Redis 模糊查询Key
有时候需要模糊匹配查询redis中的所有key,比如:当采用redis做数据缓存,需要定时根据数据库中的数据更新redis缓存,为了避免遗漏数据,通常是先删除redis中的数据,再从数据库中查出后写入redis。在删除redis数据时,需要指定key,如果此时key的数量较大,并满足一定的格式,就可以通过模糊匹配先查询出所有key。
前置条件
本文基于如下环境开发、调试:
- spring-boot:2.1.8.RELEASE
- spring-boot-starter-data-redis:2.1.8.RELEASE
间接依赖:
spring-data-redis:2.1.10.RELEASE
io.lettuce:lettuce-core:5.1.8.RELEASE - Redis Server 5.0.5
Keys 命令
https://redis.io/commands/keys
查询redis key 最简单粗暴的方法,支持glob-style patterns(通配符匹配),分别是:*,?,[]
其中:
*:通配任意多个字符
?:通配单个字符
[]:通配括号内的某一个字符
例如:
h?llo matches hello, hallo and hxllo
h*llo matches hllo and heeeello
h[ae]llo matches hello and hallo, but not hillo
h[^e]llo matches hallo, hbllo, … but not hello
h[a-b]llo matches hallo and hbllo
Spring 中通过调用RedisTemplate.keys() api可以实现:
public interface RedisOperations<K, V> {
/**
* Find all keys matching the given {@code pattern}.
*
* @param pattern must not be {@literal null}.
* @return {@literal null} when used in pipeline / transaction.
* @see Redis Documentation: KEYS
*/
@Nullable
Set<K> keys(K pattern);
}
为什么说简单粗暴
这个命令优点是简单,初学者拿来即用。(但通常运维大神会在redis服务端禁用该命令),缺点是可能会直接导致redis服务宕机。由于redis服务是单线程工作,每一条到达的指令都是串行执行,而Keys 命令会全量遍历缓存中的所有key,直到结束,此刻请求redis服务的其它指令都将被阻塞,后台服务可能会因为超时而报错。这也是为什么会禁用该命令。
Scan
为了解决Keys命令的痛点,Redis2.8版本中加入了Scan指令,特点是迭代遍历,并可以指定返回数据的条数。
https://redis.io/commands/scan
SCAN cursor [MATCH pattern] [COUNT count] [TYPE type]
- cursor:游标,当次遍历的起始位置
- pattern:与Keys命令中的patterns相同,支持通配符匹配
- count:返回数据条数,但只是一个hint(暗示),具体返回条数可多可少。
- type: Redis 6.0 支持的参数,指定返回Key的类型,类型可选值与 TYPE命令相同:string, list, set, zset, hash and stream。
本文Redis Server 为5.0.5版本,暂不讨论 type 参数。
例如:查找匹配"DBAS_ORG_LINE*"格式的key,建议最大返回10条,格式如下:
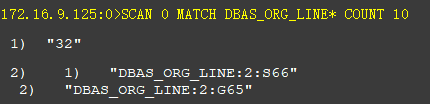
返回两组数据,第一个数字是下次迭代的游标位置,第二组是满足规则的key列表。
什么时候结束迭代
返回游标为 0,如下
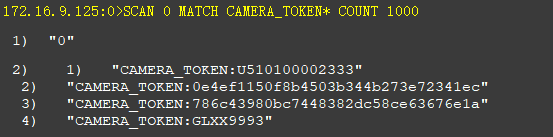
通过迭代遍历,解决了keys命令全量遍历导致的Redis Server阻塞问题,大大提高的服务的可用性。
Spring 中使用Scan,法一
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public static List<String> scanKeysSimple(RedisTemplate redisTemplate, String pattern) {
List<String> keys = (List<String>) redisTemplate.execute(connection -> {
RedisKeyCommands keyCmds = connection.keyCommands();
ScanOptions scanOpts = ScanOptions.scanOptions().match(pattern).count(1000L).build();
Cursor<byte[]> cursor = keyCmds.scan(scanOpts);
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
while (cursor.hasNext()) {
byte[] bytes = cursor.next();
set.add(new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
return new ArrayList<>(set);
}, true);
log.info("SCAN KEYS RETURN {} COUNT", CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(keys) ? keys.size() : 0);
return keys;
}
核心是调用 org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisKeyCommands#scan
/**
* Use a {@link Cursor} to iterate over keys.
*
* @param options must not be {@literal null}.
* @return never {@literal null}.
* @since 1.4
* @see Redis Documentation: SCAN
*/
Cursor<byte[]> scan(ScanOptions options);
通过org.springframework.data.redis.core.ScanOptions 指定匹配的模式字符串(pattern)和返回数据条数(count):
ScanOptions scanOpts = ScanOptions.scanOptions().match(pattern).count(1000L).build();
法一的缺陷
spring 对Scan命令进行了封装,直接返回了满足条件的key列表,并没有告诉调用者下次迭代遍历的游标,可能此次迭代并未结束(返回游标不为 0 )。有人说可以把count值取大,比如 Long.MAX_VALUE,这样可以保证一次迭代既结束,不用考虑下次迭代。那么,这和Keys 命令又有什么区别呢,不如直接用 Keys。
这种方法的适用场景是,不需要获取匹配指定格式的全量数据,类似抽样查询。
Spring 中使用Scan,法二
/**
* 获取 指定格式的所有key
* 迭代执行 SCAN 0 MATCH {pattern} COUNT 10000
*
* @param redisTemplate redisTemplate
* @param pattern 匹配规则
* @return 指定格式的所有key
*/
public static List<String> scanKeys(RedisTemplate redisTemplate, String pattern) {
//SCAN 0 MATCH {pattern} COUNT 10000
return (List<String>) redisTemplate.execute(connection -> {
//scan 迭代遍历键,返回的结果可能会有重复,需要客户端去重复
Set<String> redisKeys = new HashSet<>();
//lettuce 原生api
RedisAsyncCommands conn = (RedisAsyncCommands) connection.getNativeConnection();
//游标
ScanCursor curs = ScanCursor.INITIAL;
try {
//采用 SCAN 命令,迭代遍历所有key
while (!curs.isFinished()) {
long count = 10000L;
ScanArgs args = ScanArgs.Builder.matches(pattern).limit(count);
log.info("SCAN {} MATCH {} COUNT {}", curs.getCursor(), pattern, count);
RedisFuture<KeyScanCursor<byte[]>> future = conn.scan(curs, args);
KeyScanCursor<byte[]> keyCurs = future.get();
List<byte[]> ks = keyCurs.getKeys();
Set<String> set = ks.stream().map(bytes -> new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8)).collect(Collectors.toSet());
log.info("return size:{}", set.size());
redisKeys.addAll(set);
curs = keyCurs;
}
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
return new ArrayList<>(redisKeys);
}, true);
}
核心是采用 lettuce 原生api。spring-boot-starter-data-redis 2.0以后,redis客户端由Jedis 改成了 Lettuce。此文基于spring-boot-starter-data-redis:2.1.8.RELEASE,故采用lettuce api。Jedis客户端也有类似的实现。
io.lettuce.core.api.async.RedisAsyncCommands#scan()
/**
* Incrementally iterate the keys space.
*
* @param scanCursor cursor to resume from a previous scan, must not be {@literal null}
* @param scanArgs scan arguments
* @return KeyScanCursor<K> scan cursor.
*/
RedisFuture<KeyScanCursor<K>> scan(ScanCursor scanCursor, ScanArgs scanArgs);
- io.lettuce.core.ScanCursor 是迭代遍历的游标
- io.lettuce.core.ScanArgs 是Scan的参数,包括count和pattern字符串。
- io.lettuce.core.KeyScanCursor 是每次迭代后的返回数据,包含下次迭代的游标和此次迭代返回的keys列表。
原生api可以获取到每次迭代后下次迭代的游标,便于采用轮询的方式实现真正的迭代遍历。
Tips
采用scan 迭代遍历键,返回的结果可能会有重复,需要客户端去重复。
代码中用 Set,存储每次迭代的key列表,可实现去重。
源码地址
https://gitee.com/thanksm/redis_learn/tree/master/redis_common