leetcode刷题笔记-回溯 Backtrace
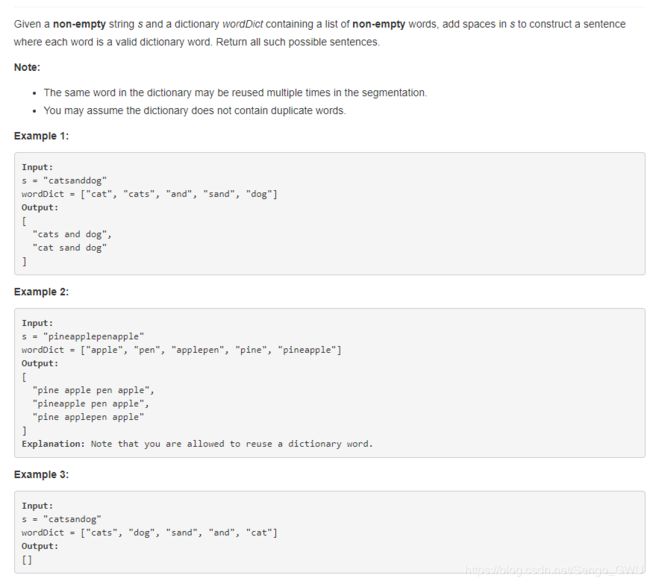
140. Word Break II
class Solution(object):
def wordBreak(self, s, wordDict):
return self.helper(s, wordDict, {})
def helper(self, s, wordDict, memo):
if s in memo: return memo[s]
if not s: return []
res = []
for word in wordDict:
if not s.startswith(word): continue
if len(word) == len(s):
res.append(word)
else:
resultOfRest = self.helper(s[len(word):], wordDict, memo)
for restWords in resultOfRest:
res.append(word + ' ' + restWords)
memo[s] = res
return res
491. Increasing Subsequences
Given an integer array, your task is to find all the different possible increasing subsequences of the given array, and the length of an increasing subsequence should be at least 2 .
Example:
Input: [4, 6, 7, 7]
Output: [[4, 6], [4, 7], [4, 6, 7], [4, 6, 7, 7], [6, 7], [6, 7, 7], [7,7], [4,7,7]]套路,和以前的题目都是一个模式。一般来说回溯法速度通不过才对。
class Solution(object):
def findSubsequences(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = []
self.helper(nums, 0, [], res)
return res
def helper(self, nums, index, temp, res):
if len(temp) >= 2:
res.append(temp[:])
used = {}
for i in xrange(index, len(nums)):
# 判断递增
if len(temp) and temp[-1] > nums[i]: continue
# 判断同个位置是否用过
if nums[i] not in used:
used[nums[i]] = True
else:
continue
self.helper(nums, i+1, temp+[nums[i]], res)46. Permutations
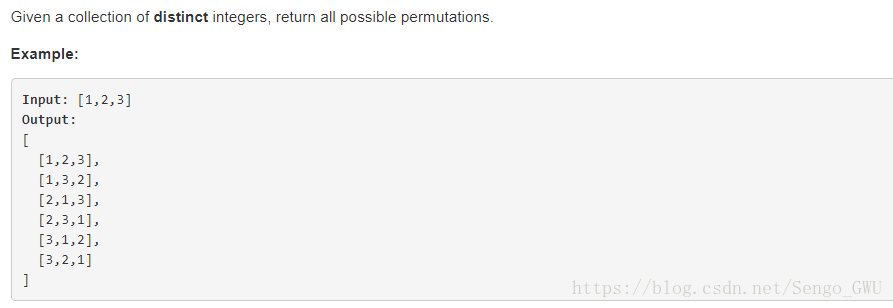
说什么回溯法,就是毫无智商的穷举,算什么算法?太弱智了吧
class Solution(object):
def permute(self, nums):
"""
:type nums: List[int]
:rtype: List[List[int]]
"""
res = []
self.helper(nums, res, [])
return res
def helper(self, nums, res, cur):
if len(cur) == len(nums):
res.append(cur)
else:
for i in xrange(len(nums)):
if nums[i] not in cur:
self.helper(nums, res, cur+[nums[i]])
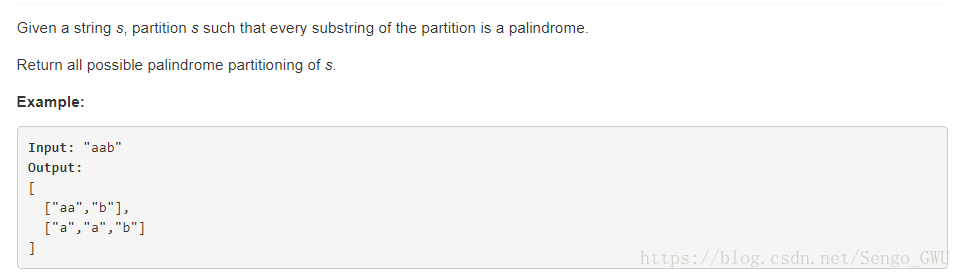
131. Palindrome Partitioning
class Solution(object):
def partition(self, s):
"""
:type s: str
:rtype: List[List[str]]
"""
res = []
self.helper(s, [], res)
return res
def helper(self, s, cur, res):
if not s:
res.append(cur)
return
for i in xrange(1, len(s) + 1):
if self.isPal(s[:i]):
self.helper(s[i:], cur + [s[:i]], res)
def isPal(self, s):
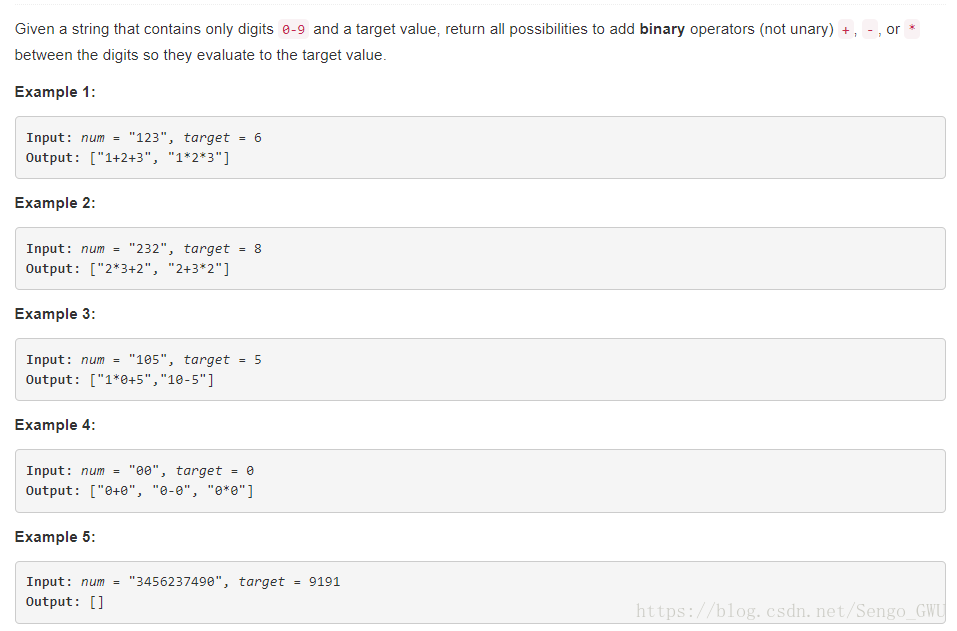
return s == s[::-1]282. Expression Add Operators
class Solution(object):
def addOperators(self, num, target):
"""
:type num: str
:type target: int
:rtype: List[str]
"""
res = []
self.helper(num, target, res, '', 0, 0, 0)
return res
def helper(self, num, target, res, path, pos, totalVal, multi):
if pos == len(num):
if target == totalVal:
res.append(path)
return
for i in xrange(pos, len(num)):
if num[pos] == '0' and i != pos:
break # 105 , 0 as a single digit is acceptable but not acceptable as 05
curVal = int(num[pos: i+1])
if pos == 0:
self.helper(num, target, res, str(curVal), i + 1, curVal, curVal)
else:
self.helper(num, target, res, path + '+' + str(curVal), i + 1, totalVal + curVal, curVal)
self.helper(num, target, res, path + '-' + str(curVal), i + 1, totalVal - curVal, -curVal)
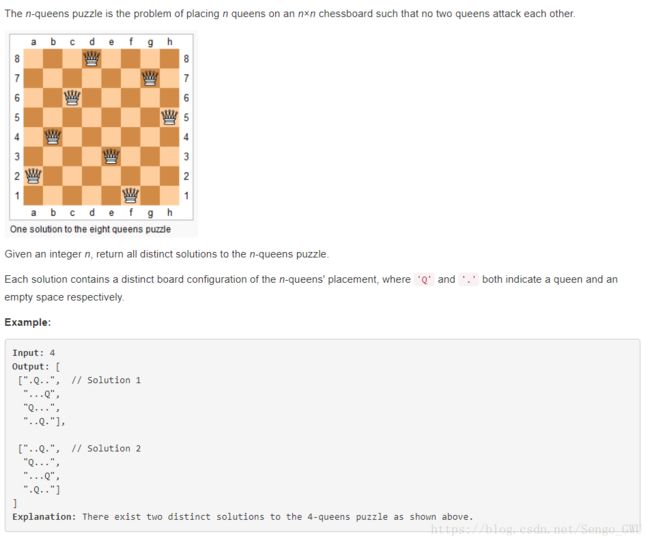
self.helper(num, target, res, path + '*' + str(curVal), i + 1, totalVal - multi + multi*curVal, multi*curVal)51. N-Queens
class Solution(object):
def solveNQueens(self, n):
"""
:type n: int
:rtype: List[List[str]]
"""
res = []
self.dfs(res, [-1]*n, 0, [])
return res
# nums like [1, 3, 0, 2] 存的是列,索引是行,第0行的Q在列1, 第一行的Q在3
# check 在之前就在curRow行加入了 num[curRow] = 某列 然后检查从0到该行的正确性
def isValid(self, nums, curRow):
for r in xrange(curRow):
if nums[r] == nums[curRow] or abs(nums[r] - nums[curRow]) == curRow - r:
return False
return True
def dfs(self, res, nums, curRow, path):
if curRow == len(nums):
res.append(path)
return
# backtracking 改行的所有列
for col in xrange(len(nums)):
nums[curRow] = col
if self.isValid(nums, curRow):
tmp = '.' * len(nums)
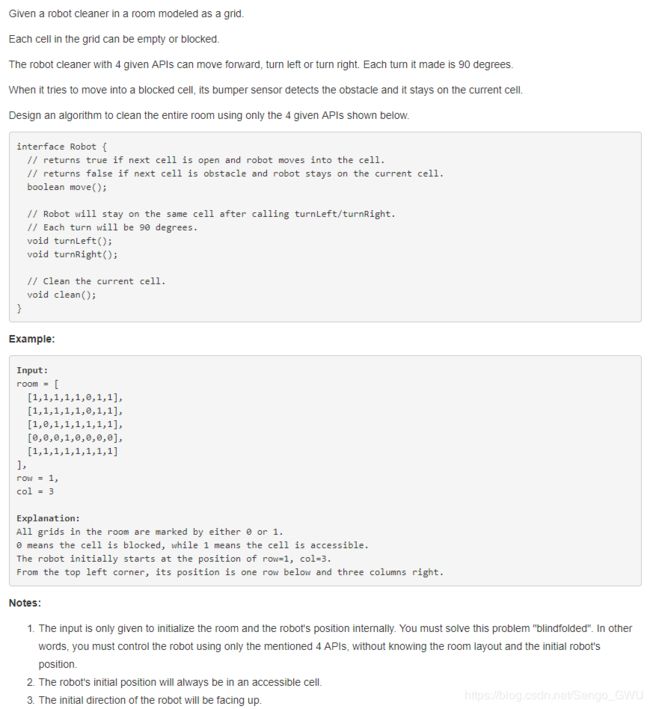
self.dfs(res, nums, curRow+1, path + [tmp[:col] + 'Q' + tmp[col+1:]])489. Robot Room Cleaner
class Solution(object):
def cleanRoom(self, robot):
"""
:type robot: Robot
:rtype: None
"""
move = ([0, 1], [1, 0], [0, -1], [-1, 0]) # 每次向右旋转的方向
def dfs(i, j, cleaned, cur_dir):
robot.clean()
cleaned.add((i, j))
for k in xrange(4):
x, y = move[(cur_dir+k) % 4]
if (i+x, j+y) not in cleaned and robot.move(): # 这里前进了一步 后面就要返回
dfs(i+x, j+y, cleaned, (cur_dir+k) % 4)
robot.turnLeft() # 返回原来位置
robot.turnLeft()
robot.move()
robot.turnLeft()
robot.turnLeft()
robot.turnRight() # 旋转90度 到下一个方向
dfs(0, 0, set(), 0) # 开始位置设置为0, 0 相对位置