Hyperledger Fabric v1.4(LTS) 系列(3.8):关键概念-Smart Contracts and Chaincode
Key Concepts-Smart Contracts and Chaincode
- Introduction
- Hyperledger Fabric Functionalities
- Hyperledger Fabric Model
- Blockchain network
- Identity
- Membership
- Peers
- Smart Contracts and Chaincode
- Ledger
- The Ordering Service
- Private data
- Use Cases
Smart Contracts and Chaincode
Audience: Architects, application and smart contract developers,administrators
From an application developer’s perspective, a smart contract, together with the ledger, form the heart of a Hyperledger Fabric blockchain system. Whereas a ledger holds facts about the current and historical state of a set of business objects, a smart contract defines the executable logic that generates new facts that are added to the ledger. A chaincode is typically used by administrators to group related smart contracts for deployment, but can also be used for low level system programming of Fabric. In this topic, we’ll focus on why both smart contracts and chaincode exist, and how and when to use them.
受众:架构师、应用和智能合约开发人员,管理员。
从应用开发人员的角度来看,智能合约,以及分类帐构成了Hyperledger Fabric区块链系统的核心。而分类帐则保存着有关一组业务对象当前和历史的状态,智能合约定义生成添加到分类帐中的新事实的执行逻辑。链码通常由管理员用于将相关智能合约分组部署,但也可用于Fabric的底层系统编程。在这个主题,我们将重点讨论为什么智能合约和链码都存在,以及如何以及何时使用它们。
In this topic, we’ll cover:
- What is a smart contract
- A note on terminology
- Smart contracts and the ledger
- How to develop a smart contract
- The importance of endorsement policies
- Valid transactions
- Smart contracts and channels
- Communicating between smart contracts
- What is system chaincode?
Smart contract
Before businesses can transact with each other, they must define a common set of contracts covering common terms, data, rules, concept definitions, and processes. Taken together, these contracts lay out the business model that govern all of the interactions between transacting parties.
在业务可以交互之前,它们必须定义一组通用的合约包括通用术语、数据、规则、概念定义和过程。综上,这些合约规定了商业模型来管理交易各方之间的所有交互。
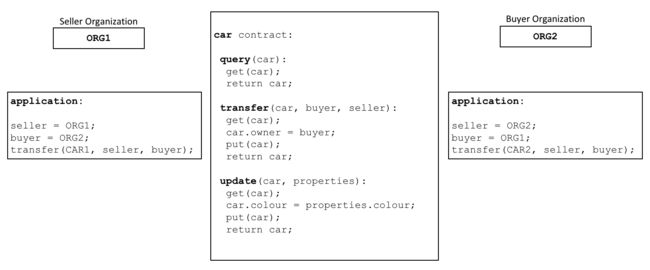
A smart contract defines the rules between different organizations in executable code. Applications invoke a smart contract to generate transactions that are recorded on the ledger.
智能合约通过可执行代码定义了不同组织之间的规则。应用调用智能合约生成记录在分类帐上的交易。
Using a blockchain network, we can turn these contracts into executable programs – known in the industry as smart contracts – to open up a wide variety of new possibilities. That’s because a smart contract can implement the governance rules for any type of business object, so that they can be automatically enforced when the smart contract is executed. For example, a smart contract might ensure that a new car delivery is made within a specified timeframe, or that funds are released according to prearranged terms, improving the flow of goods or capital respectively. Most importantly however, the execution of a smart contract is much more efficient than a manual human business process.
通过区块链网络,我们可以将这些合约转换为可执行程序–业内称为智能合约,开辟众多新的可能。这是因为智能合约可以实现用于治理任何类型业务对象的规则,以便它们可以智能合约执行时被自动强制执行。例如,智能合约可能会确保在规定的时间段内交付新车,或资金按照预定条款发放,而改善货物或资本流动。但最重要的是,智能合约执行比人工业务流程效率高得多。
In the diagram above, we can see how two organizations, ORG1 and ORG2 have defined a car smart contract to query, transfer and update cars. Applications from these organizations invoke this smart contract to perform an agreed step in a business process, for example to transfer ownership of a specific car from ORG1 to ORG2.
在上图中,我们可以看到两个组织,ORG1 和ORG2 已将智能合约car 定义为query 、transfer 和update cars。来自这些组织的应用调用此智能合约执行业务流程中商定的步骤,例如从ORG1 转移特定汽车所有权到ORG2 。
Terminology
Hyperledger Fabric users often use the terms smart contract and chaincode interchangeably. In general, a smart contract defines the transaction logic that controls the lifecycle of a business object contained in the world state. It is then packaged into a chaincode which is then deployed to a blockchain network. Think of smart contracts as governing transactions, whereas chaincode governs how smart contracts are packaged for deployment.
Hyperledger Fabric用户经常交叉使用术语智能合约和链码。一般来说,智能合约定义了控制世界范围内业务对象的生命周期的事务逻辑。其被打包为一个链码,然后部署到区块链网络。智能合约可视为对事务的治理,而chaincode控制如何打包智能合约进行部署。
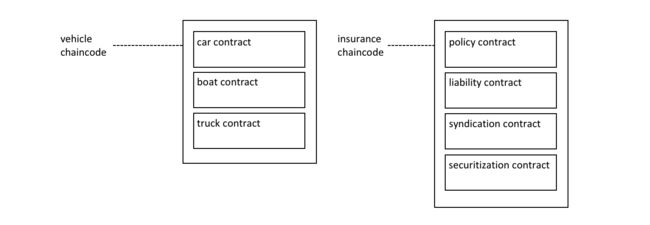
A smart contract is defined within a chaincode. Multiple smart contracts can be defined within the same chaincode. When a chaincode is deployed, all smart contracts within it are made available to applications.
智能合约定义在链码内。同一个链码中可以定义多个智能合约。部署链码时,链码中的所有智能合约都对应用可用。
In the diagram, we can see a vehicle chaincode that contains three smart contracts: cars, boats and trucks. We can also see an insurance chaincode that contains four smart contracts: policy, liability, syndication and securitization. In both cases these contracts cover key aspects of the business process relating to vehicles and insurance. In this topic, we will use the car contract as an example. We can see that a smart contract is a domain specific program which relates to specific business processes, whereas a chaincode is a technical container of a group of related smart contracts for installation and instantiation.
在图中,我们可以看到一个“交通工具”链码,其中包含三个智能合约:汽车、船和卡车。我们还可以看到链码insruance·包含四个智能合约的链码:policy政策,liability责任,syndication银团和securitization证券化。在这两种情况下,这些合约都覆盖交通工具和保险相关的业务流程的关键方面。在这个主题,我们将以car合约为例。我们可以看到一个智能合约是与特定业务流程相关的领域特定程序,而链码是安装和实例化一组相关智能合约的技术容器。
Ledger
At the simplest level, a blockchain immutably records transactions which update states in a ledger. A smart contract programmatically accesses two distinct pieces of the ledger – a blockchain, which immutably records the history of all transactions, and a world state that holds a cache of the current value of these states, as it’s the current value of an object that is usually required.
最简单的看法,区块链不可篡改地记录更新交易分类帐状态的事务。智能合约以编程方式访问分类账的两个不同片段—永久地记录了所有事务的区块链,及保存当前值缓存的世界状态。它是一个常用对象的当前值。
Smart contracts primarily put, get and delete states in the world state, and can also query the immutable blockchain record of transactions.
智能合约在world state中主要有put、get和delete状态,也可以查询不可变的区块链交易记录。
-
A get typically represents a query to retrieve information about the current state of a business object.
-
A put typically creates a new business object or modifies an existing one in the ledger world state.
-
A delete typically represents the removal of a business object from the current state of the ledger, but not its history.
-
get通常表示用于检索业务对象当前状态的查询。
-
put通常创建一个新的业务对象或修改一个账本world state中已有的业务对象。
-
delete通常表示从分类帐的当前状态中移除一个业务对象,但不是其历史记录。
Smart contracts have many APIs available to them.Critically, in all cases, whether transactions create, read, update or delete business objects in the world state, the blockchain contains an immutable record of these changes.
智能合约有很多APIs可用。至关重要的是,在所有情况下,无论事务是创建、读取、更新还是删除world state的业务对象,区块链都包含一个这些变化的不变记录。
Development
Smart contracts are the focus of application development, and as we’ve seen, one or more smart contracts can be defined within a single chaincode. Deploying a chaincode to a network makes all its smart contracts available to the organizations in that network. It means that only administrators need to worry about chaincode; everyone else can think in terms of smart contracts.
智能合约是应用开发的重点,正如我们所看到的,单个链码中可以定义一个或多个智能合约。l到网络的链码中的所有智能合约都对网络中的组织可用。这意味着只有管理员需要关心链码,其他人都可以只考虑智能合约。
At the heart of a smart contract is a set of transaction definitions. For example, look at fabcar.js, where you can see a smart contract transaction that creates a new car:
智能合约的核心是一组事务的定义。例如,看看fabcar.js,这里可以看到创建新车的智能合约事务:
async createCar(ctx, carNumber, make, model, color, owner) {
const car = {
color,
docType: 'car',
make,
model,
owner,
};
await ctx.stub.putState(carNumber, Buffer.from(JSON.stringify(car)));
}
You can learn more about the Fabcar smart contract in the Writing your first application tutorial.
您可以在编写您的第一个应用程序教程里更多了解Fabcar智能合约。
A smart contract can describe an almost infinite array of business use cases relating to immutability of data in multi-organizational decision making. The job of a smart contract developer is to take an existing business process that might govern financial prices or delivery conditions, and express it as a smart contract in a programming language such as JavaScript, GOLANG or Java. The legal and technical skills required to convert centuries of legal language into programming language is increasingly practiced by smart contract auditors. You can learn about how to design and develop a smart contract in the Developing applications topic.
智能合约可以描述关于多组织决策中数据不可变性的几乎无限多的业务用例。智能合约开发人员的工作是采用现有的业务流程,可能控制财务价格或交货条件,并将其表示为用JavaScript、GOLANG或Java编写的智能合约。转换几个世纪的法律语言到编程语言所需的法律和技术技能越来越多地被智能合约审计员担当。您可以在开发应用程序主题了解如何设计和开发智能合约。
Endorsement
Associated with every chaincode is an endorsement policy that applies to all of the smart contracts defined within it. An endorsement policy is very important; it indicates which organizations in a blockchain network must sign a transaction generated by a given smart contract in order for that transaction to be declared valid.
与每个链码关联的是一个应用于所有链码中定义的智能合约的背书策略。背书政策非常重要;
它决定区块链网络中给定智能合约生成的交易必须由哪些组织签署,以便声明该交易有效。
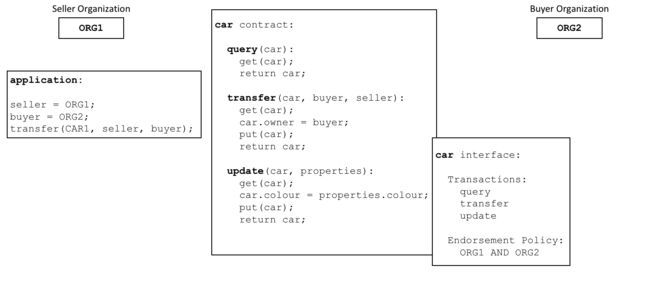
Every smart contract has an endorsement policy associated with it. This endorsement policy identifies which organizations must approve transactions generated by the smart contract before those transactions can be identified as valid.
每个智能合约都有一个与之相关联的背书政策。此背书政策确定哪些组织必须批准智能合约生成的交易,然后这些交易才可以确定为有效。
An example endorsement policy might define that three of the four organizations participating in a blockchain network must sign a transaction before it is considered valid. All transactions, whether valid or invalid are added to a distributed ledger, but only valid transactions update the world state.
例如,背书政策可能会定义参与区块链网络的四个组织中的三个必须签署事务才认为事务有效。所有事务,无论是有效还是无效,都会添加到分布式账本中,但只有有效事务才能更新全局状态。
If an endorsement policy specifies that more than one organization must sign a transaction, then the smart contract must be executed by a sufficient set of organizations in order for a valid transaction to be generated. In the example above, a smart contract transaction to transfer a car would need to be executed and signed by both ORG1 and ORG2 for it to be valid.
如果背书策略指定必须多个组织签署事务,则智能合约必须由一组足够多的组织执行以生成有效的事务。在以上例子中,转让汽车的智能合约事务将必须同时由ORG1和ORG2执行和签名才能有效。
Endorsement policies are what make Hyperledger Fabric different to other blockchains like Ethereum or Bitcoin. In these systems valid transactions can be generated by any node in the network. Hyperledger Fabric more realistically models the real world; transactions must be validated by trusted organizations in a network. For example, a government organization must sign a valid issueIdentity transaction, or both the buyer and seller of a car must sign a car transfer transaction. Endorsement policies are designed to allow Hyperledger Fabric to better model these types of real-world interactions.
背书策略使Hyperledger Fabric与以太坊或比特币这样的区块链不同。在其他系统中,网络中的任何节点都可以生成有效的事务。Hyperledger Fabric更贴近现实;事务必须由网络中受信任的组织进行验证。例如政府必须签署颁发身份事务,或汽车的买方和卖方必须签署汽车转移事务。背书政策旨在允许Hyperledger Fabric可以更好地模拟这些类型的真实交互。
Finally, endorsement policies are just one example of policy in Hyperledger Fabric. Other policies can be defined to identify who can query or update the ledger, or add or remove participants from the network. In general, policies should be agreed in advance by the consortium of organizations in a blockchain network, although they are not set in stone. Indeed, policies themselves can define the rules by which they can be changed. And although an advanced topic, it is also possible to define custom endorsement policy rules over and above those provided by Fabric.
最后,背书政策只是策略的一个例子。在Hyperledger Fabric中,其他策略可以定义为认证谁可以查询或更新分类帐,或增删网络参与者。一般来说,政策应该由区块链网络中的组织联合体事先商定,尽管他们不是一成不变的。实际上,策略本身可以定义它们更改其自身的规则。虽然这是一个高级主题,但也可以在Fabric提供的策略之上定义自定义背书策略。
Valid transactions
When a smart contract executes, it runs on a peer node owned by an organization in the blockchain network. The contract takes a set of input parameters called the transaction proposal and uses them in combination with its program logic to read and write the ledger. Changes to the world state are captured as a transaction proposal response (or just transaction response) which contains a read-write set with both the states that have been read, and the new states that are to be written if the transaction is valid. Notice that the world state is not updated when the smart contract is executed!
当智能合约执行时,它在属于组织的区块链网络中的节点上运行。合约接受一组称为事务提案的入参并将其与程序逻辑结合使用以读写账本。全局状态的变化被捕捉为事务提案响应(或仅事务响应),其中包含一个读写集,包括已读状态和如事务有效时要写入的新状态。注意,执行智能合约时并不更新全局状态!
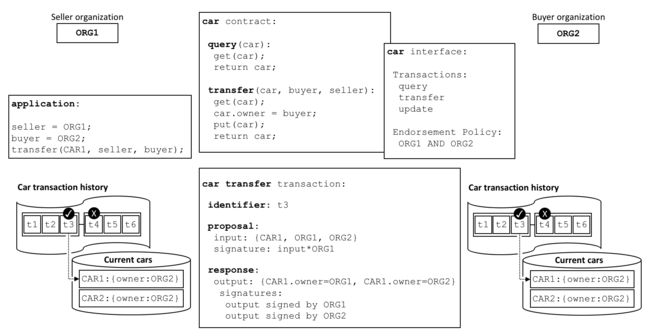
All transactions have an identifier, a proposal, and a response signed by a set of organizations. All transactions are recorded on the blockchain, whether valid or invalid, but only valid transactions contribute to the world state.
所有事务都有一个标识符、提案和由一组组织签名的响应。所有事务记录在区块链上,无论是有效还是无效,但仅限于有效的交易推动全局状态的发展。
Examine the car transfer transaction. You can see a transaction t3 for a car transfer between ORG1 and ORG2. See how the transaction has input {CAR1, ORG1, ORG2} and output {CAR1.owner=ORG1, CAR1.owner=ORG2}, representing the change of owner from ORG1 to ORG2. Notice how the input is signed by the application’s organization ORG1, and the output is signed by both organizations identified by the endorsement policy, ORG1 and ORG2. These signatures were generated by using each actor’s private key, and mean that anyone in the network can verify that all actors in the network are in agreement about the transaction details.
来看car transfer事务。您可以看到关于车在ORG1和ORG2之间转移的事务t3。事务输入{CAR1, ORG1, ORG2} ,输出{CAR1.owner=ORG1, CAR1.owner=ORG2}, 表示将所有者从ORG1 更改为ORG2。注意输入是如何由应用所属组织ORG1签名,输出由由背书政策确定的组织,即ORG1和ORG2共同签名。这些签名使用每个参与者的私钥生成,这意味着网络中的任何人都可以验证网络中的所有参与者对交易详情一致。
A transaction that is distributed to all peer nodes in the network is validated in two phases. Firstly, the transaction is checked to ensure it has been signed by sufficient organizations according to the endorsement policy. Secondly, it is checked to ensure that the current value of the world state matches the read set of the transaction when it was signed by the endorsing peer nodes; that there has been no intermediate update. If a transaction passes both these tests, it is marked as valid. All transactions are added to the blockchain history, whether valid or invalid, but only valid transactions result in an update to the world state.
分发到网络中所有节点的事务分两个阶段被验证。首先,检查事务以确保按背书政策由足够的组织签署。第二,确保全局状态的当前值匹配背书节点签名时的事务读取集而没有中间更新。如果一个事务通过这些测试,会被标记为有效。所有事务都添加到区块链历史,无论有效还是无效,但仅有效的事务会更新全局状态。
In our example, t3 is a valid transaction, so the owner of CAR1 has been updated to ORG2. However, t4 (not shown) is an invalid transaction, so while it was recorded in the ledger, the world state was not updated, and CAR2 remains owned by ORG2.
在我们的示例中,t3是一个有效的事务,因此CAR1的所有者更新为ORG2。但是,t4(未显示)是无效的事务,因此,当它被记录在分类帐中时,全局状态没有更新,并且CAR2仍归ORG2所有。
Finally, to understand how to use a smart contract or chaincode with world state, read the chaincode namespace topic.
最后,了解如何使用智能合约或链码操作全局状态,可以看chaincode 名字空间。
Channels
Hyperledger Fabric allows an organization to simultaneously participate in multiple, separate blockchain networks via channels. By joining multiple channels, an organization can participate in a so-called network of networks. Channels provide an efficient sharing of infrastructure while maintaining data and communications privacy. They are independent enough to help organizations separate their work traffic with different counterparties, but integrated enough to allow them to coordinate independent activities when necessary.
Hyperledger Fabric允许组织通过通道同时参与多个分离的区块链网络。通过加入多个通道,一个组织可以参与一个所谓的网络的网络。通道维护数据和通信隐私的同时提供了高效的基础设施共享。他们有足够的独立性来分开组织与不同的交易对手的工作流量,但是又足够整合以使他们在需要时能协调独立的活动。
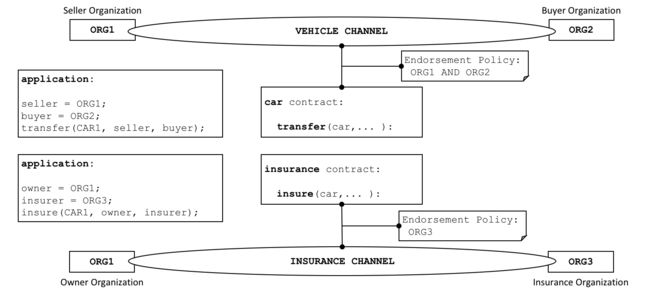
A channel provides a completely separate communication mechanism between a set of organizations. When a chaincode is instantiated on a channel, an endorsement policy is defined for it; all the smart contracts within the chaincode are made available to the applications on that channel.
通道提供了组织间完全独立的通信机制。通道实例化链码时,会定义一个共识策略;链码中的所有智能合约对该通道上的应用都可用。
An administrator defines an endorsement policy for a chaincode when it is instantiated on a channel, and can change it when the chaincode is upgraded. The endorsement policy applies equally to all smart contracts defined within the same chaincode deployed to a channel. It also means that a single smart contract can be deployed to different channels with different endorsement policies.
管理员在链码在通道上实例化时定义了链码的背书策略,并可在链码升级时更改它。背书策略平等应用于部署到通道的同一链码内定义的所有智能合约。这也意味着一个智能合约可以部署到具有不同背书策略的不同通道。
In the example above, the car contract is deployed to the VEHICLE channel, and an insurance contract is deployed to the INSURANCE channel. The car contract has an endorsement policy that requires ORG1 and ORG2 to sign transactions before they are considered valid, whereas the insurance contract has an endorsement policy that only requires ORG3 to sign valid transactions. ORG1 participates in two networks, the VEHICLE channel and the INSURANCE network, and can coordinate activity across these two networks with ORG2 and ORG3 respectively.
在上面的例子中(https://hyperledger-fabric.readthedocs.io/en/release-1.4/smartcontract/smartcontract.html#channels),将car合约部署到VEHICLE 通道,insurance 合约被部署到INSURANCE 通道。car合约背书政策要求ORG1和ORG2在事务生效前签署事务,而insurance 合约背书策略只要求ORG3签署即可生效。ORG参与两个网络,VEHICLE 通道及INSURANCE 网络,可以协调跨越两个独立网络ORG2 and ORG3 的活动。
Intercommunication
Smart Contracts are able to call to other smart contracts both within the same channel and across different channels. It this way, they can read and write world state data to which they would not otherwise have access due to smart contract namespaces.
智能合约能够调用同一个或不同通道的其他智能合约。这样他们就可以读写因智能合约名字空间而不能访问的全局状态数据。
There are limitations to this inter-contract communication, which are described fully in the chaincode namespace topic.
合约间通讯存在限制,具体描述见主题chaincode namespace。
System chaincode
The smart contracts defined within a chaincode encode the domain dependent rules for a business process agreed between a set of blockchain organizations. However, a chaincode can also define low-level program code which corresponds to domain independent system interactions, unrelated to these smart contracts for business processes.
智能合约在链码中定义了一组区块链组织认同的商业流程中与域相关的规则。但是,链码也可以定义与域无关的系统层交互的底层程序,它们与业务流程类智能合约无关。
The following are the different types of system chaincodes and their associated abbreviations:
以下是不同类型的系统链码及缩写:
-
Lifecycle system chaincode (LSCC) runs in all peers to handle package signing, install, instantiate, and upgrade chaincode requests. You can read more about the LSCC implements this process.
*生命周期系统链码(LSCC)在所有节点中运行以处理包签名,安装、实例化和升级链码的请求。处理过程里会讲LSCC的实现。 -
Configuration system chaincode (CSCC) runs in all peers to handle changes to a channel configuration, such as a policy update. You can read more about this process in the following chaincode topic.
*配置系统链码(CSCC)在所有节点中运行,以处理对通道配置如策略更新的变动。可以在下边的链码主题中阅读。 -
Query system chaincode (QSCC) runs in all peers to provide ledger APIs which include block query, transaction query etc. You can read more about these ledger APIs in the transaction context topic.
*查询系统链码(QSCC)在所有节点中运行,以提供账本API包括区块查询、事务查询等。可以在交易上下文主题深入了解分类帐API。 -
Endorsement system chaincode (ESCC) runs in endorsing peers to cryptographically sign a transaction response. You can read more about how the ESCC implements this process.
*背书系统链码(ESCC)在背书节点运行以加密签署事务响应。过程一节讲述ESCC如何实现。 -
Validation system chaincode (VSCC) validates a transaction, including checking endorsement policy and read-write set versioning. You can read more about the LSCC implements this process.
*验证系统链码(VSCC)验证事务,包括检查背书策略和读写集版本控制。你可以阅读更多关于LSCC实现了这个过程一节讲述ESCC如何实现。
It is possible for low level Fabric developers and administrators to modify these system chaincodes for their own uses. However, the development and management of system chaincodes is a specialized activity, quite separate from the development of smart contracts, and is not normally necessary. Changes to system chaincodes must be handled with extreme care as they are fundamental to the correct functioning of a Hyperledger Fabric network. For example, if a system chaincode is not developed correctly, one peer node may update its copy of the world state or blockchain differently to another peer node. This lack of of consensus is one form of a ledger fork, a very undesirable situation.
Fabric底层开发人员和管理员可以按用途修改这些系统链码。然而开发和管理系统链码与智能合约的开发相比是一项特定活动,通常也不是必需的。系统链码的变更必须极其小心地处理,因为它们是Fabric网络正确运行的基础。例如,如果系统链码错误开发,一个节点可能直接把本地的全局状态或区块链直接更新到其他节点。共识的缺乏是账本分叉的一种形式,是非常不期望出现的情况。