python学习经验积累
python日常积累
- 高阶函数map()函数
- 字符大小写转换
- python string与list互转
- list2sring
- ''.join(list)
- string2list
- list(string)方法
- string.split()方法
高阶函数map()函数
map()是 Python 内置的高阶函数,它接收一个函数 f 和一个 list,并通过把函数 f 依次作用在 list 的每个元素上,得到一个新的 list 并返回。
例如,对于list [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
如果希望把list的每个元素都作平方,就可以用map()函数:
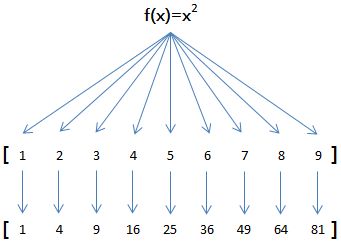
因此,我们只需要传入函数f(x)=x*x,就可以利用map()函数完成这个计算:
def f(x):
return x*x
print(map(f, [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]))
输出结果:
[1, 4, 9, 10, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]
注意:map()函数不改变原有的 list,而是返回一个新的 list。
利用map()函数,可以把一个 list 转换为另一个 list,只需要传入转换函数。
由于list包含的元素可以是任何类型,因此,map() 不仅仅可以处理只包含数值的 list,事实上它可以处理包含任意类型的 list,只要传入的函数f可以处理这种数据类型。
字符大小写转换
-
lower()、upper()、capitalize()、title()、swapcase()
-
这几个方法分别用来将字符串转换为小写、大写字符串、将字符串首字母变为大写、将每个首字母变为大写以及大小写互换,这几个方法都是生成新字符串,并不对原字符串做任何修改
s='What is Your Name?'
s2=s.lower()
print(s2) #返回小写字符串
# what iss your name?
print(s.upper()) #返回大写字符串
# WHAT IS YOUR NAME?
print(s.capitalize()) #字符串首字符大写
# What is your name?
print(s.title()) #每个单词的首字母大写
# What Is Your Name?
print(s.swapcase()) #大小写互换
# wHAT IS yOUR nAME?
python string与list互转
list2sring
‘’.join(list)
- 其中,引号中是字符之间的分割符,如“,”,“;”,“\t”等等
s_char =['t', 'h', 'e', ' ', 's', 'k', 'y', ' ', 'i', 's', ' ', 'b', 'l', 'u', 'e']
print(''.join(s_char))
print(','.join(s_char))
'''
output:
the sky is blue
output:
t,h,e, ,s,k,y, ,i,s, ,b,l,u,e
'''
string2list
list(string)方法
s_char = "the sky is blue"
print(list(s_char))
'''
output:
['t', 'h', 'e', ' ', 's', 'k', 'y', ' ', 'i', 's', ' ', 'b', 'l', 'u', 'e']
'''
string.split()方法
s_char = "the sky is blue"
print(s_char.split())
'''
output
['the', 'sky', 'is', 'blue']
'''