PCL 点云数据基于法向量边缘提取
关于边缘提取的算法,PCL官网以及《点云PCL库从入门到精通》相应章节均有,所以别在花积分下载,稍微修改一下就能够应用。那么,问题是将官方的边缘提取算法可能也得花点时间来调试,一般官方所给的例子代码是需要这样设置:
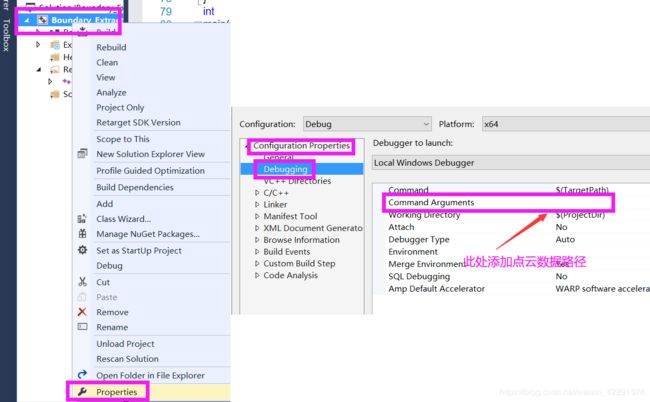
项目名称右击属性->Properties->Configuration Properties->Debegging->Debugging->Command Arguments处添加点云数据路径。
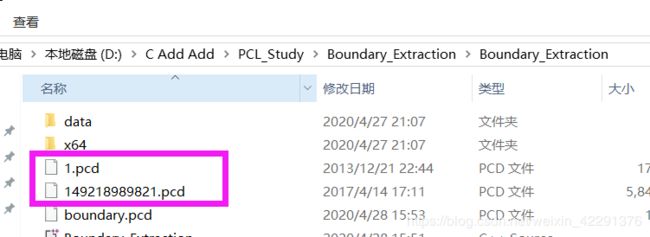
若嫌弃这种方法那就在例子代码中稍微修改一下,通过PCL读取点云的函数进行加载点云数据。以下代码所给的经稍微修改,直接点云数据拷贝至所建项目名称名称路径下,如图所示:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int estimateBorders(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr &cloud, float re, float reforn)
{
pcl::PointCloud boundaries; //保存边界估计结果
pcl::BoundaryEstimation boundEst; //定义一个进行边界特征估计的对象
pcl::NormalEstimation normEst; //定义一个法线估计的对象
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr normals(new pcl::PointCloud); //保存法线估计的结果
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_boundary(new pcl::PointCloud);
normEst.setInputCloud(pcl::PointCloud::Ptr(cloud));
normEst.setRadiusSearch(reforn); //设置法线估计的半径//normEst.setKSearch(10);//表示计算点云法向量时,搜索的点云个数
normEst.compute(*normals); //将法线估计结果保存至normals
//输出法线的个数
std:cout << "reforn: " << reforn << std::endl;
std::cerr << "normals: " << normals->size() << std::endl;
boundEst.setInputCloud(cloud); //设置输入的点云
boundEst.setInputNormals(normals); //设置边界估计的法线,因为边界估计依赖于法线
boundEst.setRadiusSearch(re); //设置边界估计所需要的半径,//这里的Threadshold为一个浮点值,可取点云模型密度的10倍
boundEst.setAngleThreshold(M_PI / 4); //边界估计时的角度阈值M_PI / 4 并计算k邻域点的法线夹角,若大于阈值则为边界特征点
boundEst.setSearchMethod(pcl::search::KdTree::Ptr(new pcl::search::KdTree)); //设置搜索方式KdTree
boundEst.compute(boundaries); //将边界估计结果保存在boundaries
std::cerr << "AngleThreshold: " << M_PI / 4 << std::endl;
//输出边界点的个数
std::cerr << "boundaries: " << boundaries.points.size() << std::endl;
//存储估计为边界的点云数据,将边界结果保存为pcl::PointXYZ类型
for (int i = 0; i < cloud->points.size(); i++)
{
if (boundaries[i].boundary_point > 0)
{
cloud_boundary->push_back(cloud->points[i]);
}
}
pcl::PCDWriter writer;
std::stringstream ss;
ss << "boundary" << ".pcd";
writer.write(ss.str(), *cloud_boundary, false);
//可视化显示原始点云与边界提取结果
boost::shared_ptr MView(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("边界提取"));
int v1(0);
MView->createViewPort(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, v1);
MView->setBackgroundColor(0.3, 0.3, 0.3, v1);
MView->addText("Raw point clouds", 10, 10, "v1_text", v1);
int v2(0);
MView->createViewPort(0.5, 0.0, 1, 1.0, v2);
MView->setBackgroundColor(0.5, 0.5, 0.5, v2);
MView->addText("Boudary point clouds", 80, 80, "v2_text", v2);
MView->addPointCloud(cloud, "sample cloud", v1);
MView->addPointCloud(cloud_boundary, "cloud_boundary", v2);
MView->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 1, 0, 0, "sample cloud", v1);
MView->setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 0, 1, 0, "cloud_boundary", v2);
//MView->addCoordinateSystem(1.0); //取消坐标系
//MView->initCameraParameters(); //设置照相机参数,使用户从默认的角度和方向观察点云
MView->spin();
return 0;
}
int
main(int argc, char** argv)
{
srand(time(NULL));
float re=1.0, reforn=20.0;
/*re = std::atof(argv[2]);
reforn = std::atof(argv[3]);*/
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_src(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::io::loadPCDFile("1.pcd", *cloud_src); // argv[1] knee_piece 149218989821
//创建滤波器对象
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_filtered(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::StatisticalOutlierRemoval sor;
sor.setInputCloud(cloud_src);
sor.setMeanK(100);//寻找每个点的50个最近邻点
sor.setStddevMulThresh(3.0);//一个点的最近邻距离超过全局平均距离的一个标准差以上,就会舍弃
sor.filter(*cloud_filtered);
std::cout << "cloud_src: " << cloud_src->points.size() << std::endl;
std::cout << "cloud_filtered: " << cloud_filtered->points.size() << std::endl;
estimateBorders(cloud_src, re, reforn);
return 0;
}
详情的介绍可以看看本文所参考的博文。
参考博文:
1、https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37957160/article/details/105404119?depth_1-utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromBaidu-4&utm_source=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-BlogCommendFromBaidu-4