Spark源码分析之任务提交流程(Client)
文章目录
- 提交命令
- 任务提交流程
- 任务提交初流程
- YarnClusterApplication提交集群流程
- 提交过程环节汇总
- 用户Yarn-Cluster提交shell命令
- 提交给SparkSubmit类的cmd命令
- 提交给集群启动driver的命令
- 任务运行结果
- 上传到hdfs的文件
- 整个任务运行日志
提交命令
假定Yarn-Cluster方式提交:
./bin/spark-submit \
--class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \
--num-executors 2 \
--master yarn \
--deploy-mode cluster \
./examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.4.3.jar
任务提交流程
此代码都是运行在Client端
任务提交初流程
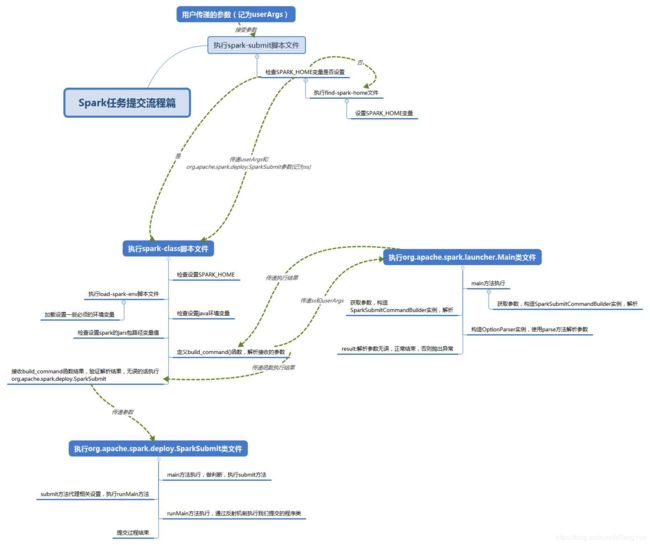
上图来之网上博客,有助于直观感受,下面详细解释。
首先看 spark-submit 文件最终会执行
exec "${SPARK_HOME}"/bin/spark-class org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit "$@"
会在 spark-class 文件中解析参数,其中重点说明如下代码:
build_command() {
"$RUNNER" -Xmx128m $SPARK_LAUNCHER_OPTS -cp "$LAUNCH_CLASSPATH" org.apache.spark.launcher.Main "$@"
printf "%d\0" $?
}
会调用build_command()方法创建命令(其新启动一个jvm,在 org.apache.spark.launcher.Main 类中根据不同的提交环境初步解析|添加|修改参数,这里不再详述),并把创建后的命令循环加到数组CMD中,最后执行exec执行CMD命令。
最终转化后的CMD命令为:
/software/servers/jdk1.8.0_121/bin/java -cp /software/conf/10k/mart_scr/bdp_jmart_fsh_union.bdp_jmart_fsh_formal/spark_conf/:/software/servers/10k/mart_scr/spark/jars/*:/software/conf/10k/mart_scr/bdp_jmart_fsh_union.bdp_jmart_fsh_formal/hadoop_conf/ org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit \
--master yarn \
--deploy-mode cluster \
--class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \
--num-executors 2 \
./examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.4.3.jar
上述命令启动一个JVM进程,最终会执行 org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit 类
下面分析入口类 org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit 类,主要是对命令行参数进行了封装,准备提交环境。在object SparkSubmit中,main(args)函数执行流程为:
override def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val submit = new SparkSubmit() {
self =>
override protected def parseArguments(args: Array[String]): SparkSubmitArguments = {
new SparkSubmitArguments(args) {
override protected def logInfo(msg: => String): Unit = self.logInfo(msg)
override protected def logWarning(msg: => String): Unit = self.logWarning(msg)
override protected def logError(msg: => String): Unit = self.logError(msg)
}
}
override protected def logInfo(msg: => String): Unit = printMessage(msg)
override protected def logWarning(msg: => String): Unit = printMessage(s"Warning: $msg")
override protected def logError(msg: => String): Unit = printMessage(s"Error: $msg")
override def doSubmit(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
try {
super.doSubmit(args)
} catch {
case e: SparkUserAppException =>
exitFn(e.exitCode)
}
}
}
submit.doSubmit(args)
}
创建一个匿名的SparkSubmit的匿名子类:在子类中重写了 parseArguments() 和 doSubmit() 等,submit.doSubmit(args)进行提交,首先调用匿名类中的 doSubmit(),其实现为:
def doSubmit(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// Initialize logging if it hasn't been done yet. Keep track of whether logging needs to
// be reset before the application starts.
val uninitLog = initializeLogIfNecessary(true, silent = true)
val appArgs = parseArguments(args)
if (appArgs.verbose) {
logInfo(appArgs.toString)
}
appArgs.action match {
case SparkSubmitAction.SUBMIT => submit(appArgs, uninitLog)
case SparkSubmitAction.KILL => kill(appArgs)
case SparkSubmitAction.REQUEST_STATUS => requestStatus(appArgs)
case SparkSubmitAction.PRINT_VERSION => printVersion()
}
}
可以看出首先解析参数 val appArgs = parseArguments(args) ,解析参数在 SparkSubmitArguments 类(注:如果要打印参数,请在启动命令添加配置 --verbose true ),其中 SparkSubmitArguments 类重点说明如下代码:
// Set parameters from command line arguments 即:解析提交命令行参数,调用父类的parse方法,最终会调用重载父类SparkSubmitOptionParser的该子类方法,例如: handle(opt, value) 对变量赋值、handleUnknown(opt)设置是否python|R。
parse(args.asJava)
// Populate `sparkProperties` map from properties file 即:获取默认配置文件参数(./conf/spark-defaults.conf) 放在sparkProperties中
mergeDefaultSparkProperties()
// Remove keys that don't start with "spark." from `sparkProperties`. 即:剔除上面默认配置文件中非spark.开头的配置参数
ignoreNonSparkProperties()
// Use `sparkProperties` map along with env vars to fill in any missing parameters 即加载环境变量中设置的参数,此代码会合并参数设置,其中优先级为:提交命令参数 > spark-defaults.conf参数 > 环境变量参数
loadEnvironmentArguments()
useRest = sparkProperties.getOrElse("spark.master.rest.enabled", "false").toBoolean
// 校验参数,根据不同的运行环境校验某些值不能为null
validateArguments()
回到 doSubmit 函数 appArgs.action 进行模式匹配(SUBMIT、KILL、REQUEST_STATUS、PRINT_VERSION)。对于模式 SUBMIT ,如果匹配成功,调用 submit(appArgs)方法提交,它的执行逻辑是
/**
* Submit the application using the provided parameters, ensuring to first wrap
* in a doAs when --proxy-user is specified.
*/
@tailrec
private def submit(args: SparkSubmitArguments, uninitLog: Boolean): Unit = {
def doRunMain(): Unit = {
if (args.proxyUser != null) {
val proxyUser = UserGroupInformation.createProxyUser(args.proxyUser,
UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser())
try {
proxyUser.doAs(new PrivilegedExceptionAction[Unit]() {
override def run(): Unit = {
runMain(args, uninitLog)
}
})
} catch {
case e: Exception =>
// Hadoop's AuthorizationException suppresses the exception's stack trace, which
// makes the message printed to the output by the JVM not very helpful. Instead,
// detect exceptions with empty stack traces here, and treat them differently.
if (e.getStackTrace().length == 0) {
error(s"ERROR: ${e.getClass().getName()}: ${e.getMessage()}")
} else {
throw e
}
}
} else {
runMain(args, uninitLog)
}
}
// In standalone cluster mode, there are two submission gateways:
// (1) The traditional RPC gateway using o.a.s.deploy.Client as a wrapper
// (2) The new REST-based gateway introduced in Spark 1.3
// The latter is the default behavior as of Spark 1.3, but Spark submit will fail over
// to use the legacy gateway if the master endpoint turns out to be not a REST server.
if (args.isStandaloneCluster && args.useRest) {
try {
logInfo("Running Spark using the REST application submission protocol.")
doRunMain()
} catch {
// Fail over to use the legacy submission gateway
case e: SubmitRestConnectionException =>
logWarning(s"Master endpoint ${args.master} was not a REST server. " +
"Falling back to legacy submission gateway instead.")
args.useRest = false
submit(args, false)
}
// In all other modes, just run the main class as prepared
} else {
doRunMain()
}
}
会进入 doRunMain() 函数,如果设置代理用户,则设置对应参数,最终继续调用 runMain(args, uninitLog) 函数,它的执行逻辑是:
/**
* Run the main method of the child class using the submit arguments.
*
* This runs in two steps. First, we prepare the launch environment by setting up
* the appropriate classpath, system properties, and application arguments for
* running the child main class based on the cluster manager and the deploy mode.
* Second, we use this launch environment to invoke the main method of the child
* main class.
*
* Note that this main class will not be the one provided by the user if we're
* running cluster deploy mode or python applications.
*/
private def runMain(args: SparkSubmitArguments, uninitLog: Boolean): Unit = {
val (childArgs, childClasspath, sparkConf, childMainClass) = prepareSubmitEnvironment(args)
// Let the main class re-initialize the logging system once it starts.
if (uninitLog) {
Logging.uninitialize()
}
if (args.verbose) {
logInfo(s"Main class:\n$childMainClass")
logInfo(s"Arguments:\n${childArgs.mkString("\n")}")
// sysProps may contain sensitive information, so redact before printing
logInfo(s"Spark config:\n${Utils.redact(sparkConf.getAll.toMap).mkString("\n")}")
logInfo(s"Classpath elements:\n${childClasspath.mkString("\n")}")
logInfo("\n")
}
val loader = getSubmitClassLoader(sparkConf)
for (jar <- childClasspath) {
addJarToClasspath(jar, loader)
}
var mainClass: Class[_] = null
try {
mainClass = Utils.classForName(childMainClass)
} catch {
case e: ClassNotFoundException =>
logError(s"Failed to load class $childMainClass.")
if (childMainClass.contains("thriftserver")) {
logInfo(s"Failed to load main class $childMainClass.")
logInfo("You need to build Spark with -Phive and -Phive-thriftserver.")
}
throw new SparkUserAppException(CLASS_NOT_FOUND_EXIT_STATUS)
case e: NoClassDefFoundError =>
logError(s"Failed to load $childMainClass: ${e.getMessage()}")
if (e.getMessage.contains("org/apache/hadoop/hive")) {
logInfo(s"Failed to load hive class.")
logInfo("You need to build Spark with -Phive and -Phive-thriftserver.")
}
throw new SparkUserAppException(CLASS_NOT_FOUND_EXIT_STATUS)
}
val app: SparkApplication = if (classOf[SparkApplication].isAssignableFrom(mainClass)) {
mainClass.getConstructor().newInstance().asInstanceOf[SparkApplication]
} else {
new JavaMainApplication(mainClass)
}
@tailrec
def findCause(t: Throwable): Throwable = t match {
case e: UndeclaredThrowableException =>
if (e.getCause() != null) findCause(e.getCause()) else e
case e: InvocationTargetException =>
if (e.getCause() != null) findCause(e.getCause()) else e
case e: Throwable =>
e
}
try {
app.start(childArgs.toArray, sparkConf)
} catch {
case t: Throwable =>
throw findCause(t)
}
}
首先看 val (childArgs, childClasspath, sparkConf, childMainClass) = prepareSubmitEnvironment(args) ,返回参数是四元组(childArgs=子进程参数,childClasspath=子进程classpath,sparkConf=Spark配置,childMainClass=子进程入口类),在该函数中工作包含:
1、在该方法中校验提交的命令参数,如果设置不合理,提前报异常;
2、根据应用配置 -- class,这个参数代表我们的Driver启动类,其中:
- Java|Scala应用:如果未设置
-- class,则取配置的Jar中的Main-Class参数(如果打包方式不对,则没有该Main-Class,此时会报错)- Python应用:此时如果是pyspark_shell则
-- class为org.apache.spark.api.python.PythonGatewayServer,否则为org.apache.spark.deploy.PythonRunner,最终相当于driver端执行PythonRunner 用户主文件.py py-files参数 [参数列表]- R应用:此时如果是sparkr_shell则
-- class为org.apache.spark.api.r.RBackend,否则为org.apache.spark.deploy.RRunner,最终相当于driver执行RRunner 用户主文件.r [参数列表]
3、根据部署模型设置childMainClass参数,childMainClass这个参数来决定下一步首先启动哪个类,childMainClass根据部署模型有不同的值:
- 1.如果是部署模式为Client模式那么直接在客户端运行启动Driver,即上面所说的
-- class参数。- 2.如果是StandaloneCluster,如果启用rest则childMainClass值为RestSubmissionClientApp全类名(
org.apache.spark.deploy.rest.StandaloneRestClient),否则childMainClass值为ClientApp全类名(org.apache.spark.deploy.Client)。- 3.如果是Yarn集群上运行,则childMainClass为
org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.YarnClusterApplication。- 4.如果是kubernetes集群上运行,则为
org.apache.spark.deploy.k8s.submit.KubernetesClientApplication。
此时客户端准备工作已完成,当拿到childMainClass后,就反射实例化类并开始调用 app.start(childArgs.toArray, sparkConf) ,进入子进程,如果是client提交直接执行启动driver,如果是cluster提交则提交集群。
YarnClusterApplication提交集群流程
由于我们以yarn-cluster举例,所以直接进入org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.YarnClusterApplication 类的 start(args, conf) ,此时就开始向集群申请资源并提交任务了。本节介绍的环节基本都位于 org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.Client中,其中YarnClusterApplication类也位于Client.scala文件内。
继续分析,调用函数为 YarnClusterApplication.start -> Client.run
private[spark] class YarnClusterApplication extends SparkApplication {
override def start(args: Array[String], conf: SparkConf): Unit = {
// SparkSubmit would use yarn cache to distribute files & jars in yarn mode,
// so remove them from sparkConf here for yarn mode.
conf.remove(JARS)
conf.remove(FILES)
new Client(new ClientArguments(args), conf, null).run()
}
}
private[spark] class Client(
val args: ClientArguments,
val sparkConf: SparkConf,
val rpcEnv: RpcEnv)
extends Logging {
...
/**
* Submit an application to the ResourceManager.
* If set spark.yarn.submit.waitAppCompletion to true, it will stay alive
* reporting the application's status until the application has exited for any reason.
* Otherwise, the client process will exit after submission.
* If the application finishes with a failed, killed, or undefined status,
* throw an appropriate SparkException.
*/
def run(): Unit = {
// 提交任务
this.appId = submitApplication()
if (!launcherBackend.isConnected() && fireAndForget) {
val report = getApplicationReport(appId)
val state = report.getYarnApplicationState
logInfo(s"Application report for $appId (state: $state)")
logInfo(formatReportDetails(report))
if (state == YarnApplicationState.FAILED || state == YarnApplicationState.KILLED) {
throw new SparkException(s"Application $appId finished with status: $state")
}
} else {
// 监控提交后任务并循环打印application状态
val YarnAppReport(appState, finalState, diags) = monitorApplication(appId)
if (appState == YarnApplicationState.FAILED || finalState == FinalApplicationStatus.FAILED) {
diags.foreach { err =>
logError(s"Application diagnostics message: $err")
}
throw new SparkException(s"Application $appId finished with failed status")
}
if (appState == YarnApplicationState.KILLED || finalState == FinalApplicationStatus.KILLED) {
throw new SparkException(s"Application $appId is killed")
}
if (finalState == FinalApplicationStatus.UNDEFINED) {
throw new SparkException(s"The final status of application $appId is undefined")
}
}
}
由上面代码可以知道,重点是 this.appId = submitApplication() ,下面主要看该函数
/**
* Submit an application running our ApplicationMaster to the ResourceManager.
*
* The stable Yarn API provides a convenience method (YarnClient#createApplication) for
* creating applications and setting up the application submission context. This was not
* available in the alpha API.
*/
def submitApplication(): ApplicationId = {
ResourceRequestHelper.validateResources(sparkConf)
var appId: ApplicationId = null
try {
// 初始化启动yarnClient
launcherBackend.connect()
yarnClient.init(hadoopConf)
yarnClient.start()
logInfo("Requesting a new application from cluster with %d NodeManagers"
.format(yarnClient.getYarnClusterMetrics.getNumNodeManagers))
// Get a new application from our RM,从集群RM获取一个NodeManager用于启动application
val newApp = yarnClient.createApplication()
val newAppResponse = newApp.getNewApplicationResponse()
// 获取ApplicationId
appId = newAppResponse.getApplicationId()
// The app staging dir based on the STAGING_DIR configuration if configured
// otherwise based on the users home directory.
val appStagingBaseDir = sparkConf.get(STAGING_DIR)
.map { new Path(_, UserGroupInformation.getCurrentUser.getShortUserName) }
.getOrElse(FileSystem.get(hadoopConf).getHomeDirectory())
stagingDirPath = new Path(appStagingBaseDir, getAppStagingDir(appId))
new CallerContext("CLIENT", sparkConf.get(APP_CALLER_CONTEXT),
Option(appId.toString)).setCurrentContext()
// Verify whether the cluster has enough resources for our AM. 验证集群是否有足够的资源
verifyClusterResources(newAppResponse)
// Set up the appropriate contexts to launch our AM. 设置用于提交的上下文设置
val containerContext = createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse)
val appContext = createApplicationSubmissionContext(newApp, containerContext)
// Finally, submit and monitor the application. 提交并监控application
logInfo(s"Submitting application $appId to ResourceManager")
yarnClient.submitApplication(appContext)
launcherBackend.setAppId(appId.toString)
reportLauncherState(SparkAppHandle.State.SUBMITTED)
appId
} catch {
case e: Throwable =>
if (stagingDirPath != null) {
cleanupStagingDir()
}
throw e
}
}
其中重点是 val containerContext = createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse) ,其主要设置ApplicationMaster的容器启动的上下文,包含上传hdfs和设置启动参数等,代码如下
/**
* Set up a ContainerLaunchContext to launch our ApplicationMaster container.
* This sets up the launch environment, java options, and the command for launching the AM.
*/
private def createContainerLaunchContext(newAppResponse: GetNewApplicationResponse)
: ContainerLaunchContext = {
logInfo("Setting up container launch context for our AM")
val appId = newAppResponse.getApplicationId
val pySparkArchives =
if (sparkConf.get(IS_PYTHON_APP)) {
findPySparkArchives()
} else {
Nil
}
// 读取需提交给集群启动ApplicationMaster的环境变量
val launchEnv = setupLaunchEnv(stagingDirPath, pySparkArchives)
// 预处理资源文件,如果是集群部署则上传资源到hdfs,如果执行则为下一个进程设置配置
val localResources = prepareLocalResources(stagingDirPath, pySparkArchives)
// 初始化ContainerLaunchContext,设置容器启动参数:env和resources
val amContainer = Records.newRecord(classOf[ContainerLaunchContext])
amContainer.setLocalResources(localResources.asJava)
amContainer.setEnvironment(launchEnv.asJava)
...
// Command for the ApplicationMaster. 根据上面拼接设置的ApplicationMaster启动命令commond
val commands = prefixEnv ++
Seq(Environment.JAVA_HOME.$$() + "/bin/java", "-server") ++
javaOpts ++ amArgs ++
Seq(
"1>", ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR + "/stdout",
"2>", ApplicationConstants.LOG_DIR_EXPANSION_VAR + "/stderr")
// TODO: it would be nicer to just make sure there are no null commands here
val printableCommands = commands.map(s => if (s == null) "null" else s).toList
// 继续设置ContainerLaunchContext,并设置容器启动参数:command
amContainer.setCommands(printableCommands.asJava)
// 打印加载ApplicationMaster启动上下文参数
logDebug("===============================================================================")
logDebug("YARN AM launch context:")
logDebug(s" user class: ${Option(args.userClass).getOrElse("N/A")}")
logDebug(" env:")
if (log.isDebugEnabled) {
Utils.redact(sparkConf, launchEnv.toSeq).foreach { case (k, v) =>
logDebug(s" $k -> $v")
}
}
logDebug(" resources:")
localResources.foreach { case (k, v) => logDebug(s" $k -> $v")}
logDebug(" command:")
logDebug(s" ${printableCommands.mkString(" ")}")
logDebug("===============================================================================")
// send the acl settings into YARN to control who has access via YARN interfaces
// 继续设置ContainerLaunchContext,并设置容器启动参数:acl
val securityManager = new SecurityManager(sparkConf)
amContainer.setApplicationACLs(
YarnSparkHadoopUtil.getApplicationAclsForYarn(securityManager).asJava)
setupSecurityToken(amContainer)
amContainer
}
如上代码,重点说明下 val localResources = prepareLocalResources(stagingDirPath, pySparkArchives) ,该方法预处理资源文件,如果是集群部署则上传资源到hdfs,如果执行则为下一个进程设置配置等;
紧接着集群设置提交给集群的容器上下文,主要包含四个参数,分别为:env、resources、command和acl,容器上下文参数(主要封装ContainerLaunchContext类)是通过rpc的参数方式传递给服务端的,其中 resources 参数用于Yarn集群调度的Node节点在加载Container容器前资源本地化使用,acl为控制集群安全机制,env和command是用于集群启动ApplicationMaster容器使用。
最终的生成的参数也能在日志中打印(注:估计公司考虑集群信息安全问题,取消了resources参数打印,因此网上又找了一个截图可以参照),其中 user class 是Driver启动类(不同的运行环境有的值,可以参照前面介绍的-- class参数设置), 如下两个图
其中摘抄一下上图中comman命令:
{{JAVA_HOME}}/bin/java -server -Xmx8192m -Djava.io.tmpdir={{PWD}}/tmp -Dspark.yarn.app.container.log.dir=<LOG_DIR> org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster \
--class 'org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi' \
--jar file:/work/code/sco_bigdata/spark/./examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.4.3.jar \
--properties-file {{PWD}}/__spark_conf__/__spark_conf__.properties 1> <LOG_DIR>/spark_stdout 2> <LOG_DIR>/spark_stderr
最后,在 def submitApplication() 函数体的 yarnClient.submitApplication(appContext) 代码正式提交给Yarn集群。可以看出后面就是在ApplicationMaster上启动Driver流程了,对应的入库类是 org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster,至此Spark任务的提交流程就分析完了 。
提交过程环节汇总
本节汇总记录一些中间重要环节。
用户Yarn-Cluster提交shell命令
./bin/spark-submit \
--class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \
--num-executors 2 \
--master yarn \
--deploy-mode cluster \
./examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.4.3.jar
提交给SparkSubmit类的cmd命令
/software/servers/jdk1.8.0_121/bin/java -cp /software/conf/10k/mart_scr/bdp_jmart_fsh_union.bdp_jmart_fsh_formal/spark_conf/:/software/servers/10k/mart_scr/spark/jars/*:/software/conf/10k/mart_scr/bdp_jmart_fsh_union.bdp_jmart_fsh_formal/hadoop_conf/ org.apache.spark.deploy.SparkSubmit \
--master yarn \
--deploy-mode cluster \
--class org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi \
--num-executors 2 \
./examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.4.3.jar
提交给集群启动driver的命令
{{JAVA_HOME}}/bin/java -server -Xmx8192m -Djava.io.tmpdir={{PWD}}/tmp -Dspark.yarn.app.container.log.dir=<LOG_DIR> org.apache.spark.deploy.yarn.ApplicationMaster \
--class 'org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi' \
--jar file:/work/code/sco_bigdata/spark/./examples/jars/spark-examples_2.11-2.4.3.jar \
--properties-file {{PWD}}/__spark_conf__/__spark_conf__.properties 1> <LOG_DIR>/spark_stdout 2> <LOG_DIR>/spark_stderr
任务运行结果
上传到hdfs的文件
![]()
其中,重点关注:application_1584006073801_1715800/__spark_conf__/__spark_conf__.properties,存在完整提交的参数信息。
整个任务运行日志
执行日志(直接在集群上执行即可复现日志),由于涉及公司集群信息,如有需要参照阅读请单独留言。
