驱动开发框架 -------内核模块结构|source insight 工程创建|模块的属性
========================================
1,驱动开发框架 -------内核模块结构
2,模块的属性
3,source insight 工程创建
4,一个完整的驱动程序的组成
5,面向对象的编程
========================================
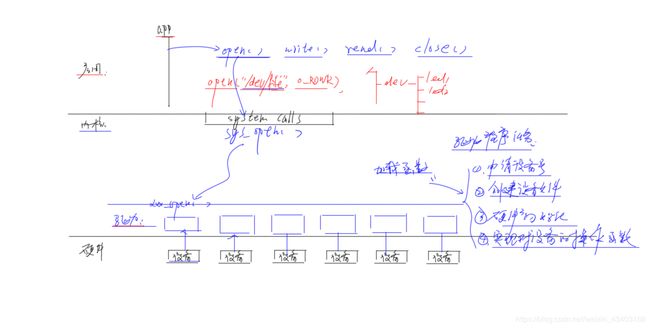
一, 驱动开发框架 -------内核模块结构
1,基本模块框架
//头文件
#include
#include
//加载函数
static int __init hello_init(void)
{
printk("---------%s-----------\n",__FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}
//卸载函数
static void __exit hello_exit(void)
{
printk("---------%s-----------\n",__FUNCTION__);
}
//模块声明和认证
module_init(hello_init); //模块声明
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); //认证
2,编译驱动模块
编写Makefile
#指定内核源码的路径
KERNEL_DIR = /home/lpf/s5pv210/kernel/linux-3.0.8
CUR_DIR = $(shell pwd)
all:
#进入内核源码目录,并告诉内核将当前路径下的源码编译为内核模块
make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(CUR_DIR) modules
clean:
#将编译生成的所有文件删除
make -C $(KERNEL_DIR) M=$(CUR_DIR) clean
install:
cp *.ko /opt/rootfs/drv_module
#指定将当前目录下哪些源文件编译为内核模块
obj-m = hello_drv.o
编译:
lpf@ubuntu:~/s5pv210/driver$ make
make -C /home/lpf/s5pv210/kernel/linux-3.0.8 M=/home/lpf/s5pv210/driver modules
make[1]: Entering directory `/home/lpf/s5pv210/kernel/linux-3.0.8'
CC [M] /home/lpf/s5pv210/driver/hello_drv.o
Building modules, stage 2.
MODPOST 1 modules
CC /home/lpf/s5pv210/driver/hello_drv.mod.o
LD [M] /home/lpf/s5pv210/driver/hello_drv.ko //*.ko就是编译生成的驱动文件
3,模块加载和卸载
1》将生成的模块拷贝到 /opt/rootfs/drv_module
cp hello_drv.ko /opt/rootfs/drv_module
2》加载模块
[root@farsight /drv_module]# insmod hello_drv.ko
---------hello_init-----------
3》查看加载的模块信息
[root@farsight /drv_module]# lsmod
hello_drv 743 0 - Live 0x7f000000
4》卸载模块:
[root@farsight /drv_module]# rmmod hello_drv
---------hello_exit-----------
二,模块的属性
1,模块传参----在加载模块时,可以同时传递参数给模块
源代码中声明:
module_param(变量名,变量类型,权限);
例如:
module_param(sno,int,0644);
module_param(name,charp,0644);
[root@farsight /drv_module]# insmod hello_drv.ko
---------hello_init-----------
sno = 1001,name = 老王
[root@farsight /drv_module]# rmmod hello_drv
---------hello_exit-----------
[root@farsight /drv_module]# insmod hello_drv.ko sno=1002 name="Jack" //给模块传参
---------hello_init-----------
sno = 1002,name = Jack
//模块中的参数在加载模块时会创建与参数相同的名称的文件,位置:/sys/module/hello_drv/parameters/
[root@farsight /]# ls sys/module/
8250 dm9000 keyboard mousedev rcutree spurious vt
block hello_drv lockd nfs scsi_mod sunrpc xz_dec
brd kernel loop printk sg tcp_cubic
[root@farsight /]# ls sys/module/hello_drv/
holders initstate notes parameters refcnt sections
[root@farsight /]# ls sys/module/hello_drv/parameters/
name sno
2,模块调用
代码实现:
被调用模块: 调用模块
//头文件
#include #include "mysum.h"
#include
static int __init hello_init(void)
int mysum(int a,int b) {
{ printk("%d + %d = %d\n",a,b,mysum(a,b));
return a +b;
} .........
EXPORT_SYMBOL(mysum); }
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
在开发板中:
[root@farsight /drv_module]# insmod mysum.ko
[root@farsight /drv_module]# insmod hello_drv.ko a=5 b=3
---------hello_init-----------
sno = 1001,name = 老王
5 + 3 = 8
三,source insight 工程创建
1,安装source insight
D:\peter\1901\初级驱动\source\Source.Insight.v3.50.0076—最新注册破解版&高手用的配置文件.zip
2,将Linux内核源码解压:
D:\peter\linux-3.0.8
3,打开source insight,创建工程
参考:2_创建source insight工程.tif
另外,也可以使用老师创建好的工程:
1,将工程文件拷贝到linux源码目录中
si_linux308-ori.tgz
------ 》
D:\peter\linux-3.0.8 -----在Windows中
或
\\192.168.7.5\lpf\s5pv210\kernel\linux-3.0.8 --------在linux中
2,解压:
例如:在linux中:
lpf@ubuntu:~/s5pv210/kernel/linux-3.0.8$ tar -xvf si_linux308-ori.tgz
linux308-ori.IAB
linux308-ori.IAD
linux308-ori.IMB
linux308-ori.IMD
linux308-ori.PFI
linux308-ori.PO
linux308-ori.PR
linux308-ori.PRI
linux308-ori.PS
linux308-ori.WK3
3,打开工程:
双击工程文件:
linux308-ori.PR
四,一个完整的驱动程序的组成
1,需要申请一个设备号
1》设备号的概率:
在linux内核中,设备号用32位整数表示:
分两个部分:
主设备号: 表示某一类设备-----高12位
次设备号: 表示某一类设备中具体的设备的编号 ----- 低20位
2》如何申请设备号:
static inline int register_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name,const struct file_operations *fops)
//功能:申请设备号
//参数1:major ---- 主设备号
如果major为0,表示动态申请设备号,该函数会返回一个主设备号
如果major不为0,表示静态指定主设备号
//参数2:name ------ 字符串,驱动程序的描述信息,自定义
//参数3:fops ------ 文件操作对象的指针
//返回值:
动态申请:成功返回:主设备号,失败返回:错误码
静态申请:成功返回:0,失败返回错误码
3》在开发板中加载驱动:
[root@farsight /drv_module]# insmod hello_drv.ko
---------hello_init-----------
[root@farsight /drv_module]# cat /proc/devices
Character devices:
1 mem
256 hello_drv //申请主设备号是成功的
2 pty
3 ttyp
4 /dev/vc/0
4 tty
4 ttyS
5 /dev/tty
5 /dev/console
5 /dev/ptmx
7 vcs
10 misc
2,创建设备文件(设备节点)
1》手动创建设备文件:
mknod 设备节点名称 类型 主设备号 次设备号
例如:
[root@farsight /drv_module]# mknod /dev/hello c 254 0
[root@farsight /drv_module]# ls -l /dev/hello
crw-r--r-- 1 0 0 254, 0 Jan 1 00:13 /dev/hello
测试:
[root@farsight /drv_module]# insmod hello_drv.ko
---------hello_init-----------
[root@farsight /drv_module]# ./test
---------hello_open-----------
---------hello_close-----------
[root@farsight /drv_module]#
2》自动创建设备节点
struct class *class_create(struct module *owner, const char *name);
//参数1 --- 当前模块
//参数2 --- 字符串,描述类,自定义
//返回值-----成功:struct class结构体地址,失败:NULL
struct device *device_create(struct class *class, struct device *parent,dev_t devt, void *drvdata, const char *fmt, ...)
//参数1 ---- class_create返回的地址
//参数2 ---- 父类,一般为NULL
//参数3 ---- 设备号:dev_t
#define MINORBITS 20
#define MINORMASK ((1U << MINORBITS) - 1)
#define MAJOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) >> MINORBITS))
#define MINOR(dev) ((unsigned int) ((dev) & MINORMASK))
#define MKDEV(ma,mi) (((ma) << MINORBITS) | (mi))
//参数4 ---- 私有数据,默认为NULL
//参数5 ---- 设备文件的名称
//变参 ----- 和参数5一起表示设备文件的名称
//返回值-----成功:struct device结构体地址,失败:NULL
3,实现设备的操作函数
int hello_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
printk("---------%s-----------\n",__FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}
int hello_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
printk("---------%s-----------\n",__FUNCTION__);
return 0;
}
const struct file_operations fops = {
.open = hello_open,
.release = hello_close,
};
4,硬件初始化
五,面向对象的编程:
例如: 把大象关进冰箱
面向过程的编程思想:---- 第一人称
第一步: 打开冰箱门
第二步: 将大象赶进去
第三步: 关上冰箱门
面向对象的编程思想:---- 第三人称
第一步:分析有几个对象
人
大象
冰箱
第二步:分析对象的功能
人:
打开冰箱门
void open_bx(bx)
{
bx.open();
}
关闭冰箱门
void close_bx(bx)
{
bx.close();
}
赶大象
void push_el(el)
{
el.run();
}
大象:
吃
void eat(void)
{
}
睡
void sleep(void)
{
}
行走
void run(void)
{
}
冰箱:
门开
void open(void)
{
}
门关
void close(void)
{
}
第三步:让不同对象做不同的事
冰箱:海尔冰箱
大象:非洲大象
人:小明
小明.open_bx(海尔冰箱)
小明.push_el(非洲大象)
小明.close_bx(海尔冰箱)