Android Sensor HAL层分析
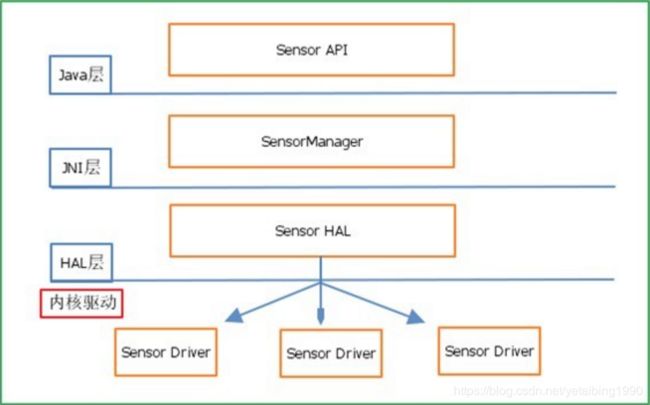
Android sensor架构
Android4系统内置对传感器的支持有很多种,它们分别是:加速度传感器 (accelerometer)、磁力传感器(magnetic field)、方向传感器(orientation)、陀螺仪(gyroscope)、环境光照传感器(light)、压力传感器(pressure)、 温度传感器(temperature)和距离传感器(proximity)等。
Android实现传感器系统包括以下几个部分:
| 类别 | 名称 | 代码 |
| 用户空间 | Java 应用程序 | 用户实现 |
| Java framework 框架层 | SensorManager.java SensorListener.java SensorEvent.java |
|
| JNI层 | com_android_server_SystemServer.cpp SensorService.cpp SensorDevice.cpp |
|
| HAL层 | Sensors.cpp Sensors.h (sensor厂商实现的各家HAL Accelerater.cpp Proximity.cpp Gyroscope.cpp ) |
|
| 内核空间 | 设备驱动程序 | 厂商实现 |
| 硬件 | 具体sensor IC | --------- |
各部分架构图:
JNI 层与HAL层接口
/frameworks/native/services/sensorservice/SensorDevice.cpp
/frameworks/native/services/sensorservice/SensorDevice.h
SensorDevcie类的 定义如下(JNI层通过这个类的对象与HAL层通信,包括控制sensor,读取sensor数据等):
class SensorDevice : public Singleton, public Dumpable {
public:
ssize_t getSensorList(sensor_t const** list);
void handleDynamicSensorConnection(int handle, bool connected);
status_t initCheck() const;
int getHalDeviceVersion() const;
ssize_t poll(sensors_event_t* buffer, size_t count);
status_t activate(void* ident, int handle, int enabled);
status_t batch(void* ident, int handle, int flags, int64_t samplingPeriodNs,
int64_t maxBatchReportLatencyNs);
// Call batch with timeout zero instead of calling setDelay() for newer devices.
status_t setDelay(void* ident, int handle, int64_t ns);
status_t flush(void* ident, int handle);
status_t setMode(uint32_t mode);
void disableAllSensors();
void enableAllSensors();
void autoDisable(void *ident, int handle);
status_t injectSensorData(const sensors_event_t *event);
// Dumpable
virtual std::string dump() const;
private:
friend class Singleton;
sensors_poll_device_1_t* mSensorDevice;
struct sensors_module_t* mSensorModule;
static const nsecs_t MINIMUM_EVENTS_PERIOD = 1000000; // 1000 Hz
mutable Mutex mLock; // protect mActivationCount[].batchParams
// fixed-size array after construction
// Struct to store all the parameters(samplingPeriod, maxBatchReportLatency and flags) from
// batch call. For continous mode clients, maxBatchReportLatency is set to zero.
struct BatchParams {
// TODO: Get rid of flags parameter everywhere.
int flags;
nsecs_t batchDelay, batchTimeout;
BatchParams() : flags(0), batchDelay(0), batchTimeout(0) {}
BatchParams(int flag, nsecs_t delay, nsecs_t timeout): flags(flag), batchDelay(delay),
batchTimeout(timeout) { }
bool operator != (const BatchParams& other) {
return other.batchDelay != batchDelay || other.batchTimeout != batchTimeout ||
other.flags != flags;
}
};
// Store batch parameters in the KeyedVector and the optimal batch_rate and timeout in
// bestBatchParams. For every batch() call corresponding params are stored in batchParams
// vector. A continuous mode request is batch(... timeout=0 ..) followed by activate(). A batch
// mode request is batch(... timeout > 0 ...) followed by activate().
// Info is a per-sensor data structure which contains the batch parameters for each client that
// has registered for this sensor.
struct Info {
BatchParams bestBatchParams;
// Key is the unique identifier(ident) for each client, value is the batch parameters
// requested by the client.
KeyedVector batchParams;
Info() : bestBatchParams(0, -1, -1) {}
// Sets batch parameters for this ident. Returns error if this ident is not already present
// in the KeyedVector above.
status_t setBatchParamsForIdent(void* ident, int flags, int64_t samplingPeriodNs,
int64_t maxBatchReportLatencyNs);
// Finds the optimal parameters for batching and stores them in bestBatchParams variable.
void selectBatchParams();
// Removes batchParams for an ident and re-computes bestBatchParams. Returns the index of
// the removed ident. If index >=0, ident is present and successfully removed.
ssize_t removeBatchParamsForIdent(void* ident);
int numActiveClients();
};
DefaultKeyedVector mActivationCount;
// Use this vector to determine which client is activated or deactivated.
SortedVector mDisabledClients;
SensorDevice();
bool isClientDisabled(void* ident);
bool isClientDisabledLocked(void* ident);
};
SensorDevcie 构造函数定义如下:
SensorDevice::SensorDevice()
: mSensorDevice(0),
mSensorModule(0) {
status_t err = hw_get_module(SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
(hw_module_t const**)&mSensorModule);
ALOGE_IF(err, "couldn't load %s module (%s)",
SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, strerror(-err));
if (mSensorModule) {
err = sensors_open_1(&mSensorModule->common, &mSensorDevice);
ALOGE_IF(err, "couldn't open device for module %s (%s)",
SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID, strerror(-err));
if (mSensorDevice) {
if (mSensorDevice->common.version == SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1 ||
mSensorDevice->common.version == SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_2) {
ALOGE(">>>> WARNING <<< Upgrade sensor HAL to version 1_3");
}
sensor_t const* list;
ssize_t count = mSensorModule->get_sensors_list(mSensorModule, &list);
mActivationCount.setCapacity(count);
Info model;
for (size_t i=0 ; iactivate(
reinterpret_cast(mSensorDevice),
list[i].handle, 0);
}
}
}
}
SensorDevcie 构造函数主要完成四部分工作
1.获得HAL层的sensors_module_t 并保存在 SensorDevcie 的数据成员 mSensorMoudle中
status_t err = hw_get_module(SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
(hw_module_t const**)&mSensorModule);HAL层的sensors_module_t定义如下(三星平台sensor HAL的实现)
struct sensors_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.version_major = 1,
.version_minor = 0,
.id = SENSORS_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "EXYNOS SENSORS Module",
.author = "Samsung",
.methods = &sensors_module_methods,
},
.get_sensors_list = sensors__get_sensors_list,
};
2.获得HAL层的sensors_poll_context_t并保存在SensorDevcie 的数据成员 mSensorDevice中
err = sensors_open_1(&mSensorModule->common, &mSensorDevice);HAL层的sensors_poll_context_t的定义如下:(三星平台sensor HAL的实现)
struct sensors_poll_context_t {
struct sensors_poll_device_1 device;// must be first
sensors_poll_context_t();
~sensors_poll_context_t();
int activate(int handle, int enabled);
int setDelay(int handle, int64_t ns);
int pollEvents(sensors_event_t* data, int count);
int batch(int handle, int flags, int64_t samplingPeriodNs, int64_t maxBatchReportLatencyNs);
int flush(int handle);
private:
enum {
PROXIMITY,
LIGHT,
SENSOR_NUMS,
};
int handleToDriver(int handle) const {
ALOGE("handleToDriver handle(%d)\n",handle);
switch (handle) {
case ID_PROXIMITY:
return PROXIMITY;
case ID_LIGHT:
return LIGHT;
default:
break;
}
return 0;
}
SensorBase* mSensors[SENSOR_NUMS];
struct pollfd mPollFds[SENSOR_NUMS];
};
如果获得sensors_poll_context_t 就可在上层通过它的成员函数控制所有的sensor。(HAL 层主要是实现这些成员函数函数)
int activate(int handle, int enabled); //使能对应sensor
int setDelay(int handle, int64_t ns);
int pollEvents(sensors_event_t* data, int count); //读取sensor上报的数据
int batch(int handle, int flags, int64_t samplingPeriodNs, int64_t maxBatchReportLatencyNs);
int flush(int handle);
HAL层对sensors_poll_device_t的初始化:(三星平台sensor HAL的实现,dev 对应sensors_poll_device_t)
static int open_sensors(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
struct hw_device_t** device)
{
int status = -EINVAL;
ALOGD("%s: name: %s! debug\r\n", __func__, name);
dev = new sensors_poll_context_t();
memset(&dev->device, 0, sizeof(sensors_poll_device_1));
dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
dev->device.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1;
dev->device.common.module = const_cast(module);
dev->device.batch = poll__batch;
dev->device.flush = poll__flush;
dev->device.common.close = poll__close;
dev->device.activate = poll__activate;
dev->device.setDelay = poll__setDelay;
dev->device.poll = poll__poll;
*device = &dev->device.common; // device 保存在SensorDevcie 的数据成员 mSensorDevice中
status = 0;
return status;
}
3.获得HAL层的sensor_list
ssize_t count = mSensorModule->get_sensors_list(mSensorModule, &list);HAL层的sensor_list定义如下:(三星平台sensor HAL的实现)
struct sensor_t sSensorList[] =
{
{
.name = "PROXIMITY",
.vendor = "Samsung",
.version = 1,
.handle = ID_PROXIMITY,
.type = SENSOR_TYPE_PROXIMITY,
.maxRange = 1.00f,
.resolution = 1.00f,
.power = 0.13f,
.reserved = {}
},
{
.name = "LIGHT",
.vendor = "Samsung",
.version = 1,
.handle = ID_LIGHT,
.type = SENSOR_TYPE_LIGHT,
.maxRange = 10240.0f,
.resolution = 1.0f,
.power = 0.13f,
.reserved = {}
}
};
4.最后一步是使用sensors_poll_context_t 的 activate方法对上面sensor列表的sensor进行激活
for (size_t i=0 ; iactivate(
reinterpret_cast(mSensorDevice),
list[i].handle, 0);
}
//reinterpret_cast是C++里的强制类型转换符。 HAL层
hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/sensors.h
hardware/samsung_slsi/exynos7570/libsensors/Sensors.cpp(三星平台的实现)
sensors.h为我们提供了HAL层的接口,实现部分则在sensors.cpp完成。sensors.cpp定义了一个hw_module_methods_t类型的变量sensors_module_methods,并且指定open函数的实现为open_sensors函数。
static struct hw_module_methods_t sensors_module_methods = {
.open = open_sensors
};
static int open_sensors(const struct hw_module_t* module, const char* name,
struct hw_device_t** device)
{
int status = -EINVAL;
ALOGD("%s: name: %s! debug\r\n", __func__, name);
dev = new sensors_poll_context_t();
memset(&dev->device, 0, sizeof(sensors_poll_device_1));
dev->device.common.tag = HARDWARE_DEVICE_TAG;
dev->device.common.version = SENSORS_DEVICE_API_VERSION_1_1;
dev->device.common.module = const_cast(module);
dev->device.batch = poll__batch;
dev->device.flush = poll__flush;
dev->device.common.close = poll__close;
dev->device.activate = poll__activate;
dev->device.setDelay = poll__setDelay;
dev->device.poll = poll__poll;
*device = &dev->device.common;
status = 0;
return status;
}
HAL层主要实现下面几个函数(具体函数的实现岁平台不同有差异)
dev->device.batch = poll__batch;
dev->device.flush = poll__flush;
dev->device.common.close = poll__close;
dev->device.activate = poll__activate;
dev->device.setDelay = poll__setDelay;
dev->device.poll = poll__poll;