图像内容分类(KNN)
一、图像内容分类原理简介:
图像分类,根据各自在图像信息中所反映的不同特征,把不同类别的目标区分开来的图像处理方法。它利用计算机对图像进行定量分析,把图像或图像中的每个像元或区域划归为若干个类别中的某一种,以代替人的视觉判读。
二、分类方法:
1.基于色彩特征的索引技术
2.基于纹理的图像分类技术
3.基于形状的图像分类技术
4.基于空间关系的图像分类技术
三、KNN(K邻近分类法):
1.原理:
把分类对象(例如一个特征向量)与训练集中已知类标记的所有对象进行对比,并由K近邻对指派到哪一类进行投票。训练样本可能是数字,字符串等。
2.步骤:
距离计算方式的选择(一般选择欧氏距离或曼哈顿距离)
k值的选取(计算测试数据与各个训练数据之间的距离之后,按照距离递增次序进行排序,然后选取距离最小的k个点)
分类的决策规则(取k个近邻训练数据中类别出现次数最多者作为输入新实例的类别)
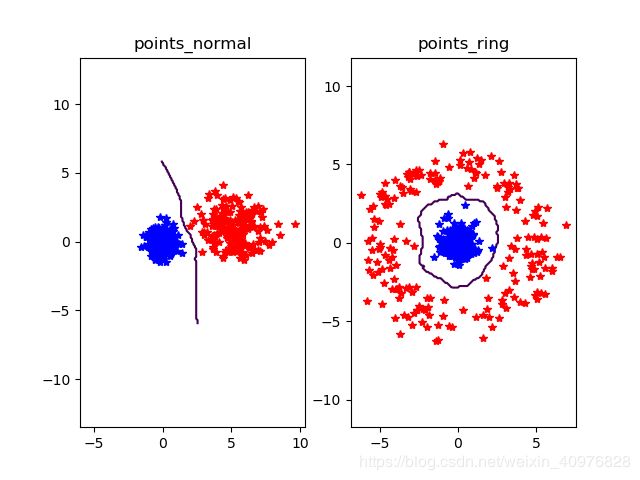
3.一个简单的二维示例:
(示例中,不同颜色代表类标记,正确的分类标记用星号表示,错误的用圆点表示,曲线为决策边界)
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from numpy.random import randn
import pickle
from pylab import *
# create sample data of 2D points
n = 200
# two normal distributions
class_1 = 0.6 * randn(n,2)
class_2 = 1.2 * randn(n,2) + array([5,1])
labels = hstack((ones(n),-ones(n)))
# save with Pickle
#with open('points_normal.pkl', 'w') as f:
with open('points_normal_test.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(class_1,f)
pickle.dump(class_2,f)
pickle.dump(labels,f)
# normal distribution and ring around it
print ("save OK!")
class_1 = 0.6 * randn(n,2)
r = 0.8 * randn(n,1) + 5
angle = 2*pi * randn(n,1)
class_2 = hstack((r*cos(angle),r*sin(angle)))
labels = hstack((ones(n),-ones(n)))
# save with Pickle
#with open('points_ring.pkl', 'w') as f:
with open('points_ring_test.pkl', 'wb') as f:
pickle.dump(class_1,f)
pickle.dump(class_2,f)
pickle.dump(labels,f)
print ("save OK!")
用KNN分类器来完成:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import pickle
from pylab import *
from PCV.classifiers import knn
from PCV.tools import imtools
pklist=['points_normal.pkl','points_ring.pkl']
figure()
# load 2D points using Pickle
for i, pklfile in enumerate(pklist):
with open(pklfile, 'rb') as f:
class_1 = pickle.load(f)
class_2 = pickle.load(f)
labels = pickle.load(f)
# load test data using Pickle
with open(pklfile[:-4]+'_test.pkl', 'rb') as f:
class_1 = pickle.load(f)
class_2 = pickle.load(f)
labels = pickle.load(f)
model = knn.KnnClassifier(labels,vstack((class_1,class_2)))
# test on the first point
print (model.classify(class_1[0]))
#define function for plotting
def classify(x,y,model=model):
return array([model.classify([xx,yy]) for (xx,yy) in zip(x,y)])
# lot the classification boundary
subplot(1,2,i+1)
imtools.plot_2D_boundary([-6,6,-6,6],[class_1,class_2],classify,[1,-1])
titlename=pklfile[:-4]
title(titlename)
show()
效果图:(通过更改数据分布环绕的半径大小即r来选取最佳的决策边界曲线,经测试 r= 0.8 * randn(n,1) + 5为佳)
改变class_2可确定边界划分的形状如当class_2 = hstack((rcos(angle),2r*sin(angle)))时
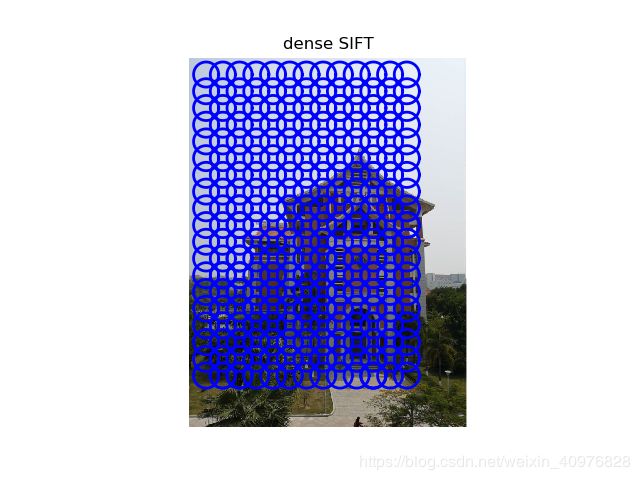
4.用稠密SIFT作为图像特征
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift, dsift
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
dsift.process_image_dsift('gesture/empire3.jpg','empire.dsift',90,40,True)
l,d = sift.read_features_from_file('empire.dsift')
im = array(Image.open('gesture/empire3.jpg'))
sift.plot_features(im,l,True)
title('dense SIFT')
show()
结果展示:
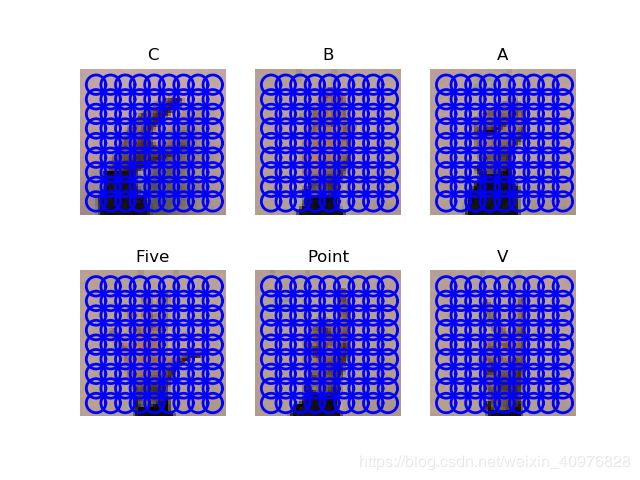
5.图像分类:手势识别
该应用中,我们调用稠密SIFT描述子表示这些手势图像,用稠密sift函数进行图像处理,得到所有图像的特征向量。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift, dsift
from pylab import *
from PIL import Image
imlist=['gesture/train/C-uniform02.ppm','gesture/train/B-uniform01.ppm',
'gesture/train/A-uniform01.ppm','gesture/train/Five-uniform01.ppm',
'gesture/train/Point-uniform01.ppm','gesture/train/V-uniform01.ppm']
figure()
for i, im in enumerate(imlist):
print (im)
dsift.process_image_dsift(im,im[:-3]+'dsift',90,40,True)
l,d = sift.read_features_from_file(im[:-3]+'dsift')
dirpath, filename=os.path.split(im)
im = array(Image.open(im))
#显示手势含义title
titlename=filename[:-14]
subplot(2,3,i+1)
sift.plot_features(im,l,True)
title(titlename)
show()
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PCV.localdescriptors import dsift
import os
from PCV.localdescriptors import sift
from pylab import *
from PCV.classifiers import knn
def get_imagelist(path):
""" Returns a list of filenames for
all jpg images in a directory. """
return [os.path.join(path,f) for f in os.listdir(path) if f.endswith('.ppm')]
def read_gesture_features_labels(path):
# create list of all files ending in .dsift
featlist = [os.path.join(path,f) for f in os.listdir(path) if f.endswith('.dsift')]
# read the features
features = []
for featfile in featlist:
l,d = sift.read_features_from_file(featfile)
features.append(d.flatten())
features = array(features)
# create labels
labels = [featfile.split('/')[-1][0] for featfile in featlist]
return features,array(labels)
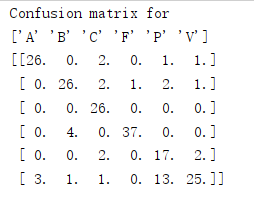
def print_confusion(res,labels,classnames):
n = len(classnames)
# confusion matrix
class_ind = dict([(classnames[i],i) for i in range(n)])
confuse = zeros((n,n))
for i in range(len(test_labels)):
confuse[class_ind[res[i]],class_ind[test_labels[i]]] += 1
print ('Confusion matrix for')
print (classnames)
print (confuse)
filelist_train = get_imagelist('gesture/train')
filelist_test = get_imagelist('gesture/test')
imlist=filelist_train+filelist_test
# process images at fixed size (50,50)
for filename in imlist:
featfile = filename[:-3]+'dsift'
dsift.process_image_dsift(filename,featfile,10,5,resize=(50,50))
features,labels = read_gesture_features_labels('gesture/train/')
test_features,test_labels = read_gesture_features_labels('gesture/test/')
classnames = unique(labels)
# test kNN
k = 2
knn_classifier = knn.KnnClassifier(labels,features)
res = array([knn_classifier.classify(test_features[i],k) for i in
range(len(test_labels))])
# accuracy
acc = sum(1.0*(res==test_labels)) / len(test_labels)
print ('Accuracy:', acc)
print_confusion(res,test_labels,classnames)
结果:
KNN测试:
用训练数据及其标记作为输入,创建分类对象
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from PIL import Image
from pylab import *
from scipy.ndimage import measurements
def find_sudoku_edges(im, axis=0):
""" 寻找对齐后数独图像的的单元边线 """
# threshold and sum rows and columns
#阈值化,像素值小于128的阈值处理后为1,大于128的为0
trim = 1*(128 > im)
#阈值处理后对行(列)相加求和
s = trim.sum(axis=axis)
print (s)
# find center of strongest lines
# 寻找连通区域
s_labels, s_nbr = measurements.label((0.5*max(s)) < s)
print (s_labels)
print (s_nbr)
#计算各连通域的质心
m = measurements.center_of_mass(s, s_labels, range(1, s_nbr+1))
print (m)
#对质心取整,质心即为粗线条所在位置
x = [int(x[0]) for x in m]
print (x)
# if only the strong lines are detected add lines in between
# 如果检测到了粗线条,便在粗线条间添加直线
if 4 == len(x):
dx = diff(x)
x = [x[0], x[0]+dx[0]/3, x[0]+2*dx[0]/3, x[1], x[1]+dx[1]/3, x[1]+2*dx[1]/3, x[2], x[2]+dx[2]/3, x[2]+2*dx[2]/3, x[3]]
if 10 == len(x):
return x
else:
raise RuntimeError('Edges not detected.')
imname = 'sudoku_images/sudoku_images/sudokus/sudoku19.jpg'
im = array(Image.open(imname).convert('L'))
print (im.shape)
figure()
gray()
imshow(im)
axis('off')
# find the cell edges
# 寻找x方向的单元边线
x = find_sudoku_edges(im, axis=0)
#寻找y方向的单元边线
y = find_sudoku_edges(im, axis=1)
figure()
gray()
y1=[y[0],y[3],y[6],y[-1]]
y2=[y[1],y[2],y[4],y[5],y[7],y[8]]
#画直线
for i, ch in enumerate(y1):
x1 = range(x[0], x[-1]+1, 1)
y1 = ch*ones(len(x1))
#画散点图
plot(x1, y1, 'r', linewidth=2)
for i, ch in enumerate(y2):
x1 = range(x[0], x[-1]+1, 1)
y1 = ch*ones(len(x1))
#画散点图
plot(x1, y1, 'b', linewidth=2)
'''for i, ch in enumerate(x):
y1 = range(x[0], x[-1]+1, 1)
x1 = ch*ones(len(x1))
#画散点图
plot(x1, y1, 'r', linewidth=2)
plot(x, y, 'or', linewidth=2)'''
imshow(im)
axis('off')
show()