Kali Linux渗透测试——信息收集
笔记内容参考安全牛课堂苑房弘老师的Kali Linux渗透测试教程
渗透测试标准(PTES:http://www.pentest-standard.org)的七个阶段:
1.前期交互阶段:讨论确定渗透测试范围、方式、限制条件等
2.情报收集阶段:通过主被动信息收集,获取目标系统的服务、系统配置、网络拓扑等
3.威胁建模阶段:根据收集的信息,确认合适的渗透测试方法
4.漏洞分析阶段:分析目标系统漏洞,编写漏洞利用代码,确定可以突破的攻击点
5.渗透攻击阶段:入侵系统,获取控制权
6.后渗透测试阶段:扩大攻击范围,入侵核心服务器,预置后门,实现持续控守,挖掘目标系统更多具有价值的信息
7.生成渗透测试报告:汇集关键情报、漏洞信息,分析安全防御系统的薄弱环节、补漏及升级方案等
文章目录
- 一、被动信息收集
- (一)DNS信息收集
- (二)搜索引擎信息收集
- (三)METADATE
- 二、主动信息收集
- (一)主机发现
- (二)端口扫描
- (三)服务扫描
- (四)操作系统识别
- (五)SNMP扫描
- (六)SMB扫描
- (七)SMTP扫描
- (八)防火墙识别
- (九)WAF识别
一、被动信息收集
被动信息收集即不向目标系统进行探测,不会留下任何痕迹。通过网络、公开渠道进行信息收集 。收集的内容包括IP地址段、域名信息、邮件地址、⽂档图⽚数据、公司地址、公司组织架构、联系电话 / 传真、⼈员姓名 / 职务、目标系统使⽤用的技术架构、公开的商业信息等。
(一)DNS信息收集
1.域名是分级的概念,而FQDN是域名下的主机(如:www.baidu.com),注意两者不同。
2.域名记录类型:A、CNAME、PTR、MX、NS、TXT、TTL
3.信息收集工具
- nslookup
eg:nslookup -type=ns baidu.com 8.8.8.8 - dig
eg:
dig @8.8.8.8 www.sina.com mx
dig +trace baidu.com
4.DNS字典爆破
- fierce
eg:firece -dnsserver 8.8.8.8 -dns sina.com.cn -wordlist a.txt - dnsdict6
eg:dnsdict6 -d4 -t 16 -x sina.com
5.DNS域名注册信息
- whois命令
(二)搜索引擎信息收集
1.shodan
常见filter:net、city、country、port、os、hostname
eg:
net:211.144.145.1/24 county:CN city:beijing port:22 os:windows hostname:baidu.com server:apache HTTP/1.1 200 OK
2.google
常见filter:+内容、-内容、intitle、intext、site、inurl、filetype
eg:
intitle:"netbotz appliance" "ok" inurl:qq.txt
(三)METADATE
图片的exif信息,可以用exiftool工具查看或修改。
二、主动信息收集
直接与目标系统交互通信,无法避免留下访问的痕迹,但可以使用第三方电脑进行探测,如控制僵尸转发扫描包。
(一)主机发现
1.二层发现
利用ARP协议发包探测,扫描速度快、可靠,但是不可路由
- arping:查看ip对应的mac地址。
eg:arping -c 1 -R 1.1.1.1 - netdiscover:专用于二层发现,可用于主被动扫描,注意主动扫描行为容易暴露。
eg:
主动发现:netdiscover -i eth0 -r 1.1.1.0/24
被动发现:netdiscover -p - scapy:可以作为单独工具使用,也可作为python包进行调用,可以进行抓包、注入网络流量等多种操作。
2. 三层发现
利用IP、ICMP协议发包探测,可路由,但是速度比二层发现慢,容易被边界防火墙过滤。
- ping
- fping:ping的升级版本,可以扫描多个地址。
eg:fping -g 192.168.1.1 192.168.1.10 - hping:能够发送几乎任意的tcp/ip包,功能强大但是每次只能扫描一个目标。
eg:hping3 1.1.1.1 --icmp -c 2 - nmap
eg:nmap -sn 1.1.1.1-254
3. 四层发现
利用TCP、UDP协议发包探测,可路由且结果可靠,不太可能被防护墙过滤,甚至能发现所有端口都被过滤的主机,但是扫描速度较慢。
- TCP发现
未经请求的ACK-RST
SYN-SYN/ACK、RST
eg:
nmap 1.1.1.1-254 -PU53 -sn
nmap 1.1.1.1-254 -PA80 –sn - UDP发现
ICMP端口不可达,UDP包一去不复返,假设ICMP响应代表发现主机,目标系统过滤ICMP包时可能产生误判。
eg:hping3 --udp 1.1.1.1 -c 1
(二)端口扫描
端口对应网络服务及应用端程序,但是不能仅凭借端口来判断服务。
1.TCP端口扫描
- 隐蔽扫描—SYN:不建立完整连接,应用日志不记录扫描行为。
eg:
nmap -sS -iL iplist.txt -p 80,21,22,23
hping3 1.1.1.1 --scan 80,21,25,443 -S
scapy: sr1(IP(dst="192.168.60.3")/TCP(dport=80),timeout=1,verbose=1) - 全连接端口扫描:
eg:
scapy : sr1(IP(dst="192.168.20.2")/TCP(dport=22,flags='S'))
nmap -sT 1.1.1.1 -p 80,21,25 #默认扫描常用的1000个端口
nc -nv -w 1 -z 192.168.60.4 1-100 - 僵尸扫描:十分隐蔽,可以伪造源地址,但是僵尸机条件必须满足:闲置系统,且IPID递增
发现僵尸机:nmap -p445 192.168.1.133 --script=ipidseq.nse
扫描目标:nmap 172.16.36.135 -sI 172.16.36.134 -Pn -p 0-100
图1 僵尸扫描原理
2.UDP端口扫描
- nmap
eg:namp -sU 1.1.1.1 -p 22 - scapy
eg:sr1(IP(dst="1.1.1.1")/UDP(dport=53),timeout=1,verbose=1)
(三)服务扫描
1. BANNER信息扫描
Banner中包含了软件开发商、软件名称、服务类型、版本号等信息,通过软件版本,可以直接发现已知的漏洞。
- nc
eg:nc -nv 1.1.1.1 22 - dmitry
eg:dmitry -pb 172.16.36.135 - nmap
eg:nmap -sT 1.1.1.1 -p 22 --script=banner - python.socket实现
import socket
bangrab = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_STREAM)
bangrab.connect(("1.1.1.1",22))
bangrab.recv(4096)
bangrab.close()
exit() #Banner不允许抓取,recv无返回将挂起
2.识别服务
可以通过Banner识别服务,也可以通过一些特征行为和响应字段识别
- nmap
eg:nmap 1.1.1.1 -p 80 -s
(四)操作系统识别
可以通过TTL等一些特征值进行识别,TTL起始值:
Windows:128(65-128)
Linux/Unix:64(1-64)
某些Unix:255
- nmap
nmap -O 1.1.1.1 - python.scapy实现
from scapy.all import *
win=“1.1.1.1”
linu=“1.1.1.2”
awin=sr1(IP(dst=win)/ICMP())
alinu=sr1(IP(dst=linu)/ICMP())
if alinu[IP].ttl<=64:
print “host is Linux”
else:
print “host is windows
(五)SNMP扫描
SNMP被称为信息的金矿,经常被错误配置,而且是明文传输,容易被抓包分析。
- snmpwalk
eg:snmpwalk 192.168.0.104 -c public -v 2c - snmpcheck
eg:snmpcheck -t 192.168.20.199 -c private -v 2
(六)SMB扫描
SMB协议是微软历史上出现安全问题最多的协议,实现非常复杂,Windows系统默认开放。
- nmap
eg:
nmap -v -p139,445 192.168.60.1-20
nmap 192.168.60.4 -p139,445 --script=smb-os-discovery.nse
nmap -v -p139,445 --script=smb-check-vulns --script-args=unsafe=1 1.1.1.1 - enum4linux
eg:enum4linux -a 1.1.1.1
(七)SMTP扫描
- nmap
eg
nmap smtp.163.com -p25 --script=smtp-enum-users.nse --script-args=smtp-enumusers.methods={VRFY}
nmap smtp.163.com -p25 --script=smtp-open-relay.nse
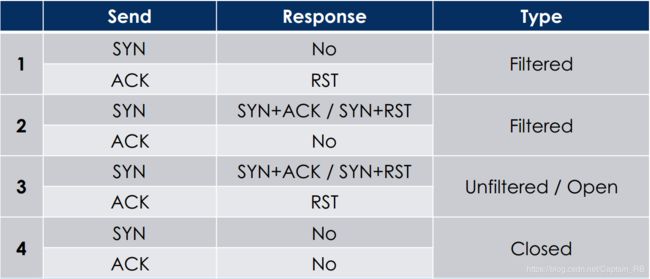
(八)防火墙识别
图2 防火墙端口识别
- nmap
eg:nmap -sA 1.1.1.1 -p 22
(九)WAF识别
WEB应用防火墙
- wafw00f
eg:wafw00f http://www.baidu.com - nmap
eg:nmap www.baidu.com --script=http-waf-detect.nse
信息收集部分最为重要的一个工具:NMAP,必须熟练掌握使用
截取nmap version 7.80man手册内容如下:
SYNOPSIS
nmap [Scan Type...] [Options] {target specification}
DESCRIPTION
...That table lists the port number and protocol, service name, and state. The
state is either open, filtered, closed, or unfiltered. Open means that an
application on the target machine is listening for connections/packets on that
port. Filtered means that a firewall, filter, or other network obstacle is
blocking the port so that Nmap cannot tell whether it is open or closed. Closed
ports have no application listening on them, though they could open up at any
time. Ports are classified as unfiltered when they are responsive to Nmap's probes,
but Nmap cannot determine whether they are open or closed. Nmap reports the state
combinations open|filtered and closed|filtered when it cannot determine which
of the two states describe a port. ...
OPTIONS SUMMARY
TARGET SPECIFICATION:
-iL : Input from list of hosts/networks
HOST DISCOVERY:
-sL: List Scan - simply list targets to scan
-sn: Ping Scan - disable port scan, only print out the available hosts that
responded to the host discovery probes
-Pn: No Ping - treat all hosts as online -- skip host discovery
-PS/PA/PU/PY[portlist]: TCP SYN/ACK, UDP or SCTP discovery to given ports
-PO[protocol list]: IP Protocol Ping
--traceroute: Trace hop path to each host
SCAN TECHNIQUES:
-sS/sT/sA/sW/sM: TCP SYN/Connect()/ACK/Window/Maimon scans
-sU: UDP Scan
-sN/sF/sX: TCP Null, FIN, and Xmas scans
-sI : Idle scan
-sY/sZ: SCTP INIT/COOKIE-ECHO scans
-sO: IP protocol scan
PORT SPECIFICATION AND SCAN ORDER:
-p : Only scan specified ports
Ex: -p22; -p1-65535; -p U:53,111,137,T:21-25,80,139,8080,S:9
--exclude-ports : Exclude the specified ports from scanning
-F: Fast mode - Scan fewer ports than the default scan
-r: Scan ports consecutively - don't randomize
--top-ports : Scan most common ports
SERVICE/VERSION DETECTION:
-sV: Probe open ports to determine service/version info
--version-intensity : Set from 0 (light) to 9 (try all probes)
--version-light: Limit to most likely probes (intensity 2)
--version-all: Try every single probe (intensity 9)
--version-trace: Show detailed version scan activity (for debugging)
SCRIPT SCAN:
-sC: equivalent to --script=default
--script=: is a comma separated list of
directories, script-files or script-categories
--script-args=: provide arguments to scripts
--script-args-file=filename: provide NSE script args in a file
--script-trace: Show all data sent and received
--script-updatedb: Update the script database.
--script-help=: Show help about scripts.
is a comma-separated list of script-files or
script-categories.
OS DETECTION:
-O: Enable OS detection
--osscan-limit: Limit OS detection to promising targets
--osscan-guess: Guess OS more aggressively
FIREWALL/IDS EVASION AND SPOOFING:
-f; --mtu : fragment packets (optionally w/given MTU)
-D : Cloak a scan with decoys
-S : Spoof source address
-e : Use specified interface
-g/--source-port : Use given port number
--proxies : Relay connections through HTTP/SOCKS4 proxies
--data : Append a custom payload to sent packets
--data-string : Append a custom ASCII string to sent packets
--data-length : Append random data to sent packets
--ip-options : Send packets with specified ip options
--ttl : Set IP time-to-live field
--spoof-mac : Spoof your MAC address
OUTPUT:
-oN/-oX/-oS/-oG : Output scan in normal, XML, s|: Output in the three major formats at once
-v: Increase verbosity level (use -vv or more for greater effect)
-d: Increase debugging level (use -dd or more for greater effect)
--open: Only show open (or possibly open) ports
--packet-trace: Show all packets sent and received
MISC:
-6: Enable IPv6 scanning
-A: Enable OS detection, version detection, script scanning, and traceroute
-V: Print version number
-h: Print this help summary page.