gsoap使用总结
WebService、soap、gsoap基本概念
WebService服务基本概念:就是一个应用程序,它向外界暴露出一个可以通过web进行调用的API,是分布式的服务组件。本质上就是要以标准的形式实现企业内外各个不同服务系统之间的互调和集成。
soap概念:简单对象访问协议,是一种轻量的、简单的、基于 XML 的协议,它被设计成在WEB 上交换结构化的和固化的信息。
从这里的概念可以看得出来,soap是一个基于xml格式的web交互协议,而webservice是一种使用web方式实现的功能。就好像是网络视频服务器和http的关系,就是这里的webservice服务器和soap的关系。其实从历史上来说,先有的soap这种协议,然后微软用基于这种协议制作了webservice这种服务。
gsoap概念:是一种能够把C/C++语言的接口转换成基于soap协议的webservice服务的工具。
gSOAP简介
gSOAP是一个开发SOAP和XML应用(它们组成了webservice)的工具,在英文中叫toolkit。它是跨平台的,webservice的客户端和服务器端,都可以用它来辅助开发。它主要的功能(特征)如下:
- C/C++数据绑定工具,支持XML-RPCfrom/to JSON from/to C/C++ serialization
- 支持WSDL 1.1,2.0, SOAP 1.1, 1.2
- 支持REST HTTP(S) 1.0/1.1 operations (GET,PUT,POST etc) for XML, JSON,etc
- 支持MIME and MTOM 附件
- 支持IPv4,IPv6, TCP 和UDP
- 支持CGI,FastCGI
- 支持嵌入到Apache,IIS中发布
- 自带了一个Web server (multithreaded, SSL, compression)用于发布
- 可适用于WinCE, Palm, Symbian, VxWorks, Andriod, iPhone等小设备
- ...(拣主要的,其余忽略)
gsoap下载地址
http://sourceforge.net/project/showfiles.php?group_id=52781
gSOAP结构
目前gSOAP的版本是2.8.12,作者认为,gSOAP的组织结构以及使用的方便性,在开源项目中是比较好的。
在应用中,我们首先要应用它的两个工具: soapcpp2和 wsdl2h。所幸的是这个两个工具在gSOAP包中已经被编译生成(bin目录下),所以我们只要拿来用即可,gSOAP使用的方便性就体现出来了。另一个方便性是它的源文件个数较少,如果我们不去研究,少的文件个数包含在我们的工程中,也减少了维护的成本。
1.soapcpp2的用法
Soapcpp2是一个根据.h文件生成若干支持webservice的代码生成工具,生成的代码文件包括webservice客户端和服务器的实现框架,XML数据绑定等,具体说明如下:
| 文件 |
描述 |
| soapStub.h |
根据输入的.h文件生成的数据定义文件,一般我们不直接引用它。 |
| soapH.h soapC.cpp |
客户端和服务器端应包含该头文件,它包含了soapStub.h。针对soapStub.h中的数据类型,cpp文件实现了序列化、反序列化方法。 |
| soapXYZProxy.h soapXYZProxy.cpp |
这两个文件用于客户端,是客户端调用webservice的框架文件,我们的代码主要在此实现或从它继承。 |
| soapXYZService.h soapXYZService.cpp |
这两个文件用于服务器端,是服务器端实现webservice的框架文件,我们的代码主要在此实现或从它继承。 |
| .xsd |
传输消息的schema,,我们可以看看是否满足我们的协议格式(如果有此要求) |
| .wsdl |
这个就不用说了。 |
| .xml |
满足webservice定义的例子message,即实际的传输消息,我们可以看看是否满足我们的协议格式(如果有此要求)。 |
| .nsmap |
命名空间的定义,对命名空间不敏感的,不用关注。 |
使用soapcpp2时,可选项如下:
| 选项 |
描述 |
| -1 |
Soap1.1绑定 |
| -2 |
SOAP1.2绑定 |
| -C |
只生成客户端代码 |
| -S |
只生成服务器端代码 |
| -T |
生成自动测试代码 |
| -L |
不生成 soapClientLib/soapServerLib |
| -a |
用 SOAPAction 和WS-Addressing调用服务器端方法 |
| -A |
用 SOAPAction 调用服务器端方法 |
| -b |
采用char[N]这样的方式来表示string |
| -c |
生成的是C代码,不是C++代码 |
| -d < path > |
将代码生成在 < path >下 |
| -e |
生成 SOAP RPC 样式的绑定 |
| -f N |
File split of N XML serializer implementations per file |
| -h |
显示一个简要的用法信息 |
| -i |
生成的服务代理类和对象从struct soap继承而来 |
| -j |
生成的服务代理类和对象包含struct soap而来(C代码的唯一选择) |
| -I < path > |
包含其他文件时使用,指明 < path > (多个的话,用`:'分割),相当于#import ,该路径一般是gSOAP目录下的import目录,该目录下有一堆文件供soapcpp2生成代码时使用。 |
| -n |
用于生成支持多个客户端和服务器端(具体内容参考gSOAP文档) |
| -p < name > |
生成的文件前缀采用< name > ,而不是缺省的 "soap" |
| -q < name > |
C++代码中,所有声明的命名空间 |
| -s |
生成的代码在反序列化时,严格检查XML的有效性 |
| -t |
生成的代码在发送消息时,采用xsi:type方式 |
| -u |
在 WSDL/schema 输出文件中不产生XML注释 |
| -v |
显示版本信息 |
| -w |
不生成 WSDL 和 schema 文件 |
| -x |
不生成 XML 形式的传输消息文件 |
| -y |
在XML 形式的传输消息文件中,包含 C/C++类型信息 |
2. wsdl2h的用法
该工具是可以根据输入的wsdl或XSD或URL,产生相应的C/C++形式的.h(不能直接引用),供soapcpp2使用。
wsdl2h主要的运行选项如下:
| 选项 |
描述 |
| -a |
对匿名类型,产生基于顺序号的结构体名称 |
| -c |
生成C代码 |
| -f |
对schema扩展,产生flat C++类 |
| -g |
产生全局的元素声明 |
| -h |
显示帮助信息 |
| -I path |
包含文件时指明路径,相当于#import |
| -j |
不产生 SOAP_ENV__Header 和SOAP_ENV__Detail 定义 |
| -k |
不产生 SOAP_ENV__Header mustUnderstand qualifiers |
| -l |
在输出中包含license信息 |
| -m |
用 xsd.h 模块来引入类型信息 |
| -N name |
用name 来指定服务命名空间的前缀。 |
| -n name |
用name 作为命名空间的前缀,取代缺省的ns |
| -o file |
输出文件名 |
| -q name |
所有的声明采用 name 作命名空间 |
| -s |
不产生 STL代码 (即不用 std::string,std::vector) |
| -t file |
使用自己指定的type map file而不是缺省的typemap.dat |
| -u |
不生成 unions |
| -v |
产生详细的输出信息 |
| -w |
always wrap response parameters in a response struct |
| -y |
为structs,enums产生 typedef定义 |
| -_ |
不产生 _USCORE (用UNICODE _x005f代替) |
| -? |
显示帮助信息 |
用gsoap开发web service的大致思路
我们开发webservice应用,大致有两个方向:
1. API接口固定,不关心底层的通讯,将SOAP作为应用层协议
此时,我们先定义接口,编写好.h文件,运行soapcpp2生成出相应的代码,对服务器端,修改XXXService文件,实现业务逻辑,对客户端,修改XXXProxy文件,实现业务逻辑。
2. 通讯协议固定(当然需要基于XML的)或只有wsdl,将SOAP作为“传输层”协议
此时,我们必须根据通讯协议或wsdl生成相应的C/C++类型的.h文件,如果需要我们自己编写wsdl,则需要一点其相关知识,不过我们可以用C#等生成一个简单的wsdl,照猫画虎即可。运用wsdl2h,我们可以生成.h文件,有了.h后,按上面的步骤继续。
接口定义
可参考《GSoap接口定义》。这里我将给出C#引用这个webserver所对应的接口形式。
gsoap是根据我们定义好的.h文件,然后用工具产生了我们所需的.c文件。所以我们必须根据gsoap的要求编写.h。
1. 单个参数的传出:
int ns__add( int a, int b, int *c );
需要说明的是,这里的ns__是必须的,必须以开始注释中的ns加两个下划线开始。返回值必须是int。
但是这里的int并不是接口的返回值,而是gsoap内部的返回值。真正的返回值是int *c。
C#中对应的接口: int add( int a, int b );返回值就是上述的int *c参数。
2. 多个参数传出,在接口中必须使用结构体
typedef char * xsd__string;
typedef long xsd__int;
struct ns__personResponse{
xsd__int age;
xsd__string name;
xsd__string address;
};
int ns__person( xsd__string buf_in, struct ns__personResponse * buf_out );
在C#中,并不是我们所声明的这样。而是:int person( string buf_in, out string name, out string address);
即,结构体中的第一个域会变成返回值,其他的变成一个个的输出参数。
3. 返回结构体。如果要返回结构图,那么必须在结构体中再套一层结构体:
typedef char * xsd__string;
typedef long xsd__int;
struct ns__person{
xsd__int age;
xsd__string name;
xsd__string address;
};
struct ns__personResponse{
xsd__int ret;
struct ns__person person;
};
int ns__person( xsd__string buf_in, struct ns__personResponse * buf_out );
那么在C#中,看到的接口是这样的:int person( string buf_in, person对应的结构类 );
4. 接口中的下划线,如果接口中的交易名有下划线,必须这么声明:
int ns__echo_USCOREreverse( char * buf_in, char ** buf_out );
那么,C#中实际上的接口名就是:string echo_reverse( string buf_in );
注意事项
gsoap传输中文。
使用utf-8编码格式来支持汉字的传输。
1. 设置gsoap为utf-8传输数据
soap_set_mode( &SmsWBS_soap, SOAP_C_UTFSTRING ); //设置编码
SmsWBS_soap.mode|=SOAP_C_UTFSTRING;
2. 使用下面得函数转换我们的传输内容,即将我们的数据转成UTF-8编码:
int conv_charset( const char *dest, const char *src, char *input, size_t ilen,char *output, size_t olen )
{
int convlen = olen;
iconv_t conv = iconv_open( dest, src );
if( conv == (iconv_t) -1 )
return -1;
memset( output, 0, olen );
if( iconv( conv, &input, &ilen, &output, &olen ) ){
iconv_close(conv);
return -1;
}
iconv_close(conv);
return convlen-olen;
}
例子: conv_charset( "UTF-8", "GBK", "林学任.linxr", strlen("林学任.linxr"), buf_out->name,100 );
//编码转换函数int code_convert(char *from_charset,char *to_charset,char *inbuf,int inlen,char *outbuf,int outlen)
{
iconv_t cd;
int rc;
char **pin = &inbuf;
char **pout = &outbuf;
cd = iconv_open(to_charset,from_charset);
if (cd==0) return -1;
memset(outbuf,0,outlen);
if (iconv(cd,pin,&inlen,pout,&outlen)==-1) return -1;
iconv_close(cd);
return 0;
}
//UNICODE 2 GB2312
int u2g(char *inbuf,int inlen,char *outbuf,int outlen)
{
return code_convert("utf-8","gb2312",inbuf,inlen,outbuf,outlen);
}
//GB2312 2 UNICODE
int g2u(char *inbuf,size_t inlen,char *outbuf,size_t outlen)
{
return code_convert("gb2312","utf-8",inbuf,inlen,outbuf,outlen);
}
gsoap处理http post和http get
gsoap自带post和get的插件,路径:gsoap-2.8/gsoap/plugin/httppost.c httpget.c
在两个文件中定义了两个重要的函数,http_post,http_get这两个函数用于被作为插件调用,
在gsoap的主函数中用如下方法调用:
/* Register HTTP GET plugin */
if (soap_register_plugin_arg(&soap, http_get, (void*)http_get_handler))
soap_print_fault(&soap, stderr);
/* Register HTTP POST plugin */
if (soap_register_plugin_arg(&soap, http_form, (void*)http_form_handler))
soap_print_fault(&soap, stderr);
插件的作用就是当用户的请求是POST时就会自动调用http_form_handler,否则调用http_get_handler
http_get_handler和http_form_handler请求解析函数
其中(void*)http_get_handler和(void*)http_form_handler是需要自定义的函数
int http_get_handler(struct soap*); /* HTTP get handler */
int http_form_handler(struct soap*); /* HTTP form handler */
在这两个函数中需要解析用户的请求,得到用户请求的路径是什么,其中soap->path就是路径,如下代码
if (!strcmp(soap->path, "/calc"))
return calcget(soap );
当路径是”/calc“就调用calcget函数处理请求。
gsoap之soap版本不匹配
问题背景:
WCF server with basicHttpBinding use soap1.1, while gSoap generates client that uses soap1.2.
所以WCF server 和 gSoap产生的 client端之间通讯的soap message format不匹配。当客户端发起请求时,server端无法识别请求。
解决办法:
gSoap 生成的代码中,删除所有的soap1.2 namespace,换上对应的saop 1.1 namespace.
对于所有的gSoap工具生成的*Proxy.cpp 文件和*.nsmp文件,都要按如下格式将其中的soap 1.2 namespace 换成 soap 1.1 namespace.
{"SOAP-ENV", "http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-envelope", "http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/", NULL},
{"SOAP-ENC", "http://www.w3.org/2003/05/soap-encoding", "http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/", NULL},
{"xsi", "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance", "http://www.w3.org/*/XMLSchema-instance", NULL},
{"xsd", "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema", "http://www.w3.org/*/XMLSchema", NULL},
替换为:
{"SOAP-ENV", "http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/envelope/", NULL, NULL},
{"SOAP-ENC", "http://schemas.xmlsoap.org/soap/encoding/", NULL, NULL},
{"xsi", "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance", NULL, NULL},
{"xsd", "http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema", NULL, NULL},
内存管理
C/C++最大的麻烦,也是最大的优点是它要求用户自己管理内存。我们在实现web service方式时,同样需要考虑内存的分配与释放。
分配内存有两类:
- 分配n个字节,采用
void*soap_malloc(struct soap *soap, size_tn)
- 分配某个类,采用
Class*soap_new_Class(struct soap*soap) 一个类
Class*soap_new_Class(struct soap *soap, intn) n个类
这里的类是通讯xml中定义的元素,在response构造时,必然要创建若干此类元素。为简化类的创建,可定义如下宏:
#defineNEW_ELEMENT(classtype) soap_new_##classtype(GetSoapStruct(),-1)
#defineNEW_ELEMENT_X(classtype,n) soap_new_##classtype(GetSoapStruct(),n)
其中 GetSoapSturct()是返回继承的或包含的structsoap结构,对继承方式的代码,它的定义如下:
struct soap *GetSoapStruct() { return(struct soap*)this; }
在我们的Web方法实现中,可以随意使用上面的new方法,在每次web方法完结后,调用soap_destroy(structsoap *soap) ,它会为我们清除掉这部分内存。
gsoap中有若干释放内存的方法,几个有用的函数(还有其它的,忽略)及其说明如下:
| Function Call |
Description |
| soap_destroy(struct soap *soap) |
释放所有动态分配的C++类,必须在soap_end()之前调用。 |
| soap_end(struct soap *soap) |
释放所有存储临时数据和反序列化数据中除类之外的空间(soap_malloc的数据也属于反序列化数据)。 |
| soap_done(struct soap *soap) |
Detach soap结构(即初始化化soap结构) |
| soap_free(struct soap *soap) |
Detach 且释放soap结构 |
上表中,动态分配的C++类,指上面用"soap_new"分配的类;临时数据是指那些在序列化/反序列化过程中创建的例如hash表等用来帮助解析、跟踪xml的数据;反序列化数据是指在接收soap过程中产生的用malloc和new分配空间存储的数据。在gsoap中,纯数据空间与类空间管理不同,采用两个方法,可以保留soap的反序列化数据(这时你需要自己释放)。
gsoap输出
为提升服务性能,减少数据传输量,建议所有输出都采用字符方式的xml(UTF-8),不要采用结构或对象输出(输入可以),采用结构或对象输出优点是在客户端无需解析,自动生成相关对象和结构,但是会导致服务性能下降和传输的数量增大.例如:
int ns2__login(xsd__string username,xsd__stringpassword,xsd__string &rsp);
rsp为字符串格式的xml,在客户端需要解析后方可使用.我自己定义的rsp有三种输出格式,所有节点名称都大写,所有属性名称都小写,节点之间无换行,客户端按下面的三种规则编写解析器即可.
第一种为服务器异常消息
第二种为正常输入
更多ROW.......................................
更多ROWS.......................................
第三种为字段描述信息
更多字段描述信息.......................................
更多FIELDS.......................................
type,size, required均为数字,type可以自己定义,解析时按自定义规则转换数据即可,size为字段大小, required值一般为0和1,为0表示不是必填,否则为必填项.
字符转换为保证可移值性,可采用iconv转换,windows和linux均支持,windows需要自己下载LibIconv for Windows -GnuWin32库.只需要记住UTF-8单个字符最多使用4字节存储即可.转换时一次性分配 tcslen(szBuffer) * 4 + sizeof(TCHAR)大小的内存.
webserver发布
1. 在C#中,可以直接引用一个webserver,但是我们写得webserver如何能用被其引用呢。其实只要实现gsoap的fget回调函数即可:
SmsWBS_soap.fget = http_get;
2. http_get函数实现
int http_get(struct soap * soap)
{
FILE *fd = NULL;
char *s = strchr( soap->path, '?' );
if( !s || strcmp( s, "?wsdl" ) ){
return SOAP_GET_METHOD;
}
fd = fopen( "SmsWBS.wsdl", "rb" );
if (!fd){
return 404;
}
soap->http_content = "text/xml";
soap_response(soap, SOAP_FILE);
for (;;){
size_t r = fread(soap->tmpbuf, 1, sizeof(soap->tmpbuf), fd);
if( !r ){
break;
}
if( soap_send_raw( soap, soap->tmpbuf, r) ){
break;
}
}
fclose(fd);
soap_end_send(soap);
return SOAP_OK;
}
CGI方式执行
server端可以编译成CGI方式执行,而并不是绑定到某个端口,这种方式我没有实践。
if (argc < 2)// no args: assume this is a CGIapplication
{
soap_serve(&soap); // serve request, one thread, CGI style
soap_destroy(&soap); // dealloc C++ data
soap_end(&soap); // dealloc data and clean up
}
gsoap上层缓冲区大小设置
通过更改在stdsoap2.h文件中 SOAP_BUFLEN 宏,增加缓存大小,默认缓存大小为65536
实现高性能gsoap服务
代码请参看gSOAP 2.8.14 User Guide中的7.2.4 How to Create aMulti-Threaded Stand-Alone Service.
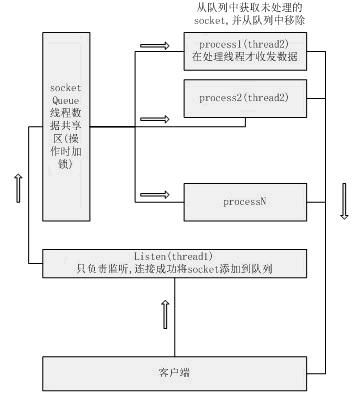
listen : 监听soap_accept方法,返回一个SOAP_SOCKET,然后交SOAP_SOCKET添加到队列,并发送一个信号通知process(处理线程)处理.
process(处理线程)启动后立即阻塞等待信号,收到信号后才执行相应的任务(soap_serve
),执行任务后继续阻塞等待信号.注意:soap_serve方法如果客户端提交的xml文档格式不正确或其它数据(恶意攻击)时会一直阻塞到下一个请求,导到服务器性能严重下降,客户端无法收到数据一直等待的情况,因此在初始化处理线程的soap成功后,应该立即设置处理线程soap的超时时间,单位为秒:
soap_thr[i] = soap_copy(&soap);//在这一行示例代码后一加下面三行代码
soap_thr[i] ->send_timeout = 1;
soap_thr[i] ->recv_timeout = 1;
soap_set_mode(soap_thr[i], SOAP_C_UTFSTRING); /*设置采用UTF-8字符编码*/
gSOAP写服务器端程序
http://blog.csdn.net/mseaspring/article/details/1713283
gSOAP写服务器端程序,现在将gSOAP文档中的算术服务器的程序与文档中的多线程服务器结合,写了个多线程算术服务器。
一 gSOAP需要的头文件:
//gsoap ns servicename: calc
//gsoap ns service style: rpc
//gsoap ns service encoding: encoded
//gsoap ns service namespace: http://127.0.0.1:8089/calc.wsdl
//gsoapns service location: http://127.0.0.1:8089/cal
//gsoapns schema namespace: urn:calc
int ns__add(double a, double b, double *result);
int ns__sub(double a, double b, double *result);
int ns__mul(double a, double b, double *result);
int ns__div(double a, double b, double *result);
int ns__pow(double a, double b, double *result);
二多线程服务器关键代码
#include
#include "calc.nsmap"
#include "soapH.h"
/////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
///宏与全局变量的定义
#define BACKLOG (100)
#define MAX_THR (10)
#define MAX_QUEUE (1000)
pthread_mutex_tqueue_cs; //队列锁
pthread_cond_t queue_cv; //条件变量
SOAP_SOCKET queue[MAX_QUEUE]; //数组队列
int head =0, tail =0; //队列头队列尾初始化
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
void * process_queue(void*); //线程入口函数
int enqueue(SOAP_SOCKET); //入队列函数
SOAP_SOCKET dequeue(void); //出队列函数
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//线程入口函数
void * process_queue(void * soap)
{
struct soap * tsoap = (struct soap *)soap;
for(;;)
{
tsoap->socket = dequeue();
if(!soap_valid_socket(tsoap->socket))
{
break;
}
soap_serve(tsoap);
soap_destroy(tsoap);
soap_end(tsoap);
}
return NULL;
}
//入队列操作
int enqueue(SOAP_SOCKET sock)
{
int status = SOAP_OK;
int next;
pthread_mutex_lock(&queue_cs);
next = tail +1;
if (next >= MAX_QUEUE)
next = 0;
if (next == head)
status = SOAP_EOM;
else
{
queue[tail] =sock;
tail = next;
}
pthread_cond_signal(&queue_cv);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&queue_cs);
return status;
}
//出队列操作
SOAP_SOCKET dequeue()
{
SOAP_SOCKET sock;
pthread_mutex_lock(&queue_cs);
while (head == tail )
{
pthread_cond_wait(&queue_cv,&queue_cs);
}
sock = queue[head++];
if (head >= MAX_QUEUE)
{
head =0;
}
pthread_mutex_unlock(&queue_cs);
return sock;
}
//////////////////////////具体服务方法////////////////////////////////////////
//加法的实现
int ns__add(struct soap *soap, double a, double b, double *result)
{
*result = a + b;
return SOAP_OK;
}
//减法的实现
int ns__sub(struct soap *soap, double a, double b, double *result)
{
*result = a - b;
return SOAP_OK;
}
//乘法的实现
int ns__mul(struct soap *soap, double a, double b, double *result)
{
*result = a * b;
return SOAP_OK;
}
//除法的实现
int ns__div(struct soap *soap, double a, double b, double *result)
{
if (b)
*result = a / b;
else
{
char *s = (char*)soap_malloc(soap,1024);
sprintf(s,"Can't">http://tempuri.org/">Can't divide %f by %f", a, b);
return soap_sender_fault(soap,"Division by zero", s);
}
return SOAP_OK;
}
//乘方的实现
int ns__pow(struct soap *soap, double a, double b, double *result)
{
*result = pow(a, b);
if (soap_errno == EDOM) /* soap_errno 和errorno类似,但是和widnows兼容 */
{
char *s = (char*)soap_malloc(soap, 1024);
sprintf(s, "Can't take the power of %f to %f", a, b);
sprintf(s,"Can't">http://tempuri.org/">Can't take power of %f to %f", a, b);
return soap_sender_fault(soap, "Power function domainerror", s);
}
return SOAP_OK;
}
//////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
//主函数
int main(int argc,char ** argv)
{
struct soap ServerSoap;
//初始话运行时环境
soap_init(&ServerSoap);
//如果没有参数,当作CGI程序处理
if (argc <2)
{
//CGI 风格服务请求,单线程
soap_serve(&ServerSoap);
//清除序列化的类的实例
soap_destroy(&ServerSoap);
//清除序列化的数据
soap_end(&ServerSoap);
}else
{
struct soap * soap_thr[MAX_THR];
pthread_t tid[MAX_THR];
int i,port = atoi(argv[1]);
SOAP_SOCKET m,s;
//锁和条件变量初始化
pthread_mutex_init(&queue_cs,NULL);
pthread_cond_init(&queue_cv,NULL);
//绑定服务端口
m = soap_bind(&ServerSoap,NULL,port,BACKLOG);
//循环直至服务套接字合法
while (!soap_valid_socket(m))
{
fprintf(stderr,"Bind port error! ");
m = soap_bind(&ServerSoap,NULL,port,BACKLOG);
}
fprintf(stderr,"socket connection successful %d",m);
//生成服务线程
for(i = 0; i
{
soap_thr[i] = soap_copy(&ServerSoap);
fprintf(stderr,"Starting thread %d",i);
pthread_create(&tid[i],NULL,(void*(*)(void*))process_queue,(void*)soap_thr[i]);
}
for(;;)
{
//接受客户端的连接
s = soap_accept(&ServerSoap);
if (!soap_valid_socket(s))
{
if (ServerSoap.errnum)
{
soap_print_fault(&ServerSoap,stderr);
continue;
}else
{
fprintf(stderr,"Server timed out ");
break;
}
}
//客户端的IP地址
fprintf(stderr,"Accepted connection fromIP= %d.%d.%d.%d socket = %d ",
((ServerSoap.ip)>>24)&&0xFF,((ServerSoap.ip)>>16)&0xFF,((ServerSoap.ip)>>8)&0xFF,(ServerSoap.ip)&0xFF,(ServerSoap.socket));
//请求的套接字进入队列,如果队列已满则循环等待
while(enqueue(s) == SOAP_EOM)
Sleep(1000);
}
//服务结束后的清理工作
for(i = 0; i < MAX_THR; i++)
{
while (enqueue(SOAP_INVALID_SOCKET) ==SOAP_EOM)
{
Sleep(1000);
}
}
for(i=0; i< MAX_THR; i++)
{
fprintf(stderr,"Waiting for thread %d toterminate ..",i);
pthread_join(tid[i],NULL);
fprintf(stderr,"terminated ");
soap_done(soap_thr[i]);
free(soap_thr[i]);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&queue_cs);
pthread_cond_destroy(&queue_cv);
}
//分离运行时的环境
soap_done(&ServerSoap);
return 0;
}
在windows下配置pthread
Pthread是由POSIX提出的一套通用的线程库,在linux平台下,它被广泛的支持,而windows平台下,却并不被支持,而pthreads-w32为我们提供了解决方案,本文我们准备在我们的windows平台下进行pthread-w32的安装,在网络上有类似的文章,但是讲的都是比较老的平台,在windows8下支持并不全面,不过可以作为参考。我们在这里贴出几个网址,供参考使用。
Windows 7 64bit和Visual Studio 2010下安装及使用Pthread-w32 2.8
windows下使用pthread库(转)
如果你的是XP系统或者win7 32位系统,那么,那两篇文章已经足以你完成pthread-w32的安装了。现在,我们开始讲我们的尝试过程。
一、安装平台
windows8 64位系统,MicrosoftVisual Studio 2012
二、pthreads-w32下载地址
我们这里下载最新版本pthreads-w32-2-9-1
ftp://sourceware.org/pub/pthreads-win32/pthreads-w32-2-9-1-release.zip
下载后解压,可以看到共有三个文件夹
我们用到的主要是“Pre-built.2”这个文件夹下的三个文件夹,分别是动态链接库、头文件、静态链接库
三、配置头文件及静态链接库
这里有多种方式,我们这里只提到我们用到的一种,总之目的是让我们建立的工程能够找到对应的头文件、静态库文件,以及运行时程序能够找到动态链接库文件。
这里,我们直接把头文件拷贝到Visual Studio的默认路径的头文件中,即把include文件夹中的三个文件直接拷贝到VisualStudio安装目录下VC->include文件夹下,例如我将include中文件拷贝到的位置是
E:\ProgramFiles\Microsoft Visual Studio 11.0\VC\include
这样,我们就不必每次在项目用到时都配置一遍,特别是在Visual Studio2012貌似不支持全局的头文件配置时(不确定,如果谁找到了可以告诉我一声),这种方式对于经常会建一些小项目的人来说,相对节省时间。
同样的办法与原因,我们也可以把lib文件夹下的内容拷贝到Visual Studio安装目录下默认的lib寻找路径中,即VC->lib中,例如我将lib文件夹下的x64与x86两个文件直接拷贝到
E:\Program Files\Microsoft Visual Studio 11.0\VC\lib
的下面。
四、配置动态链接库
和头文件和静态链接库的配置方式相似,我们这里将dll文件夹的内容放到我们程序能够找到的位置,我们的方案是
把dll下的x64文件夹下的两个文件,即pthreadGC2.dll与pthreadVC2.dll拷贝到C:\Windows\System32下(用于64位程序的运行)
把dll下的x86文件夹下的五个文件,拷贝到C:\Windows\SysWOW64下(用于32位程序的运行),注意一下,千万不能将这些文件拷贝反位置,否则,程序运行时会提示说找不到对应的dll文件。这些在网上的很多文章中都被忽略掉了,所以我们特别提出。
五、运行测试
完成以上配置之后,我们运行一下测试程序,证明我们的配置完成了
//main.cpp
#include
#include
#include
#pragmacomment(lib,"x86/pthreadVC2.lib")
void* Function_t(void* Param)
{
printf("我是线程! ");
pthread_tmyid = pthread_self();
printf("线程ID=%d ", myid);
returnNULL;
}
int main()
{
pthread_tpid;
pthread_attr_tattr;
pthread_attr_init(&attr);
pthread_attr_setscope(&attr,PTHREAD_SCOPE_PROCESS);
pthread_attr_setdetachstate(&attr,PTHREAD_CREATE_DETACHED);
pthread_create(&pid,&attr, Function_t, NULL);
printf("========================================");
getchar();
pthread_attr_destroy(&attr);
return0;
}
这里,我们需要注意的是我们的第6行代码,我们需要在代码中包含入静态链接库(注意,根据不同的编译选项,选择x86还是x64,如果不相配,将无法链接完成)
#pragmacomment(lib,"x86/pthreadVC2.lib")
gsoap实例代码下载:http://download.csdn.net/detail/byxdaz/9549883
参考资料:
官网源代码: https://sourceforge.net/projects/gsoap2/
帮助文档:http://www.cs.fsu.edu/~engelen/soapdoc2.html
gsoap使用总结:http://www.cnblogs.com/linxr/archive/2011/10/17/2215285.html
C#访问gsoap的服务:http://blog.csdn.net/caowei880123/article/details/49129211#
windows下使用pthread库:http://blog.csdn.net/g_spider/article/details/6023698#comments