Spring5 源码阅读笔记(1.4.2.6)registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, mbd) 注册DisposableBean如有必要
本小节的作用可以说和 Spring5 源码阅读笔记(1.4.2.5)initializeBean(beanName, exposedObject, mbd) 是有关联的,那一节我们看到了三种初始化方法,这一节可以看到三种销毁方法。
public class DestroyMethodBean implements DisposableBean {
//jdk的注解
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy(){
System.out.println("======@PreDestroy======");
}
@Override
public void destroy(){
System.out.println("======DisposableBean.destroy()======");
}
//基于配置
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println("============" );
}
}
spring.xml 配置:
<bean id="destroyMethodBean" class="com.test.DestroyMethodBean" destroy-method="destroyMethod"/>
结果:

本节重点
所谓销毁方法,并不是用来销毁 bean 的方法,而是 bean 销毁前会自动执行的方法。
DisposableBeanAdapter 和其 destroy() 方法
跟源码
类 AbstractBeanFactory
protected void registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(String beanName, Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
AccessControlContext acc = (System.getSecurityManager() != null ? getAccessControlContext() : null);
//如果不是多例的且需要销毁 见1.4.2.6.1
if (!mbd.isPrototype() && requiresDestruction(bean, mbd)) {
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
//注册一个DisposableBean的实现为以下三种给出的bean做所有的销毁工作:
//DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor,DisposableBean,自定义destroy方法
//1.4.2.6.2
registerDisposableBean(beanName,
//1.4.2.6.3
new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc));
}
else {
// A bean with a custom scope...
Scope scope = this.scopes.get(mbd.getScope());
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + mbd.getScope() + "'");
}
scope.registerDestructionCallback(beanName,
new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, mbd, getBeanPostProcessors(), acc));
}
}
}
1.4.2.6.1 requiresDestruction
protected boolean requiresDestruction(Object bean, RootBeanDefinition mbd) {
return (bean.getClass() != NullBean.class &&
(DisposableBeanAdapter.hasDestroyMethod(bean, mbd) || (hasDestructionAwareBeanPostProcessors() &&
DisposableBeanAdapter.hasApplicableProcessors(bean, getBeanPostProcessors()))));
}
跟 hasDestroyMethod:
public static boolean hasDestroyMethod(Object bean, RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
//实现了DisposableBean就为true了
if (bean instanceof DisposableBean || bean instanceof AutoCloseable) {
return true;
}
String destroyMethodName = beanDefinition.getDestroyMethodName();
if (AbstractBeanDefinition.INFER_METHOD.equals(destroyMethodName)) {
return (ClassUtils.hasMethod(bean.getClass(), CLOSE_METHOD_NAME) ||
ClassUtils.hasMethod(bean.getClass(), SHUTDOWN_METHOD_NAME));
}
return StringUtils.hasLength(destroyMethodName);
}
1.4.2.6.2 registerDisposableBean
类 DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
public void registerDisposableBean(String beanName, DisposableBean bean) {
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
this.disposableBeans.put(beanName, bean);
}
}
1.4.2.6.3 DisposableBeanAdapter
public DisposableBeanAdapter(Object bean, String beanName, RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition,
List<BeanPostProcessor> postProcessors, @Nullable AccessControlContext acc) {
Assert.notNull(bean, "Disposable bean must not be null");
this.bean = bean;
this.beanName = beanName;
this.invokeDisposableBean =
//实现了DisposableBean && 没有叫destroy的被@PreDestroy注解的方法
(this.bean instanceof DisposableBean && !beanDefinition.isExternallyManagedDestroyMethod("destroy"));
this.nonPublicAccessAllowed = beanDefinition.isNonPublicAccessAllowed();
this.acc = acc;
//设置的值
String destroyMethodName = inferDestroyMethodIfNecessary(bean, beanDefinition);
// 有值 && (没有既实现DisposableBean,值又叫destroy) && 被@PreDestroy注解的方法不叫值
//其实就是三种方法的名字互相不能相同
if (destroyMethodName != null && !(this.invokeDisposableBean && "destroy".equals(destroyMethodName)) &&
!beanDefinition.isExternallyManagedDestroyMethod(destroyMethodName)) {
this.destroyMethodName = destroyMethodName;
this.destroyMethod = determineDestroyMethod(destroyMethodName);
if (this.destroyMethod == null) {
if (beanDefinition.isEnforceDestroyMethod()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionValidationException("Could not find a destroy method named '" +
destroyMethodName + "' on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
else {
Class<?>[] paramTypes = this.destroyMethod.getParameterTypes();
if (paramTypes.length > 1) {
throw new BeanDefinitionValidationException("Method '" + destroyMethodName + "' of bean '" +
beanName + "' has more than one parameter - not supported as destroy method");
}
else if (paramTypes.length == 1 && boolean.class != paramTypes[0]) {
throw new BeanDefinitionValidationException("Method '" + destroyMethodName + "' of bean '" +
beanName + "' has a non-boolean parameter - not supported as destroy method");
}
}
}
//可以过滤出InitDestroyAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
this.beanPostProcessors = filterPostProcessors(postProcessors, bean);
}
@Nullable
private List<DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor> filterPostProcessors(List<BeanPostProcessor> processors, Object bean) {
List<DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor> filteredPostProcessors = null;
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(processors)) {
filteredPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(processors.size());
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : processors) {
//只要这种类型的BeanPostProcessor
if (processor instanceof DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor dabpp = (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor) processor;
if (dabpp.requiresDestruction(bean)) {
filteredPostProcessors.add(dabpp);
}
}
}
}
return filteredPostProcessors;
}
跟 DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor 和 requiresDestruction:

看到有一个熟悉的实现类,里面有重写的方法

这个知识点就和 Spring5 源码阅读笔记(1.4.2.2)applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors(mbd, beanType, beanName) 里的知识点衔接上了。
再看看同在这个类里的 destroy() 方法,就知道为什么那三种销毁方法是那种顺序了:
@Override
public void destroy() {
//调用有@PreDestroy注解的方法
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.beanPostProcessors)) {
for (DestructionAwareBeanPostProcessor processor : this.beanPostProcessors) {
processor.postProcessBeforeDestruction(this.bean, this.beanName);
}
}
//调用重写的destroy()方法
if (this.invokeDisposableBean) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking destroy() on bean with name '" + this.beanName + "'");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged((PrivilegedExceptionAction<Object>) () -> {
((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();
return null;
}, this.acc);
}
else {
((DisposableBean) this.bean).destroy();
}
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
String msg = "Invocation of destroy method failed on bean with name '" + this.beanName + "'";
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.info(msg, ex);
}
else {
logger.info(msg + ": " + ex);
}
}
}
//调用自定义的方法,这个其实也可以用注解实现
if (this.destroyMethod != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethod);
}
else if (this.destroyMethodName != null) {
Method methodToCall = determineDestroyMethod(this.destroyMethodName);
if (methodToCall != null) {
invokeCustomDestroyMethod(methodToCall);
}
}
}
那么问题来了,在我们的 web 应用里,谁会来调用这个 destroy() 方法呢?
当然是 Tomcat。
在 web.xml 里,我们有这样一个配置:
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListenerlistener-class>
listener>
跟 ContextLoaderListener:
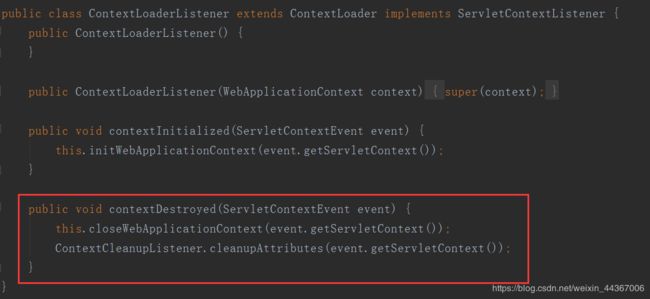
当 Tomcat 关闭的时候,一定会调用 contextDestroyed 方法。
跟 closeWebApplicationContext:
类 ContextLoader
public void closeWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) {
servletContext.log("Closing Spring root WebApplicationContext");
try {
if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) {
//这里
((ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context).close();
}
}
finally {
ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) {
currentContext = null;
}
else if (ccl != null) {
currentContextPerThread.remove(ccl);
}
servletContext.removeAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
}
跟 close:
类 ConfigurableApplicationContext:

类 AbstractApplicationContext
@Override
public void close() {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
doClose();
// If we registered a JVM shutdown hook, we don't need it anymore now:
// We've already explicitly closed the context.
if (this.shutdownHook != null) {
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
// ignore - VM is already shutting down
}
}
}
}
跟 doClose:
protected void doClose() {
if (this.active.get() && this.closed.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Closing " + this);
}
LiveBeansView.unregisterApplicationContext(this);
try {
// Publish shutdown event.
publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this));
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from ApplicationListener handling ContextClosedEvent", ex);
}
// Stop all Lifecycle beans, to avoid delays during individual destruction.
if (this.lifecycleProcessor != null) {
try {
this.lifecycleProcessor.onClose();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
logger.warn("Exception thrown from LifecycleProcessor on context close", ex);
}
}
// Destroy all cached singletons in the context's BeanFactory.
destroyBeans();
// Close the state of this context itself.
closeBeanFactory();
// Let subclasses do some final clean-up if they wish...
onClose();
this.active.set(false);
}
}
跟 destroyBeans:
protected void destroyBeans() {
getBeanFactory().destroySingletons();
}
跟 destroySingletons:
类 ConfigurableBeanFactory

类 DefaultListableBeanFactory:
@Override
public void destroySingletons() {
super.destroySingletons();
this.manualSingletonNames.clear();
clearByTypeCache();
}
跟 destroySingletons:
类 DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
public void destroySingletons() {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Destroying singletons in " + this);
}
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
this.singletonsCurrentlyInDestruction = true;
}
String[] disposableBeanNames;
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
disposableBeanNames = StringUtils.toStringArray(this.disposableBeans.keySet());
}
for (int i = disposableBeanNames.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
//这里
destroySingleton(disposableBeanNames[i]);
}
this.containedBeanMap.clear();
this.dependentBeanMap.clear();
this.dependenciesForBeanMap.clear();
clearSingletonCache();
}
跟 destroySingleton:
public void destroySingleton(String beanName) {
// Remove a registered singleton of the given name, if any.
removeSingleton(beanName);
// Destroy the corresponding DisposableBean instance.
DisposableBean disposableBean;
//是不是看到熟悉的容器了呢?
synchronized (this.disposableBeans) {
disposableBean = (DisposableBean) this.disposableBeans.remove(beanName);
}
destroyBean(beanName, disposableBean);
}
跟 destroyBean:
protected void destroyBean(String beanName, @Nullable DisposableBean bean) {
// Trigger destruction of dependent beans first...
Set<String> dependencies;
synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) {
// Within full synchronization in order to guarantee a disconnected Set
dependencies = this.dependentBeanMap.remove(beanName);
}
if (dependencies != null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Retrieved dependent beans for bean '" + beanName + "': " + dependencies);
}
for (String dependentBeanName : dependencies) {
destroySingleton(dependentBeanName);
}
}
// Actually destroy the bean now...
if (bean != null) {
try {
//注意这里
bean.destroy();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Destroy method on bean with name '" + beanName + "' threw an exception", ex);
}
}
}
// Trigger destruction of contained beans...
Set<String> containedBeans;
synchronized (this.containedBeanMap) {
// Within full synchronization in order to guarantee a disconnected Set
containedBeans = this.containedBeanMap.remove(beanName);
}
if (containedBeans != null) {
for (String containedBeanName : containedBeans) {
destroySingleton(containedBeanName);
}
}
// Remove destroyed bean from other beans' dependencies.
synchronized (this.dependentBeanMap) {
for (Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Set<String>>> it = this.dependentBeanMap.entrySet().iterator(); it.hasNext();) {
Map.Entry<String, Set<String>> entry = it.next();
Set<String> dependenciesToClean = entry.getValue();
dependenciesToClean.remove(beanName);
if (dependenciesToClean.isEmpty()) {
it.remove();
}
}
}
// Remove destroyed bean's prepared dependency information.
this.dependenciesForBeanMap.remove(beanName);
}


