openfoam学习心得—fvOptions详解
openfoam学习心得—fvOptions详解
fvOptions–Options可以理解为源项,版本:v7
声明:本文是读此篇博客http://xiaopingqiu.github.io/2016/03/20/fvOptions1/后的感悟。
#include "createFvOptions.H"展开后如下:
fv::options& fvOptions(fv::options::New(mesh));
if (!fvOptions.optionList::size())
{
Info << "No finite volume options present" << endl;
}
从以上可以看出的信息是:fvOptions是一个fv::options类对象的引用,New(mesh)是fv::options类中的一个静态static方法,其返回fv::options类对象,对象访问方法通常是用点运算符,但是求解器中经常出现fvOptions(U)有理由猜测()运算符在fv::options类或其基类中被重载过!
头文件
namespace Foam
{namespace fv
{
class options
:
public IOdictionary,
public optionList
{
IOobject createIOobject(const fvMesh& mesh) const;
public:
ClassName("fvOptions");
options(const fvMesh& mesh);
options(const options&) = delete;
static options& New(const fvMesh& mesh);
virtual ~options(){}
//- Inherit read from optionList
using optionList::read;
//- Read dictionary
virtual bool read();
void operator=(const options&) = delete;
};
fv::options类继承于optionList与IOdictionary类,复制与赋值构造= delete意味着编译器不会为你生成这些构造函数,其还有一个私有方法createIOobject意味着这个对象可以与case目录下的某些文件交互,其果然有一个static New函数,这与RTS机制有关。再来看看源文件。
namespace Foam
{namespace fv
{
defineTypeNameAndDebug(options, 0);
}
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * Private Member Functions * * * * * ** * * //
Foam::IOobject Foam::fv::options::createIOobject
(
const fvMesh& mesh
) const
{
IOobject io
(
typeName,
mesh.time().constant(),
mesh,
IOobject::MUST_READ,
IOobject::NO_WRITE
);
if (io.typeHeaderOk<IOdictionary>(true))
{
Info<< "Creating finite volume options from "
<< io.instance()/io.name() << nl
<< endl;
io.readOpt() = IOobject::MUST_READ_IF_MODIFIED;
return io;
}
else
{
// Check if the fvOptions file is in system
io.instance() = mesh.time().system();
if (io.typeHeaderOk<IOdictionary>(true))
{
Info<< "Creating finite volume options from "
<< io.instance()/io.name() << nl
<< endl;
io.readOpt() = IOobject::MUST_READ_IF_MODIFIED;
return io;
}
else
{
io.readOpt() = IOobject::NO_READ;
return io;
}
}
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Constructors * * * * * * * * * * *//
Foam::fv::options::options
(
const fvMesh& mesh
)
:
IOdictionary(createIOobject(mesh)),
optionList(mesh, *this)
{}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * New * * * * * * * * * * *//
Foam::fv::options& Foam::fv::options::New(const fvMesh& mesh)
{
if (mesh.thisDb().foundObject<options>(typeName))
{
return const_cast<options&>
(
mesh.lookupObject<options>(typeName)
);
}
else
{
if (debug)
{
InfoInFunction
<< "Constructing " << typeName
<< " for region " << mesh.name() << endl;
}
options* objectPtr = new options(mesh);
regIOobject::store(objectPtr);
return *objectPtr;
}
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * read * * * * * * * * * * *//
bool Foam::fv::options::read()
{
if (IOdictionary::regIOobject::read())
{
optionList::read(*this);
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
createIOobject方法创建了一个IOobject对象与文件options建立了链接,此文件可以位于constant之下也可位于system之下。我们在学习一个类的时候,首要就是搞清楚其构造函数。在这里构造函数调用了基类构造函数IOdictionary(createIOobject(mesh))、optionList(mesh, *this)这说明fvoptions可以向options文件进行读写操作,且调用的我们知道fvoptions只是一个引用,真正创建类对象的是该类中的New方法。
optionList(mesh, *this)参数一个是fvmesh类,一个是options类,我们去源文件中寻找,发现optionList(const fvMesh& mesh, const dictionary& dict),这里体现了多态,真正传入的隐含于options类对象中的dictionary类对象。这里还出现了()重载函数。
class optionList:public PtrList<option>
{
//- Construct null
optionList(const fvMesh& mesh);
//- Construct from mesh and dictionary
optionList(const fvMesh& mesh, const dictionary& dict);
#仅列出部分
template<class Type>
tmp<fvMatrix<Type>> operator()
(
GeometricField<Type, fvPatchField, volMesh>& field
);
//- Return source for equation with specified name
template<class Type>
tmp<fvMatrix<Type>> operator()
(
GeometricField<Type, fvPatchField, volMesh>& field,
const word& fieldName
);
//- Return source for equation
template<class Type>
tmp<fvMatrix<Type>> operator()
(
const volScalarField& rho,
GeometricField<Type, fvPatchField, volMesh>& field
);
}
重点关注构造函数,这是一个小tip,在学习一个类的时候,先理清构造函数,再看构造函数中调用的成员方法,其余的成员方法可以先不看,等碰到了再看:
Foam::fv::optionList::optionList(const fvMesh& mesh, const dictionary& dict)
:
PtrList<option>(),
mesh_(mesh),
checkTimeIndex_(mesh_.time().startTimeIndex() + 2)
{
reset(optionsDict(dict));
}
从上面可以发现,其调用了父类的无参构造,使用了reset与optionsDict函数,这两个函数可能在子类也可能在父类,往回理一理,可以知道,这里的dict实际就是options文件。
const Foam::dictionary& Foam::fv::optionList::optionsDict
(
const dictionary& dict
) const
{
if (dict.found("options"))
{
return dict.subDict("options");
}
else
{
return dict;
}
}
void Foam::fv::optionList::reset(const dictionary& dict)
{
// Count number of active fvOptions
label count = 0;
forAllConstIter(dictionary, dict, iter)
{
if (iter().isDict())
{
count++;
}
}
this->setSize(count);
label i = 0;
forAllConstIter(dictionary, dict, iter)
{
if (iter().isDict())
{
const word& name = iter().keyword();
const dictionary& sourceDict = iter().dict();
this->set
(
i++,
option::New(name, sourceDict, mesh_)
);
}
}
}
optionsDict函数,在文件内容中搜索options关键字,并返回options关键字所对应的子字典中的内容。要注意的是options关键字下的子字典中可能还有子字典,有几个源就有几个子字典,每一个类均生成option基类对象指针。且将该指针存到 PtrList 模板类定义的 List 里。这说明文件中可以设置多个源。最后看一个基类option类,注意开头那个是options类,是不一样的。从其包含头文件runTimeSelectionTables.H可以看出,这个类是所有源项类型的基类。
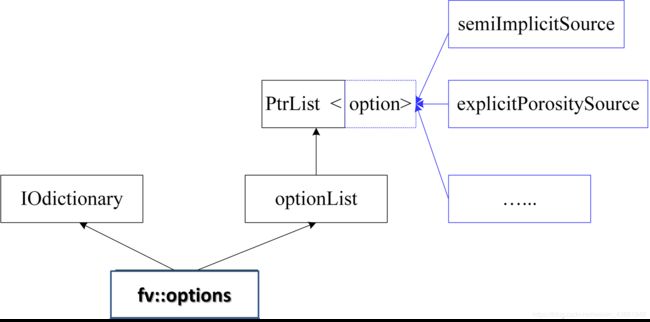 综上所述,实际上当fvOptions这个对象创立时,其根据options子字典中的源项个数以及类型创建了相应的指针,这些指针是
综上所述,实际上当fvOptions这个对象创立时,其根据options子字典中的源项个数以及类型创建了相应的指针,这些指针是option类型(基类),可以指向任何子类源项对象。