非极大值抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression,NMS)算法与c和python代码详解
背景:非极大值抑制算法(Non-maximum suppression, NMS)的本质是搜索局部极大值,抑制非极大值元素。在目标检测之中用到非常多。
目的:搞懂此算法原理且看懂代码。
目录
一、算法解析
1.1 算法概览
1.2 算法过程
二、c代码解析
2.1 输入参量
2.2 按置信概率排序
sort函数
2.3 IOU的确定
string.compare函数
vector.at函数
2.4 概率最大框保留,重叠抑制
vector::inerator
2.5 最终保留的框
三、python代码解析
np.empty
s_sort
3.1 按照置信概率排序
numpy.argsort函数
numpy.zeros_like函数
3.2 IOU的计算
一、算法解析
1.1 算法概览
非极大值抑制(Non-Maximum Suppression,NMS),顾名思义就是抑制不是极大值的元素,可以理解为局部最大搜索。这个局部代表的是一个邻域,邻域有两个参数可变,一是邻域的维数,二是邻域的大小。这里不讨论通用的NMS算法(参考论文《Efficient Non-Maximum Suppression》对1维和2维数据的NMS实现),而是用于目标检测中提取分数最高的窗口的。例如在行人检测中,滑动窗口经提取特征,经分类器分类识别后,每个窗口都会得到一个分数。但是滑动窗口会导致很多窗口与其他窗口存在包含或者大部分交叉的情况。这时就需要用到NMS来选取那些邻域里分数最高(是行人的概率最大),并且抑制那些分数低的窗口。
NMS在计算机视觉领域有着非常重要的应用,如视频目标跟踪、数据挖掘、3D重建、目标识别以及纹理分析等。
1.2 算法过程
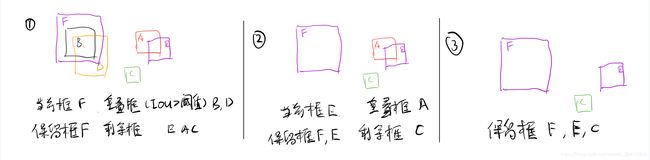
Step1:按置信概率排列相应的备选框
Step2:取最大的框作为保留框,与其IOU大于阈值的框删除掉
Step3:剩下的框执行Step2
很容易理解
根据候选框的类别分类概率做排序:A A 就这样一直重复下去,直到剩下的矩形框没有了,标记完所有要保留下来的矩形框 vector 其中包括四个点的坐标,置信概率,区域大小,是否存在的概率。 vector const float overlap_threshold, string modelname 分别为抑制框的IOU阈值与相应的nms的方法分为Union与Min 程序开始时,需要将相应的备选框排序 与之对应的cmpScore函数为: 头文件 http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/algorithm/sort/ 程序意思即对备选框按照置信概率升序排列(注意这里是置信概率,置信概率之中包含了原始的备选框的位置)。 这部分函数相当于确定num位置和order位置的bBox之间的IOU。 http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/compare/ string在c与python之中都有出现且常用,所以应当仔细研读,熟练运用。 返回值为0表示相等。modelname.compare("Union")表示modelname为 "Union"时候则返回0. http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/vector/at/ 概率最大的框的在Bbox向量组中的序列存于order之中,存于向量hero之中,然后当前boundingBox删掉,其exist设为false 与最大概率框IOU大于阈值的框也删掉。首先是boundingBox的exist设为false,然后bboxScore的oriOrder设为-1 http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/vector/vector/ 只是将最终保留的框的exist设为true,删掉的框exist设为false,但是其内存空间还是占用的。 https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.empty.html https://blog.csdn.net/HHTNAN/article/details/78590780 这个表示若是没有输入相应的框则返回空数组,数组中带0则数组不存在,输出为空 [] https://blog.csdn.net/HARDBIRD123/article/details/82261651 这部分代码计算了相应的区域的面积,然后运用numpy.argsort函数对置信概率进行排序。 https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.argsort.html 针对s排序的顺序存在s_sort数组之中。 https://docs.scipy.org/doc/numpy/reference/generated/numpy.zeros_like.html 返回一个与初始置信概率数组相同结构的数组 s=boxes[:,4],(这里数据类型为int16)。pick为最终选用的置信概率。
二、c代码解析
void nms(vector2.1 输入参量
struct Bbox
{
float score;
int x1;
int y1;
int x2;
int y2;
float area;
bool exist;
mydataFmt regreCoord[4];
};struct orderScore
{
mydataFmt score;
int oriOrder;
};2.2 按置信概率排序
//sort the score
sort(bboxScore_.begin(), bboxScore_.end(), cmpScore);bool cmpScore(struct orderScore lsh, struct orderScore rsh){
if(lsh.scoresort函数
2.3 IOU的确定
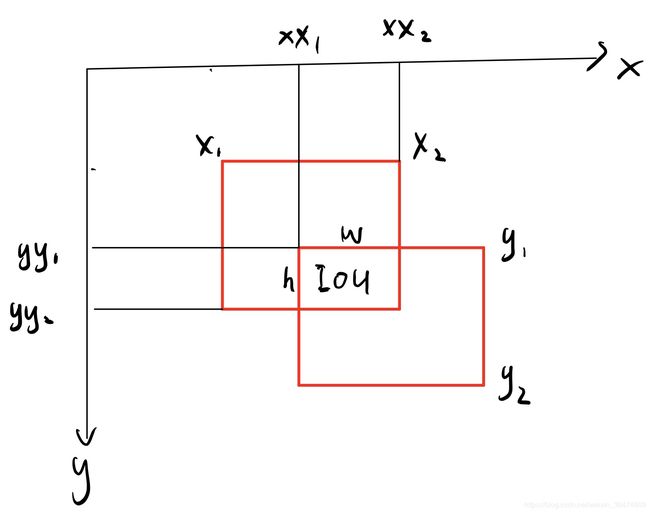
maxX = (boundingBox_.at(num).x1>boundingBox_.at(order).x1)?boundingBox_.at(num).x1:boundingBox_.at(order).x1;
maxY = (boundingBox_.at(num).y1>boundingBox_.at(order).y1)?boundingBox_.at(num).y1:boundingBox_.at(order).y1;
minX = (boundingBox_.at(num).x2string.compare函数
vector.at函数
std::vector2.4 概率最大框保留,重叠抑制
while(bboxScore_.size()>0){
order = bboxScore_.back().oriOrder;
bboxScore_.pop_back();
if(order<0)continue;
heros.push_back(order);
boundingBox_.at(order).exist = false;//delete itif(IOU>overlap_threshold){
boundingBox_.at(num).exist=false;
for(vectorvector::inerator
2.5 最终保留的框
for(int i=0;i三、python代码解析
def nms(boxes, threshold, method):
if boxes.size == 0:
return np.empty((0, 3))
x1 = boxes[:, 0]
y1 = boxes[:, 1]
x2 = boxes[:, 2]
y2 = boxes[:, 3]
s = boxes[:, 4]
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
s_sort = np.argsort(s)
pick = np.zeros_like(s, dtype=np.int16)
counter = 0
while s_sort.size > 0:
i = s_sort[-1]
pick[counter] = i
counter += 1
idx = s_sort[0:-1]
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[idx])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[idx])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[idx])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[idx])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
if method is 'Min':
o = inter / np.minimum(area[i], area[idx])
else:
o = inter / (area[i] + area[idx] - inter)
s_sort = s_sort[np.where(o <= threshold)]
pick = pick[0:counter]
return picknp.empty
if boxes.size == 0:
return np.empty((0, 3))s_sort
3.1 按照置信概率排序
def nms(boxes, threshold, method):
if boxes.size == 0:
return np.empty((0, 3))
x1 = boxes[:, 0]
y1 = boxes[:, 1]
x2 = boxes[:, 2]
y2 = boxes[:, 3]
s = boxes[:, 4]
area = (x2 - x1 + 1) * (y2 - y1 + 1)
s_sort = np.argsort(s)
pick = np.zeros_like(s, dtype=np.int16)
counter = 0numpy.argsort函数
numpy.zeros_like函数
3.2 IOU的计算
while s_sort.size > 0:
i = s_sort[-1]
pick[counter] = i
counter += 1
idx = s_sort[0:-1]
xx1 = np.maximum(x1[i], x1[idx])
yy1 = np.maximum(y1[i], y1[idx])
xx2 = np.minimum(x2[i], x2[idx])
yy2 = np.minimum(y2[i], y2[idx])
w = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 1)
h = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 1)
inter = w * h
if method is 'Min':
o = inter / np.minimum(area[i], area[idx])
else:
o = inter / (area[i] + area[idx] - inter)
s_sort = s_sort[np.where(o <= threshold)]