MyBatis框架核心之注解使用resultMap及多表查询
前几天还觉得注解麻烦,突然恍然大悟,觉得注解相较于传统的mapper.xml+接口,xml使用接口映射相对较麻烦,所以我们可以使用注解来简化开发。
本文简单介绍一下常见注解的用法和大量实例 学艺不精 还望多多指教
一.常见注解列表
| 常见注解 | 用法 |
|---|---|
| @Insert | 插入sql , 和xml insert sql语法完全一样 @Select : 查询sql, 和xml select sql语法完全一样 |
| @Update | 更新sql, 和xml update sql语法完全一样 |
| @Delete | 删除sql, 和xml delete sql语法完全一样 |
| @Param | 入参 |
| @Results | 设置结果集合 @Result : 结果 |
| @ResultMap | 引用结果集合 |
| @SelectKey | 获取最新插入id |
二.增删改查
比较常用也好理解 上代码直接 crud也是相当常用的用法 注解也是我看来几个简单且常用的注解
| 注解 | 使用方法 |
|---|---|
| @Insert | 插入sql , 和xml insert sql语法完全一样 @Select : 查询sql, 和xml select sql语法完全一样 |
| @Update | 更新sql, 和xml update sql语法完全一样 |
| @Delete | 删除sql, 和xml delete sql语法完全一样 |
附上一个例子 是对某分类下的产品做一些增删改查工作:
@Insert({" insert into category_ ( name ) values (#{name}) "})
int add(Category var1);
@Delete({" delete from category_ where id= #{id} "})
void delete(int var1);
@Select({"select * from category_ where id= #{id} "})
Category get(int var1);
@Update({"update category_ set name=#{name} where id=#{id} "})
int update(Category var1);
@Select("select count(*) from category_")
public int count();
public class TestMybatis {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
CategoryMapper mapper = session.getMapper(CategoryMapper.class);
// add(mapper);
// delete(mapper);
// get(mapper);
// update(mapper);
listAll(mapper);
session.commit();
session.close();
}
private static void update(CategoryMapper mapper) {
Category c= mapper.get(8);
c.setName("修改了的Category名稱");
mapper.update(c);
listAll(mapper);
}
private static void get(CategoryMapper mapper) {
Category c= mapper.get(8);
System.out.println(c.getName());
}
private static void delete(CategoryMapper mapper) {
mapper.delete(2);
listAll(mapper);
}
private static void add(CategoryMapper mapper) {
Category c = new Category();
c.setName("新增加的Category");
mapper.add(c);
listAll(mapper);
}
private static void listAll(CategoryMapper mapper) {
List<Category> cs = mapper.list();
for (Category c : cs) {
System.out.println(c.getName());
}
}
}
和xml映射方法不同的只不过是将sql语句写到上面去了
三.结果集映射
算是一个难点 此处将举一个user的例子帮助理解
结果集映射指的是,将数据库表的字段映射到Java实体的属性上。mybatis支持多种结果集映射方式:
1、resultType
2、resultType+起别名
3、resultMap
4、@ResultMap注解
1. resultType
resultType适用于数据库表字段和java实体类属性是一 一对应的,如:
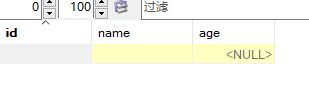
user表
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private int age;
//...setters and getters
}
此时我们可以在xml文件中这样配置select元素
select id,name,age from user where id= #{id} mybatis在查询数据库记录后,会首先尝试调用User类的属性方法进行设置值。以user表的name字段为例:1、首先查看resultType元素指向的User类中有没有对应的setName方法,如果有,调用setName方法设置值
2、如果没有setName方法,则会尝试通过反射技术,查看User类中有没有一个字段叫做name,如果有,通过反射技术给其赋值(说明set方法不是必须的)
3、如果既没有setName方法,也没有name字段,则mybatis放弃这个字段的映射,也不会抛出异常
2、resultType+起别名
当数据库表字段与实体属性就是不一致的,如user表中,表示的用户名的字段叫name,而在User类中,只有username字段和对应的setUsername方法。那么只给select元素设置resultType属性,就无法给User类的username字段赋值。此时可以通过起别名的方式:
<select id="selectById" parameterType="int" resultType="com.tianshouzhi.mybatis.quickstart.domain.User">
select id,name as username,age from user where id= #{id}
</select>
上面使用as,给name列起了一个别名为username,通过这种方式,就可以将user表的username字段映射到User类的name字段上。
3、resultMap
如果数据库表多个字段与实体类中的字段或属性名称都不相同,那么通过起别名的方式,就显得太麻烦了,因为我们在一个映射文件中可能需要写多个元素,每个里面都要其别名,极容易出错。
此时我们可以在mappers配置文件中配置一个元素,如下
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">;
<mapper namespace="com.tianshouzhi.mybatis.quickstart.mapper.UserMapper">
<!--定义resultMap元素-->
<resultMap id="userMap" type="com.tianshouzhi.mybatis.resultmap.User">
<id column="id" property="id" javaType="java.lang.Integer" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
<result column="name" property="username" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR"/>
<result column="age" property="age" javaType="java.lang.Integer" jdbcType="INTEGER"/>
</resultMap>
<!--使用resultMap属性代替resultType,其值为上面<resultType>元素的id属性值-->
<select id="testResultMap" parameterType="int" resultMap="userMap">
select id,name,age from user where id= #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
在上面的代码中,我们配置了一个resultMap元素,然后在select元素中,通过resultMap属性指向resultMap元素的id字段的值。
注意这里经常会有人忘记将resultType改成resultMap,
在属性名和字段名不一致的情况,请务必使用resultMap!
如:
<!--错误的用法:直接将resultType值改为userMap,resultType的属性值应该是java类全路径或者别名-->
<select id="testResultMap" parameterType="int" resultType="userMap">
select id,name,age from user where id= #{id}
</select>
如果这样写了,mybatis会抛出异常,因为resultType的属性值应该是java类全路径或者别名(alias).
关于resultMap元素的解释:
id属性用于表示这个resultMap唯一标识(说明我们可以在一个映射文件中配置多个resultMap元素),type属性表示这个resultMap元素配置的是哪一个Java类的映射关系。
上面的resultMap中,内部还配置了子元素和子元素,分别表示:数据库表主键与Java类属性的映射关系、数据库表其他字段与Java类属性的映射关系。这两个元素都包含以下属性:
| column | 数据库表字段名称 |
| property | java类的属性名称 |
| javaType | java类属性的类型 |
| jdbcType | 数据库字段对应的Jdbc type类型 |
对于javaType属性和jdbcType属性暂时可以不配置,mybatis会自动进行检测
4. 结果集映射相关注解
1、通过@Results、@Result注解定义结果集映射
如果实体字段的名称与数据库表字段名称不一致时,我们就需要显式的指定映射关系。这是通过@Results、@Result注解来指定的,例如为UserMapper的selectById指定映射关系:
@Select("SELECT id,name FROM user where id= #{id}")
@Results(id = "userMap", value = {
@Result(property = "id", column = "id", javaType = Integer.class,jdbcType = JdbcType.INTEGER,id = true),
@Result(property = "name", column = "name",javaType = String.class,jdbcType = JdbcType.VARCHAR)})
public User selectById(int id);
其中:
@Results注解:id属性用于给这个映射关系起一个名字(这里指定的为userMap),其内部还包含了一个@Result[]来表示实体属性和数据库表字段的映射关系
@Result注解:property属性是java实体属性的名称,column表示对应的数据库字段的名称。javaType和JdbcType属性可以不指定。
2、通过@ResultMap复用结果集映射
上述方法electById方法已经通过@Results注解指定了结果映射关系,可以通过@ResultMap来引用@Results的id属性值进行复用。如在UserMapper的selectAll方法进行复用:
@Select("SELECT id,name FROM user")
@ResultMap("userMap")
public List<User> selectAll();
3.多表查询one,many
先介绍下one和many的用法格式
和one many的中文释义相同:
- @One:替代了association,在注解中用来指定子查询返回单一对象。 @Result(column="
“,property=”",one=@One(select="")) - @Many 替代了collection 在注解中用来指定自查询返回集合
@Result(property="",column="",many=@Many(select=""))
举个例子
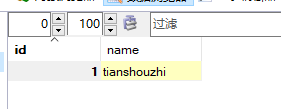
假设有作者(author)和文章(article)两张数据库表,一个author可以有多个article,一个article只能属于一个author。相关表结构以及初始数据如下所示:
–author表
CREATE TABLE `author` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `author` (`id`, `name`)
VALUES
(1, 'tianshouzhi');
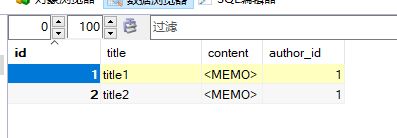
–article表
CREATE TABLE `article` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`title` varchar(255) NOT NULL,
`content` longtext NOT NULL,
`author_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `article` (`id`, `title`, `content`, `author_id`)
VALUES
(1, 'title1', 'content1', 1),
(2, 'title2', 'content2', 1);
相应的Java实体类如下所示:
public class Article {
private Integer id;
private String title;
private String content;
private Author author;
//...setters getters and toString...
}
public class Author {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private List<Article> articles;
//...setters getters and toString...
}
映射器接口定义分别如下:
ArticleMapper
public interface ArticleMapper {
//1、根据文章id查询文章Article对象,同时通过One注解关联查询出作者Author信息
@Select("SELECT id,title,content,author_id FROM article where id= #{articleId}")
@Results(id = "articleWithAuthor", value = {
@Result(property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "title", column = "title"),
@Result(property = "content", column = "content"),
//property属性:指定将关联查询的结果封装到Article对象的author属性上
//column属性指定:指定在执行@One注解中定义的select语句时,把article表的author_id字段当做参数传入
//one属性:通过@One注解定义关联查询的语句是AuthorMapper中的findAuthorByAuthorId方法
@Result(property = "author",column = "author_id”,
one = @One(select = "com.tianshouzhi.mapper.AuthorMapper.findAuthorByAuthorId"))})
public Article findArticleWithAuthorByArticleId(@Param("articleId") int articleId);
//2、根据作者(Author)的id查询其所有的文章(Article)
@Select("SELECT id,title,content,author_id FROM article WHERE author_id=#{authorId}")
@Results(id = "articlesWithoutAuthor", value = {
@Result(property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "title", column = "title"),
@Result(property = "content", column = "content")})
List<Article> findArticlesByAuthorId(@Param("authorId") int authorId);
}
AuthorMapper
public interface AuthorMapper {
//根据作者id查询Author信息
@Select("SELECT id,name FROM author WHERE id=#{authorId}")
Author findAuthorByAuthorId(int authorId);
//根据作者id查询Author信息,通过@Many注解关联查询出所有的文章信息
@Select("SELECT id,name FROM author WHERE id=#{authorId}")
@Results(id = "authorWithArticles", value = {
@Result(property = "id", column = "id"),
@Result(property = "name", column = "name”),
//property属性:指定将关联查询的结果封装到Author对象的articles属性上
//column属性指定:指定在执行@Many注解中定义的select语句时,把author表的id字段当做参数传入
//many属性:指定通过@Many注解定义关联查询的语句是ArticleMapper中的findArticlesByAuthorId方法
@Result(property = "articles",column = "id”,
many = @Many(select = "com.tianshouzhi.mapper.ArticleMapper.findArticlesByAuthorId"))})
Author findAuthorWithArticlesByAuthorId(int authorId);
}
测试如下:
@Test
public void testOneAndMany(){
System.out.println("===========通过@One注解查询出Article关联的Auhtor===========");
Article article = articleMapper.findArticleWithAuthorByArticleId(1);
System.out.println(article);
System.out.println("===========通过@Many注解查询出Auhtor关联的Article==========");
Author author = authorMapper.findAuthorWithArticlesByAuthorId(1);
System.out.println(author);
}
控制台输出结果为:
===========通过@One注解查询出Article关联的Auhtor===========
Article{id=1, title='title1', content='content1', author=Author{id=1, name='tianshouzhi', articles=null}}
===========通过@Many注解查询出Auhtor关联的Article==========
Author{id=1, name='tianshouzhi', articles=[Article{id=1, title='title1', content='content1', author=null}, Article{id=2, title='title2', content='content2', author=null}]}