nginx-haproxy实现7层负载均衡
LB负载均衡集群分两类: LVS (四层)和 nginx或haproxy (七层)。LVS是基于IP的,而nginx和haproxy是基于应用的。
客户端通过访问分发器的IP来访问网站。分发器根据请求的类型,将请求转发到后端相应的机器上。
使用nginx实现动静分离的负载均衡集群
拓扑图:
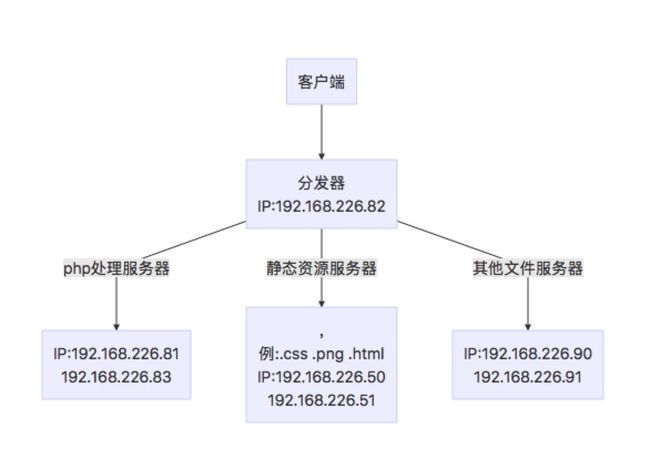
分发器的IP是192.168.226.81。其他几种在后端,处理实际访问的相应类型的服务器各两台。这里默认每台机器的处理服务器均已装好。其中分发器是安装的nginx,另外的机器可以是apache也可以是nginx。下面只需要讲解实际是如何配置的。
- 分发器配置
修改nginx的配置文件nginx.conf。找到配置文件中server段中的location配置段,在location配置段中增加:
# 匹配到html的请求,就转发到htmlservers
if ($request_uri ~* \.html$){
proxy_pass http://htmlservers;
}
# 匹配到php的请求,就转发到phpservers
if ($request_uri ~* \.php$){
proxy_pass http://phpservers;
}
# 非上面两种请求,就转发到picservers
proxy_pass http://picservers;然后再在http段的末端加入:
upstream htmlservers {
#定义负载均衡服务器组名称
server 192.168.226.50:80;
server 192.168.226.51:80;
}
upstream phpservers{
server 192.168.226.81:80;
server 192.168.226.83:80;
}
upstream picservers {
server 192.168.226.90:80;
server 192.168.226.91:80;
}如果要为每个服务器增加轮询的权重,就在每个转发IP后添加weight权重值即可。即:
upstream htmlservers {
#定义负载均衡服务器组名称
server 192.168.226.50:80 weight=1;
server 192.168.226.51:80 weight=2;
}
upstream phpservers{
server 192.168.226.81:80 weight=1;
server 192.168.226.83:80 weight=2;
}
upstream picservers {
server 192.168.226.90:80 weight=1;
server 192.168.226.91:80 weight=2;
}最后,将nginx配置文件中解析php的部分注释掉,否则会在访问php文件的时候,分发器就直接解析了php,而不是转发给后端的php服务器。
# location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# #fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /usr/local/nginx/html$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
# }PS:
* 其中htmlservers、phpservers、picservers都是自己命的名,只要满足一个要求:添加到两个地方的相应名称一致即可。即添加到proxy_pass后的服务器名称和添加到upstream后的服务器名称对应。
2. 重启nginx
[root@cos-7 nginx]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t
nginx: the configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf syntax is ok
nginx: configuration file /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf test is successful
[root@cos-7 nginx]# /usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reloadok,配置完成。要测试的话,可以在相应的服务器中添加内容可识别的文件,然后访问分发器的ip即可。
这里我的nginx版本是1.12.2。这里附上我配置完成后的nginx完整配置文件
user nginx nginx;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm index.php;
# 添加转发配置
if ($request_uri ~* \.html$){
proxy_pass http://htmlserver;
}
if ($request_uri ~* \.php$){
proxy_pass http://phpserver;
}
proxy_pass http://picserver;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
# location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# #fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /usr/local/nginx/html$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
# }
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# 添加转发服务器,这里采用权重轮询的方式
upstream htmlserver {
#定义负载均衡服务器组名称
server 192.168.226.50:80 weight=1;
server 192.168.226.51:80 weight=2;
}
upstream phpserver{
server 192.168.226.81:80 weight=1;
server 192.168.226.83:80 weight=2;
}
upstream picserver{
server 192.168.226.90:80 weight=1;
server 192.168.226.91:80 weight=2;
}
}使用haproxy实现负载均衡
HAProxy提供高可用性、负载均衡以及基于TCP和HTTP应用的代理,支持虚拟主机,它是免费、快速并且可靠的一种解决方案。根据官方数据,其最高极限支持10G的并发。
HAProxy特别适用于那些负载特大的web站点, 这些站点通常又需要会话保持或七层处理。HAProxy运行在当前的硬件上,完全可以支持数以万计的并发连接。并且它的运行模式使得它可以很简单安全的整合进您当前的架构中, 同时可以保护你的web服务器不被暴露到网络上。
其支持从4层至7层的网络交换,即覆盖所有的TCP协议。就是说,Haproxy 甚至还支持 Mysql的均衡负载。
相同点: 在功能上,haproxy通过反向代理方式实现 WEB均衡负载。和 Nginx,ApacheProxy,lighttpd,Cheroke 等一样。
不同点: Haproxy 并不是 web 服务器。以上提到所有带反向代理均衡负载的产品,都是 WEB 服务器。简单说,就是他们能处理解析页面。而Haproxy 仅仅是一款的用于均衡负载的应用代理。其自身并不能提供web服务。但其配置简单,拥有非常不错的服务器健康检查功能还有专门的系统状态监控页面,当其代理的后端服务器出现故障, HAProxy会自动将该服务器摘除,故障恢复后再自动将该服务器加入。
haproxy官网
这里安装的版本是1.7.10
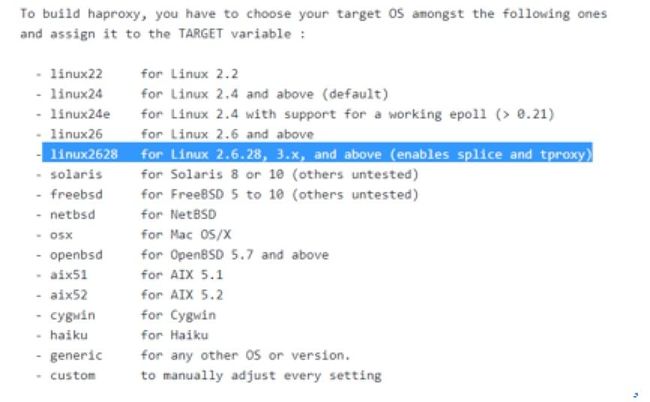
- 查看系统版本(haproxy安装是需要根据系统内核版本的不同来输入不同的make参数的)
[root@cos-7 soft]# uname -a
Linux cos-7.4-90 3.10.0-693.el7.x86_64 #1 SMP Tue Aug 22 21:09:27 UTC 2017 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux[root@cos-7 soft]# tar xf haproxy-1.7.10.tar.gz -C /usr/local/src/
[root@cos-7 soft]# cd /usr/local/src/haproxy-1.7.10
[root@cos-7 soft]# make TARGET=linux2628 PREFIX=/usr/local/haproxy
[root@cos-7 soft]# make install PREFIX=/usr/local/haproxyPS: 如果不想在make的时候,后面输入参数,也可以直接修改源码包中的Makefile文件。将其中的PREFIX的值改为你的安装路径。TARGET的值改为相应的内核版本。
3. 为haproxy生成配置文件haproxy.cfg
[root@cos-7 ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/haproxy/etc
[root@cos-7 etc]# cd /usr/local/haproxy/etc
[root@cos-7 etc]# vim haproxy.cfghaproxy.cfg文件内容是
global
log 127.0.0.1 local0
#log 127.0.0.1 local1 notice
#log loghost local0 info
maxconn 4096
chroot /usr/local/haproxy
uid 99 #所属运行的用户uid
gid 99 #所属运行的用户组
daemon #以后台形式运行haproxy
nbproc 1 #启动1个haproxy实例。# #工作进程数量(CPU数量) ,实际工作中,应该设置成和CPU核心数一样。 这样可以发挥出最大的性能。
pidfile /usr/local/haproxy/run/haproxy.pid #将所有进程写入pid文件
#debug #调试错误时用
#quiet #安静
defaults
log global
log 127.0.0.1 local3 #日志文件的输出定向。产生的日志级别为local3. 系统中local1-7,用户自己定义
mode http #工作模式,所处理的类别,默认采用http模式,可配置成tcp作4层消息转发
option httplog #日志类别,记载http日志
option httpclose #每次请求完毕后主动关闭http通道,haproxy不支持keep-alive,只能模拟这种模式的实现
option dontlognull #不记录空连接,产生的日志
option forwardfor #如果后端服务器需要获得客户端真实ip需要配置的参数,可以从Http Header中获得客户端ip
option redispatch #当serverid对应的服务器挂掉后,强制定向到其他健康服务器
retries 2 #2次连接失败就认为服务器不可用,主要通过后面的check检查
maxconn 2000 #最大连接数
balance roundrobin #负载均衡算法
stats uri /haproxy-stats #haproxy 监控页面的访问地址 # 可通过 http://localhost:80/haproxy-stats 访问
timeout connect 5000 #连接超时时间。 单位:ms 毫秒
timeout client 50000 #客户端连接超时时间
timeout server 50000 #服务器端连接超时时间
mode http
option httpchk GET /index.html #健康检测#注意实际工作中测试时,应该下载某一个页面来进行测试,因此这个页面应该是个小页面,而不要用首页面。这里是每隔一秒检查一次页面。
frontend http #前端配置,http名称可自定义
bind 0.0.0.0:80 #发起http请求80端口,会被转发到设置的ip及端口
default_backend http_back #转发到后端 写上后端名称
backend http_back #后端配置,名称上下关联
server s1 192.168.226.81:80 weight 3 check #后端的主机 IP &权衡
server s2 192.168.226.83:80 weight 3 check #后端的主机 IP &权衡
#server node1 192.168.179.131:8081 check inter 2000 rise 3 fall 3 weight 30
# inter 2000 健康检查时间间隔2秒
# rise 3 检测多少次才认为是正常的
# fall 3 失败多少次才认为是不可用的
# weight 30 权重PS:关于负载均衡算法
* source 根据请求源IP
* static-rr 根据权重
* leastconn 最少连接者先处理
* uri 根据请求的uri
* url_param 根据请求的url参数
* rdp-cookie 据据cookie(name)来锁定并哈希每一次请求
* hdr(name) 根据HTTP请求头来锁定每一次HTTP请求
* roundrobin 轮询方式
4. 赋值haproxy启动脚本到/etc/init.d/目录下
[root@cos-7 ~]# cp /usr/local/src/haproxy-1.7.10/examples/haproxy.init /etc/init.d/haproxy
[root@cos-7 ~]# chmod 755 /etc/init.d/haproxy
[root@cos-7 ~]# mkdir -p /usr/local/haproxy/run
[root@cos-7 ~]# cp /usr/local/haproxy/sbin/haproxy /usr/sbin/
[root@cos-7 ~]# chown nobody /usr/local/haproxyhaproxy启动脚本赋值过来后,还有一些地方需要修改。
* 将BASENAME的值改为haproxy
* BIN的值改为/usr/sbin/haproxy
* CFG的值改为/usr/local/haproxy/etc/haproxy.cfg
* PIDFILE的值改为/usr/local/haproxy/run/haproxy.pid
* LOCKFILE的值改为/usr/local/haproxy/run/haproxy
修改后的文件内容
#!/bin/sh
#
# chkconfig: - 85 15
# description: HA-Proxy is a TCP/HTTP reverse proxy which is particularly suited \
# for high availability environments.
# processname: haproxy
# config: /etc/haproxy/haproxy.cfg
# pidfile: /var/run/haproxy.pid
# Script Author: Simon Matter
5. 配置日志收集
[root@cos-7 ~]# vim /etc/rsyslog.conf将#$ModLoad imudp和#$UDPServerRun 514两行的注释打开。然后在local7.*这一行下面添加两行
local3.* /var/log/haproxy.log
local0.* /var/log/haproxy.log重启系统日志服务
[root@cos-7 ~]# systemctl restart rsyslog
6. 启动haproxy
[root@cos-7 ~]# /etc/init.d/haproxy start启动方法2
[root@cos-7 ~]# systemctl start haproxy启动方法3
[root@cos-7 ~]# /usr/local/haproxy/sbin/haproxy -f /usr/local/haproxy/etc/haproxy.cfg 这种方法没有start、restart、stop的参数。要重启只能先杀进程,然后在开启。
此时haproxy就配置完成了(后端的两台服务器默认已经配置好了)。可以访问分发器的ip来测试。
另外haproxy能通过web页面来监控后端服务器。
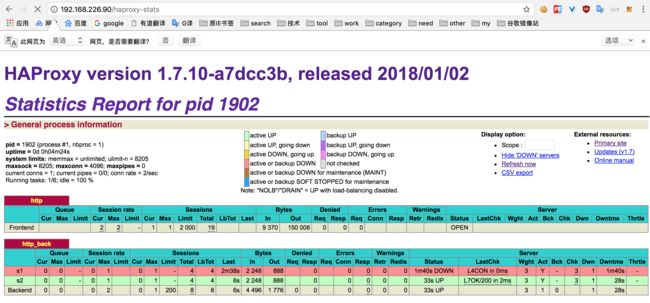
PS: 如果启动过程中报错Starting haproxy (via systemctl): Warning: haproxy.service changed on disk. Run 'systemctl daemon-reload' to reload units.。就按照提示内容,直接执行一下systemctl daemon-reload命令即可