控和性能分析工具,支持Kubernetes和CoreOS。
2、K8S集群的HPA功能的实现就依赖于这些metric数据,HPA将Heapster作为Resource Metrics API,向其获取metric。
3、Kubernetes有个cAdvisor监控(在1.9版本里面,cAdvisor已经和kubelet整合在一起)。
在每个kubernetes Node上都会运行cAdvisor,它会收集本机以及容器的监控数据(cpu,memory,filesystem,network,uptime)。Heapster是一个收集者,Heapster可以收集Node节点上的cAdvisor数据,将每个Node上的cAdvisor的数据进行汇总,还可以按照kubernetes的资源类型来集合资源,比如Pod、Namespace,可以分别获取它们的CPU、内存、网络和磁盘的metric。默认的metric数据聚合时间间隔是1分钟。还可以把数据导入到第三方工具(如InfluxDB)。
Influxdb数据库介绍
2、Influxdb数据库的相关知识介绍,可参考文档:https://www.jianshu.com/p/d2935e99006e
2、如果对Heapster收集到的metric数据没有持久化的需求,可以不配置Influxdb数据库
3、本文Influxdb数据库的存储采用emptydir的方式实现,实际使用过程中,可以选择吧Influxdb数据库部署在k8s集群外部,或者使用其他存储方案。
4、如果有需要的话,还可以集成一个grafana做web展示。Grafana配置可参考文档:http://blog.51cto.com/ylw6006/2084403
一、获取相关镜像
需要科学上网方式获取到dashboard相关的镜像文件,仓库可纳入本地仓库统一管理
# cat /etc/systemd/system/docker.service.d/http-proxy.conf
[Service]
Environment="HTTP_PROXY=http://192.168.115.2:1080"
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl restart docker
# docker pull k8s.gcr.io/kubernetes-dashboard-amd64:v1.8.3
# docker pull k8s.gcr.io/heapster-influxdb-amd64:v1.3.3
# docker pull k8s.gcr.io/heapster-amd64:v1.4.2二、准备配置文件
1、k8s-dashborad-sa.yaml文件,secrct和serviceaccount配置
# cat k8s-dashborad-sa.yaml
# ------------------- Dashboard Secret ------------------- #
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
namespace: kube-system
type: Opaque
---
# ------------------- Dashboard Service Account ------------------- #
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system2、k8s-dashborad-rbac.yaml文件,配置 Role和Role Binding
# cat k8s-dashborad-rbac.yaml
# ------------------- Dashboard Role & Role Binding ------------------- #
kind: Role
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: kubernetes-dashboard-minimal
namespace: kube-system
rules:
# Allow Dashboard to create 'kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder' secret.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
verbs: ["create"]
# Allow Dashboard to create 'kubernetes-dashboard-settings' config map.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
verbs: ["create"]
# Allow Dashboard to get, update and delete Dashboard exclusive secrets.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["secrets"]
resourceNames: ["kubernetes-dashboard-key-holder", "kubernetes-dashboard-certs"]
verbs: ["get", "update", "delete"]
# Allow Dashboard to get and update 'kubernetes-dashboard-settings' config map.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["configmaps"]
resourceNames: ["kubernetes-dashboard-settings"]
verbs: ["get", "update"]
# Allow Dashboard to get metrics from heapster.
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services"]
resourceNames: ["heapster"]
verbs: ["proxy"]
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["services/proxy"]
resourceNames: ["heapster", "http:heapster:", "https:heapster:"]
verbs: ["get"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: RoleBinding
metadata:
name: kubernetes-dashboard-minimal
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: Role
name: kubernetes-dashboard-minimal
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system3、k8s-dashborad-deployment.yaml配置文件,定义创建pod的模板和副本数
# cat k8s-dashborad-deployment.yaml
# ------------------- Dashboard Deployment ------------------- #
kind: Deployment
apiVersion: apps/v1beta2
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system
spec:
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
template:
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
spec:
containers:
- name: kubernetes-dashboard
image: k8s.gcr.io/kubernetes-dashboard-amd64:v1.8.3
ports:
- containerPort: 8443
protocol: TCP
args:
- --auto-generate-certificates
# Uncomment the following line to manually specify Kubernetes API server Host
# If not specified, Dashboard will attempt to auto discover the API server and connect
# to it. Uncomment only if the default does not work.
# - --apiserver-host=http://my-address:port
volumeMounts:
- name: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
mountPath: /certs
# Create on-disk volume to store exec logs
- mountPath: /tmp
name: tmp-volume
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
scheme: HTTPS
path: /
port: 8443
initialDelaySeconds: 30
timeoutSeconds: 30
volumes:
- name: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
secret:
secretName: kubernetes-dashboard-certs
- name: tmp-volume
emptyDir: {}
serviceAccountName: kubernetes-dashboard
# Comment the following tolerations if Dashboard must not be deployed on master
tolerations:
- key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master
effect: NoSchedule4、 k8s-dashborad-service.yaml配置文件,定义service
# cat k8s-dashborad-service.yaml
# ------------------- Dashboard Service ------------------- #
kind: Service
apiVersion: v1
metadata:
labels:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard
name: kubernetes-dashboard
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- port: 443
targetPort: 8443
nodePort: 8490
type: NodePort
selector:
k8s-app: kubernetes-dashboard三、通过配置文件创建dashboard
# kubectl create -f .
# kubectl get pod,deployment,svc -n kube-system四、配置使用basic认证方式
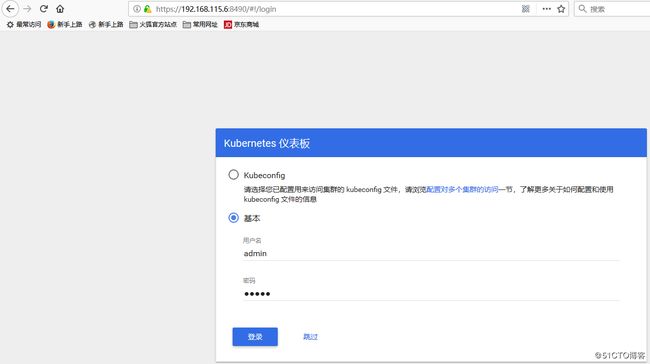
# echo 'admin,admin,1' > /etc/kubernetes/basic_auth_file
# grep 'auth' /usr/lib/systemd/system/kube-apiserver.service
--authorization-mode=Node,RBAC \
--runtime-config=rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1alpha1 \
--enable-bootstrap-token-auth=true \
--token-auth-file=/etc/kubernetes/token.csv \
--basic-auth-file=/etc/kubernetes/basic_auth_file \
# grep ‘basic’ k8s-dashborad-deployment.yaml (配置在args下面)
- --authentication-mode=basic
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl restart kube-apiserver
# kubectl apply -f k8s-dashborad-deployment.yaml 将admin用户和cluter-admin role进行角色绑定
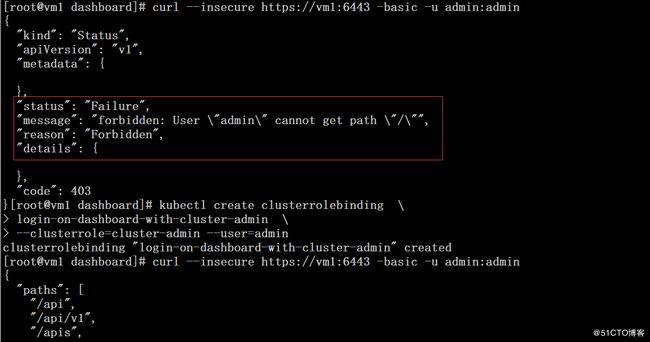
# curl --insecure https://vm1:6443 -basic -u admin:admin
# kubectl create clusterrolebinding \
login-on-dashboard-with-cluster-admin \
--clusterrole=cluster-admin --user=admin
# curl --insecure https://vm1:6443 -basic -u admin:admin 五、访问测试
六、整合heapster和influxdb
在没有配置heapster和influxdb的情况下,pod的metric信息是无法获取到的,而早前版本K8S的HPA特性依赖的metric数据来源恰巧就是heapster和influxdb。
1、准备yaml配置文件
# cat heapster-sa.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: heapster
namespace: kube-system# cat heapster-rbac.yaml
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
metadata:
name: heapster
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:heapster
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: heapster
namespace: kube-system# cat heapster-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: heapster
namespace: kube-system
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
k8s-app: heapster
spec:
serviceAccountName: heapster
containers:
- name: heapster
image: k8s.gcr.io/heapster-amd64:v1.4.2
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
command:
- /heapster
- --source=kubernetes:https://kubernetes.default
- --sink=influxdb:http://monitoring-influxdb.kube-system.svc:8086# cat heapster-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: 'true'
kubernetes.io/name: Heapster
name: heapster
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8082
selector:
k8s-app: heapster# cat influxdb-deployment.yaml
apiVersion: extensions/v1beta1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: monitoring-influxdb
namespace: kube-system
spec:
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
k8s-app: influxdb
spec:
containers:
- name: influxdb
image: k8s.gcr.io/heapster-influxdb-amd64:v1.3.3
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /data
name: influxdb-storage
volumes:
- name: influxdb-storage
emptyDir: {}# cat influxdb-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
task: monitoring
kubernetes.io/cluster-service: 'true'
kubernetes.io/name: monitoring-influxdb
name: monitoring-influxdb
namespace: kube-system
spec:
ports:
- port: 8086
targetPort: 8086
selector:
k8s-app: influxdb# kubectl run -i --tty curl --namespace=kube-system \
--image=registry.59iedu.com/webwurst/curl-utils /bin/sh
# curl http://heapster/api/v1/model/metrics
# curl http://heapster/api/v1/model/debug/allkeys # kubectl get node
# kubectl top node 
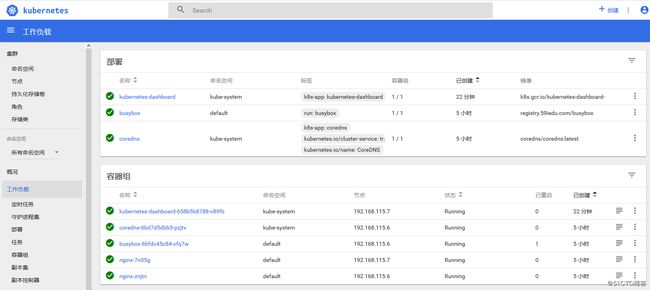
当heapster和influxdb pod都正常运行的时候,在dashboard里面就可以看到CPU和内存的监控数据了。
七、配置用户权限
1、删除apiserver里面basic认证相关的配置后重启apiserver
--basic-auth-file=/etc/kubernetes/basic_auth_file
# systemctl daemon-reload
# systemctl restart kube-apiserver2、删除clusterrolebinding
# kubectl delete clusterrolebinding login-on-dashboard-with-cluster-admin3、修改k8s-dashborad-deployment.yaml文件
去掉- --authentication-mode=basic参数
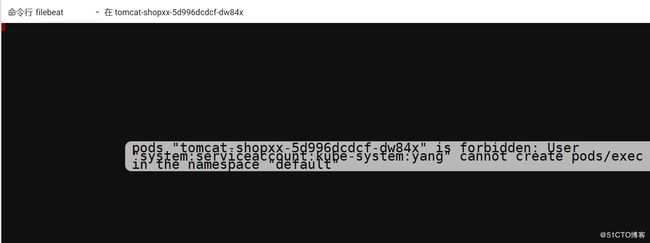
4、创建普通用户,赋予所有namespace下资源的get、watch和list权限。
这里通过clusterrole和culsterrolebinding赋予所有namespace相关资源的get、watch、list权限,实际应用环境建议使用创建role和rolebinding指定特定的namespace相关资源权限,各资源权限的赋予规则遵循最小权限原则。
# cat rbac-yang.yaml
kind: ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: role-yang
rules:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["get","watch","list" ]
- apiGroups: ["storage.k8s.io"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["get","watch","list" ]
- apiGroups: ["rbac.authorization.k8s.io"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["get","watch","list" ]
- apiGroups: ["batch"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["get","watch","list" ]
- apiGroups: ["apps"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["get","watch","list" ]
- apiGroups: ["extensions"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["get","watch","list" ]
---
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: role-bind-yang
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: yang
namespace: kube-system
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: role-yang
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io# kubectl create sa yang -n kube-system
# kubectl create -f rbac-yang.yaml
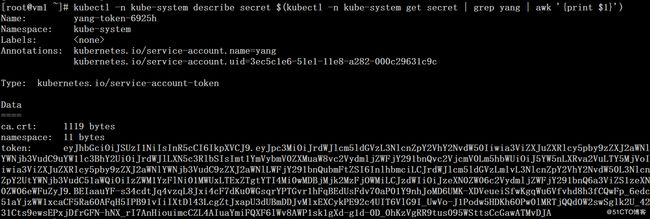
# kubectl -n kube-system describe secret $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | grep yang | awk '{print $1}')# kubectl create sa admin -n kube-system
# cat rbac-admin.yaml
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: admin
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-admin
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: admin
namespace: kube-system
# kubectl create -f rbac-admin.yaml
# kubectl -n kube-system describe secret $(kubectl -n kube-system get secret | grep admin | awk '{print $1}')
使用admin用户的token登陆后继承cluster-admin的权限
参考:
https://github.com/kubernetes/dashboard/wiki/Creating-sample-user
https://github.com/kubernetes/dashboard/wiki/Access-control
https://github.com/kubernetes/heapster/blob/master/docs/model.md